systems of particles
... • With no external horizontal forces, it follows from the impulse-momentum principle that the horizontal component of momentum is conserved. This relation can be solved for the velocity of B at its maximum elevation. • The conservation of energy principle can be applied to relate the initial kinetic ...
... • With no external horizontal forces, it follows from the impulse-momentum principle that the horizontal component of momentum is conserved. This relation can be solved for the velocity of B at its maximum elevation. • The conservation of energy principle can be applied to relate the initial kinetic ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 18: equilibrium & revision
... A ‘smart’ student decides to save energy by connecting his exercise treadmill to his laptop battery. If it takes 70 J to move the belt on the treadmill by 1 meter and 50% of the generated energy is stored in the battery, how ‘far’ must the student run to use his 100 W laptop for free for 2 hours? ...
... A ‘smart’ student decides to save energy by connecting his exercise treadmill to his laptop battery. If it takes 70 J to move the belt on the treadmill by 1 meter and 50% of the generated energy is stored in the battery, how ‘far’ must the student run to use his 100 W laptop for free for 2 hours? ...
Momentum and Collisions
... Elastic and perfectly inelastic collisions are limiting cases, most actual collisions fall in between these two types Momentum is conserved in all collisions ...
... Elastic and perfectly inelastic collisions are limiting cases, most actual collisions fall in between these two types Momentum is conserved in all collisions ...
Document
... (a) Calculate the impulse experienced when a 70. Kg person lands on firm ground after jumping from a height of 3.0 m. (b) Estimate the average force exerted on the person’s feet by the ground if the landing is stiff-legged, and again (c) with bent legs. With stiff legs, assume the body moves 1.0 cm ...
... (a) Calculate the impulse experienced when a 70. Kg person lands on firm ground after jumping from a height of 3.0 m. (b) Estimate the average force exerted on the person’s feet by the ground if the landing is stiff-legged, and again (c) with bent legs. With stiff legs, assume the body moves 1.0 cm ...
I. Setting the Stage: Star Formation and Hydrogen Burning in Single
... accurate. These laws were once thought inviolate. Recent theoretical developments have suggested that this is not strictly true. One of the suggestions arising from the work of constructing a Grand Unified Theory of the strong and electroweak forces is that baryons may not be completely conserved. T ...
... accurate. These laws were once thought inviolate. Recent theoretical developments have suggested that this is not strictly true. One of the suggestions arising from the work of constructing a Grand Unified Theory of the strong and electroweak forces is that baryons may not be completely conserved. T ...
Quantum Optics and Photonics S. Ezekiel, S. M. Shahriar
... Recently, we reported near 100% efficient EIT in a Pr3+ doped Y2SiO5 (Pr:YSO) crystal14 wherein transparency of probe field was demonstrated at line center in an optically thick sample. At low temperatures, this "dark resonance" has a width on the order of 10's kHz. This potentially makes it suitabl ...
... Recently, we reported near 100% efficient EIT in a Pr3+ doped Y2SiO5 (Pr:YSO) crystal14 wherein transparency of probe field was demonstrated at line center in an optically thick sample. At low temperatures, this "dark resonance" has a width on the order of 10's kHz. This potentially makes it suitabl ...
POP4e: Ch. 1 Problems
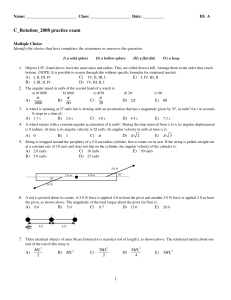
... 5. Two forces are acting on an object. Which of the following statements is correct? (a) The object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. (b) The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. (c) The object is in equilibrium if the forc ...
... 5. Two forces are acting on an object. Which of the following statements is correct? (a) The object is in equilibrium if the forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. (b) The object is in equilibrium if the net torque on the object is zero. (c) The object is in equilibrium if the forc ...
Motor Control Theory 1
... then the other must twist in the other, to maintain overall zero • But you can change moment of inertia, too... • So twist one half with little inertia (relative to the axis of rotation), and the other half with a lot of ...
... then the other must twist in the other, to maintain overall zero • But you can change moment of inertia, too... • So twist one half with little inertia (relative to the axis of rotation), and the other half with a lot of ...