LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
... - Chemical buffers can tie up excess acids or bases, but they cannot eliminate them from the body -The lungs can eliminate carbonic acid by eliminating carbon dioxide - Only the kidneys can rid the body of metabolic acids (phosphoric, uric, and lactic acids and ketones) and prevent metabolic acidosi ...
... - Chemical buffers can tie up excess acids or bases, but they cannot eliminate them from the body -The lungs can eliminate carbonic acid by eliminating carbon dioxide - Only the kidneys can rid the body of metabolic acids (phosphoric, uric, and lactic acids and ketones) and prevent metabolic acidosi ...
Chapter 02 - Moore Public Schools
... oceans. This may seem extensive, but if you could shrink Earth to the size of an apple, the biosphere would be thinner than the apple’s peel. Although it is thin, the biosphere supports a diverse group of organisms in a wide range of climates. The climate, soils, plants, and animals in one part of t ...
... oceans. This may seem extensive, but if you could shrink Earth to the size of an apple, the biosphere would be thinner than the apple’s peel. Although it is thin, the biosphere supports a diverse group of organisms in a wide range of climates. The climate, soils, plants, and animals in one part of t ...
COOL FACt Learn with BODY WORLDS
... The locomotive system is the system in the body that makes movement possible. It consists of the bones that make up the skeleton, the joints that hold the bones together and the muscles that contract and relax to actually make you move. The skeleton is the framework of the body, and it is made up of ...
... The locomotive system is the system in the body that makes movement possible. It consists of the bones that make up the skeleton, the joints that hold the bones together and the muscles that contract and relax to actually make you move. The skeleton is the framework of the body, and it is made up of ...
Example
... together Compounds- a combination of different types of atoms working together Cells- The smallest structural unit of an organism that is capable of independent functioning, consisting of one or more nuclei, cytoplasm, and ...
... together Compounds- a combination of different types of atoms working together Cells- The smallest structural unit of an organism that is capable of independent functioning, consisting of one or more nuclei, cytoplasm, and ...
Chapter 2: Principles of Ecology
... oceans. This may seem extensive, but if you could shrink Earth to the size of an apple, the biosphere would be thinner than the apple’s peel. Although it is thin, the biosphere supports a diverse group of organisms in a wide range of climates. The climate, soils, plants, and animals in one part of t ...
... oceans. This may seem extensive, but if you could shrink Earth to the size of an apple, the biosphere would be thinner than the apple’s peel. Although it is thin, the biosphere supports a diverse group of organisms in a wide range of climates. The climate, soils, plants, and animals in one part of t ...
How Living Things Interact
... Most producers are green plants and algae. They make food using a process called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis comes from two Greek words that mean "putting together with light." Carbohydrates, which are food for plants and many animals, are created during photosynthesis. There are four things that ...
... Most producers are green plants and algae. They make food using a process called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis comes from two Greek words that mean "putting together with light." Carbohydrates, which are food for plants and many animals, are created during photosynthesis. There are four things that ...
Requirements of Animals Ch 5 Pt D - SandyBiology1-2
... Osmoregulators: expend energy to control their internal chemical balance Osmoconformers: organisms whose internal environment varies with their external environment. ...
... Osmoregulators: expend energy to control their internal chemical balance Osmoconformers: organisms whose internal environment varies with their external environment. ...
Michigan Department of Natural Resources 2010-97 Status of the Fishery Resource Report
... pumpkinseed and perch were all growing about one inch slower than state average. The growth rate of the few bass captured appeared to be similar to the panfish at age I, but then much slower by age 2. The reason for the slower growth at age 2 is unknown at this time. However, angling efforts earlier ...
... pumpkinseed and perch were all growing about one inch slower than state average. The growth rate of the few bass captured appeared to be similar to the panfish at age I, but then much slower by age 2. The reason for the slower growth at age 2 is unknown at this time. However, angling efforts earlier ...
Chapter 2: Principles of Ecology - Seymour Community School District
... the habitat of salmon shown in Figure 2.5. These biotic factors include all of the organisms that live in the water, such as other fish, algae, frogs, and microscopic organisms. In addition, organisms that live on the land adjacent to the water might be biotic factors for the salmon. Migratory anima ...
... the habitat of salmon shown in Figure 2.5. These biotic factors include all of the organisms that live in the water, such as other fish, algae, frogs, and microscopic organisms. In addition, organisms that live on the land adjacent to the water might be biotic factors for the salmon. Migratory anima ...
Chapter 2: Principles of Ecology - Bellbrook
... the habitat of salmon shown in Figure 2.5. These biotic factors include all of the organisms that live in the water, such as other fish, algae, frogs, and microscopic organisms. In addition, organisms that live on the land adjacent to the water might be biotic factors for the salmon. Migratory anima ...
... the habitat of salmon shown in Figure 2.5. These biotic factors include all of the organisms that live in the water, such as other fish, algae, frogs, and microscopic organisms. In addition, organisms that live on the land adjacent to the water might be biotic factors for the salmon. Migratory anima ...
Life Processes - DronStudy.com
... Respiration The process of releasing energy from food is called respiration. The process of respiration involves taking in oxygen (of air) into the cells, using it for releasing energy by burning food, and then eliminating the waste products (carbon dioxide and water) from the body. ...
... Respiration The process of releasing energy from food is called respiration. The process of respiration involves taking in oxygen (of air) into the cells, using it for releasing energy by burning food, and then eliminating the waste products (carbon dioxide and water) from the body. ...
Analysis of Elements and Foods for the Human Body and
... of water in the body. Chlorine (0.15%) is usually found in the body as a negative ion, called chloride. This electrolyte is important for maintaining a normal balance of fluids. Iron (0.006%) is a key element in the metabolism of almost all living organisms. It is also found in haemoglobin, which is ...
... of water in the body. Chlorine (0.15%) is usually found in the body as a negative ion, called chloride. This electrolyte is important for maintaining a normal balance of fluids. Iron (0.006%) is a key element in the metabolism of almost all living organisms. It is also found in haemoglobin, which is ...
Name - grade8structureoflivingthings
... 12. Use a Clorox Wipe to clean: all used tools, the blue mat, gray dissecting tray, lab table. 13. Return all clean materials to the drawer you got them from. Part D: What I learned Summary Questions 14. Compare the organs in the frog to what you saw at the Bodies Exhibit. How are they similar and d ...
... 12. Use a Clorox Wipe to clean: all used tools, the blue mat, gray dissecting tray, lab table. 13. Return all clean materials to the drawer you got them from. Part D: What I learned Summary Questions 14. Compare the organs in the frog to what you saw at the Bodies Exhibit. How are they similar and d ...
PH Balance and You - Midwest Health and Wellness
... A surprising number and variety of physical problems and diseases can be caused by the problem of foods that are acid-producing after digestion. Today the vast majority of the populace in industrialized nations suffer from problems caused by the stress of acidosis, because both modern lifestyle and ...
... A surprising number and variety of physical problems and diseases can be caused by the problem of foods that are acid-producing after digestion. Today the vast majority of the populace in industrialized nations suffer from problems caused by the stress of acidosis, because both modern lifestyle and ...
Chapter 18: Vertebrate Animals
... living in water. Think about some of the things an amphibian must deal with in its environment. Temperature changes more quickly and more often in air than in water. More oxygen is available in air than in water. However, air doesn’t support body weight as well as water does. Amphibians are adapted ...
... living in water. Think about some of the things an amphibian must deal with in its environment. Temperature changes more quickly and more often in air than in water. More oxygen is available in air than in water. However, air doesn’t support body weight as well as water does. Amphibians are adapted ...
Abdominopelvic Cavity
... divides a structure into superior and inferior portions; also called a horizontal, or cross section ...
... divides a structure into superior and inferior portions; also called a horizontal, or cross section ...
Renal, Fluid Balance, and Acid-Base Objectives
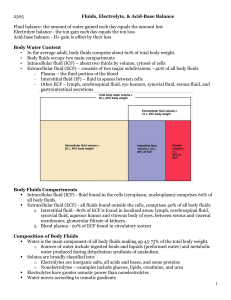
... R 1. Given the body weight and percent body fat, estimate the a) total body water, b) lean body mass, c) extracellular fluid volume, d) intracellular fluid volume, e) blood volume, and f) plasma volume. Identify normal extracellular fluid (plasma) osmolarity and concentrations of Na+, K+, Cl-, HCO3- ...
... R 1. Given the body weight and percent body fat, estimate the a) total body water, b) lean body mass, c) extracellular fluid volume, d) intracellular fluid volume, e) blood volume, and f) plasma volume. Identify normal extracellular fluid (plasma) osmolarity and concentrations of Na+, K+, Cl-, HCO3- ...
LARGE ANIMALS ANATOMY ORGAN SYSTEMS
... storage and insulation), epithelial tissue (protecting and lining surfaces of many body organs), muscle (allowing movement) or nervous tissue (generating and conducting electric signals in the body). Each body organ has a specific shape and is composed of various types of tissue that provide complex ...
... storage and insulation), epithelial tissue (protecting and lining surfaces of many body organs), muscle (allowing movement) or nervous tissue (generating and conducting electric signals in the body). Each body organ has a specific shape and is composed of various types of tissue that provide complex ...
NSC Chapter 3
... Abdominal – located in the trunk between the diaphragm and the pelvis. It contains the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, intestines, stomach, kidneys and spleen. Because most of the abdominal cavity is not protected by bones, the organs within it are especially vulnerable to injury Pelvic – located in ...
... Abdominal – located in the trunk between the diaphragm and the pelvis. It contains the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, intestines, stomach, kidneys and spleen. Because most of the abdominal cavity is not protected by bones, the organs within it are especially vulnerable to injury Pelvic – located in ...
CONDICIÓN FÍSICA Y CAPACIDADES FÍSICAS BÁSICAS
... - Increases heart volume. - Strengthens and expands the wall of the heart. - Reduces heart rate at rest. - It allows for better recovery during rest periods. - It increases blood circulation. - Stimulates the metabolism in general. ...
... - Increases heart volume. - Strengthens and expands the wall of the heart. - Reduces heart rate at rest. - It allows for better recovery during rest periods. - It increases blood circulation. - Stimulates the metabolism in general. ...