You Can*t Have One Without the Other
... cell in the body! • I am the heart, the veins, the arteries, capillaries and blood. • I transport the white blood cells to all the infections and injuries. • Without me, the oxygen and the CO2 in the body couldn’t reach the cells or lungs. ...
... cell in the body! • I am the heart, the veins, the arteries, capillaries and blood. • I transport the white blood cells to all the infections and injuries. • Without me, the oxygen and the CO2 in the body couldn’t reach the cells or lungs. ...
Requirements of Living Organisms (from external environment)
... • Atom- particles which make up matter • Organelle• Cell- basic unit of structure and function • Tissue- specialized cells organized into layers or masses that have specific functions. • Organs• Organ systems- groups of organs that function closely together • Organism- ...
... • Atom- particles which make up matter • Organelle• Cell- basic unit of structure and function • Tissue- specialized cells organized into layers or masses that have specific functions. • Organs• Organ systems- groups of organs that function closely together • Organism- ...
File
... allowing it access to greater scarce resources. In this sense the impeding organism can be said to be negatively affected by the other's very existence, making it a +/interaction. A third simple example is when sheep or cattle make trails in grass that they trample on, and without realizing, they ar ...
... allowing it access to greater scarce resources. In this sense the impeding organism can be said to be negatively affected by the other's very existence, making it a +/interaction. A third simple example is when sheep or cattle make trails in grass that they trample on, and without realizing, they ar ...
Chapter 2
... • Marine Ecology is the scientific study of marine-life habitat, populations, and interactions among organisms and the surrounding environment including their • abiotic factors - non-living physical and chemical factors that affect the ability of organisms to survive and reproduce and • biotic facto ...
... • Marine Ecology is the scientific study of marine-life habitat, populations, and interactions among organisms and the surrounding environment including their • abiotic factors - non-living physical and chemical factors that affect the ability of organisms to survive and reproduce and • biotic facto ...
ecosystems - Kawameeh Middle School
... that provides food, water, shelter, and other biotic and abiotic factors that an organism needs to survive and reproduce Population: All the organisms of the same species that live in the same area at the same time Community: ALL of the populations living in the SAME area at the SAME time ...
... that provides food, water, shelter, and other biotic and abiotic factors that an organism needs to survive and reproduce Population: All the organisms of the same species that live in the same area at the same time Community: ALL of the populations living in the SAME area at the SAME time ...
Organ Systems Working Together
... your cells are organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems To keep your body healthy all of your systems must work together For example: Digestive system gets nutrients and circulatory system disperses the nutrients around the body Organ systems can be divided into 2 main groups: ...
... your cells are organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems To keep your body healthy all of your systems must work together For example: Digestive system gets nutrients and circulatory system disperses the nutrients around the body Organ systems can be divided into 2 main groups: ...
You Can`t Have One Without the Other
... cell in the body! • I am the heart, the veins, the arteries, capillaries and blood. • I transport the white blood cells to all the infections and injuries. • Without me, the oxygen and the CO2 in the body couldn’t reach the cells or lungs. ...
... cell in the body! • I am the heart, the veins, the arteries, capillaries and blood. • I transport the white blood cells to all the infections and injuries. • Without me, the oxygen and the CO2 in the body couldn’t reach the cells or lungs. ...
CP-Bio Ch. 27 (Populations)
... species living in the same place at the same time • Species- Any group of organisms that are able to reproduce and produce fertile offspring • Birthrate- # of organisms born in a period of time, usually expressed as the number of births each year for every 1000 people ...
... species living in the same place at the same time • Species- Any group of organisms that are able to reproduce and produce fertile offspring • Birthrate- # of organisms born in a period of time, usually expressed as the number of births each year for every 1000 people ...
Section 1
... The largest population that an environment can support at any given time is called carrying capacity. ...
... The largest population that an environment can support at any given time is called carrying capacity. ...
04populations2 3564KB Nov 01 2012 07:59:58 AM
... 3. competition: each organism has the same need as any other. They compete for resources such as ...
... 3. competition: each organism has the same need as any other. They compete for resources such as ...
Populations - WordPress.com
... 2. Logistic Growth: Population grows rapidly until some factor limits growth a. ...
... 2. Logistic Growth: Population grows rapidly until some factor limits growth a. ...
Marine Ecology
... • Biological factors – larval supply, competition, predation, parasitism, – can also limit where an organism can be found ...
... • Biological factors – larval supply, competition, predation, parasitism, – can also limit where an organism can be found ...
Chap 10- Ecosystems notes.pptx
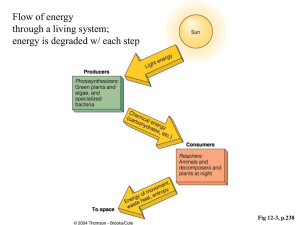
... • An Energy Pyramid shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another. • Most energy is at the producer level, less as you move up. • The wide base of pyramid show the ...
... • An Energy Pyramid shows the amount of energy that moves from one feeding level to another. • Most energy is at the producer level, less as you move up. • The wide base of pyramid show the ...
Science 10
... If the place is near the equator than the temperature mostly stays the same but if it is higher to the north the temperature is higher in the 7th and 8th months and lower in the 1st and 12th months. And in the south they have higher temperatures in the 1st and 12th months and lower in the 7th and 8t ...
... If the place is near the equator than the temperature mostly stays the same but if it is higher to the north the temperature is higher in the 7th and 8th months and lower in the 1st and 12th months. And in the south they have higher temperatures in the 1st and 12th months and lower in the 7th and 8t ...
Ecology 1-
... Symbiotic relationships • Mutualism: When both organisms benefit (ex. Lichen = photosynthetic algae and fungus) Algae provides food (sugar) for the fungus Fungus provides algae with water • Commensalism: One organism benefits, while the other is neither helped nor harmed. • Parasitism: One organism ...
... Symbiotic relationships • Mutualism: When both organisms benefit (ex. Lichen = photosynthetic algae and fungus) Algae provides food (sugar) for the fungus Fungus provides algae with water • Commensalism: One organism benefits, while the other is neither helped nor harmed. • Parasitism: One organism ...
the lost world
... natural selection theory. The species evolved to be green because this color was well adapted to the frog’s environment, and individuals with green backs survived better and left more green backed offspring to the next generation. If you were given an unknown organism, could you, by observing it, ex ...
... natural selection theory. The species evolved to be green because this color was well adapted to the frog’s environment, and individuals with green backs survived better and left more green backed offspring to the next generation. If you were given an unknown organism, could you, by observing it, ex ...
What is a Human?
... in the image of God, in that he can make moral decisions and is accountable for them. Men, unlike angels, are limited to physical bodies; men, unlike animals, have spirits with their bodies. ...
... in the image of God, in that he can make moral decisions and is accountable for them. Men, unlike angels, are limited to physical bodies; men, unlike animals, have spirits with their bodies. ...
Biodiversity
... The modern view is that organisms changed over time and evolution is accepted as the basis for classification Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of an organism determined by radioactive dating, comparative biochemistry, physiology and DNA studies. ...
... The modern view is that organisms changed over time and evolution is accepted as the basis for classification Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of an organism determined by radioactive dating, comparative biochemistry, physiology and DNA studies. ...
Mid Ecology Unit Test Review
... i. All the zebras living in the same area ii. Zebras and giraffes in the same area iii. Zebras, giraffes, and grass in the same area 3. Energy Flow a. The sun is the primary source of energy in most ecosystems. b. Organisms that can convert sunlight into food (glucose) are called producers or autotr ...
... i. All the zebras living in the same area ii. Zebras and giraffes in the same area iii. Zebras, giraffes, and grass in the same area 3. Energy Flow a. The sun is the primary source of energy in most ecosystems. b. Organisms that can convert sunlight into food (glucose) are called producers or autotr ...
Chapter 7 Animal Classification, Phylogeny, and
... • 3. Closely related species are placed in the same genus; closely related genera are placed in the same family, and so on. • 4.Taxon is a general term used to represent a group of animals at any level of the classification scheme. • B. To decide how closely related one taxon is to another, biologi ...
... • 3. Closely related species are placed in the same genus; closely related genera are placed in the same family, and so on. • 4.Taxon is a general term used to represent a group of animals at any level of the classification scheme. • B. To decide how closely related one taxon is to another, biologi ...
Ecology - Images
... of the Arctic region. Polar bears prefer the ice packs to other parts of their habitat because it allows them to remain in close contact with their main food source, the seal. ...
... of the Arctic region. Polar bears prefer the ice packs to other parts of their habitat because it allows them to remain in close contact with their main food source, the seal. ...
s1-biology-unit-1-need-to-know
... Cells are the basic unit of the body. They are organised together into tissue. Different tissues come together to make organs. Organs work together in body systems. An example of a body system is the respiratory system. The organs in this system are lungs, diaphragm, trachea. The respiratory system ...
... Cells are the basic unit of the body. They are organised together into tissue. Different tissues come together to make organs. Organs work together in body systems. An example of a body system is the respiratory system. The organs in this system are lungs, diaphragm, trachea. The respiratory system ...