Momentum - ClassZone
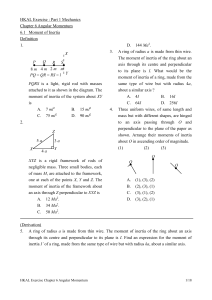
... product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum is similar to inertia. To calculate an object’s momentum, you can use the following formula: momentum = mass · velocity p = mv In this formula, p stands for momentum, m for mass, and v for velocity. Momentum is usually measured in units of kilogram mete ...
... product of its mass and its velocity. Momentum is similar to inertia. To calculate an object’s momentum, you can use the following formula: momentum = mass · velocity p = mv In this formula, p stands for momentum, m for mass, and v for velocity. Momentum is usually measured in units of kilogram mete ...
Chapter 3: Relativistic dynamics
... the resulting motion. To integrate the relativistic equations (3.4.1), you need initial conditions plus a four-vector force f (τ ). This would appear to be more information (four components instead of three), and yet relativistic dynamics must reduce to non-relativistic dynamics when velocities are ...
... the resulting motion. To integrate the relativistic equations (3.4.1), you need initial conditions plus a four-vector force f (τ ). This would appear to be more information (four components instead of three), and yet relativistic dynamics must reduce to non-relativistic dynamics when velocities are ...
Assemblage: Exercises in Statistical Mechanics ====== [A] Ensemble Theory - classical gases
... A01. Assume that the entropy S and the number of states in phase space Ω of a physical system are related through an arbitrary function, S = f (Ω). Show that the additive character of S and the multiplicative character of Ω necessarily require that f (Ω) ∼ ln Ω. A02. Consider mixing of two gases wit ...
... A01. Assume that the entropy S and the number of states in phase space Ω of a physical system are related through an arbitrary function, S = f (Ω). Show that the additive character of S and the multiplicative character of Ω necessarily require that f (Ω) ∼ ln Ω. A02. Consider mixing of two gases wit ...
arXiv:1705.00333v1 [cond-mat.supr
... We can see from Eq.(20), that if the coupling constant is g ≡ λνF = 0 then ∆ = 0. This means, that only electronb υ is an external electron coupling is the cause of superconductivity but not the potential υ. In this case the operator H field acting on the Cooper pairs only, and υ is energy of the pa ...
... We can see from Eq.(20), that if the coupling constant is g ≡ λνF = 0 then ∆ = 0. This means, that only electronb υ is an external electron coupling is the cause of superconductivity but not the potential υ. In this case the operator H field acting on the Cooper pairs only, and υ is energy of the pa ...
A Wave Interpretation of the Compton Effect As a Further
... where ks cos ϕ = ki − k cos θ is used. It is easy to show that this relation is identical to (1). Thus the Compton effect can be interpreted in an entirely different way. Based on the wave interpretation, the Compton scattering can be viewed as a demonstration of the wave nature of electrons, of the ...
... where ks cos ϕ = ki − k cos θ is used. It is easy to show that this relation is identical to (1). Thus the Compton effect can be interpreted in an entirely different way. Based on the wave interpretation, the Compton scattering can be viewed as a demonstration of the wave nature of electrons, of the ...
Spin or, Actually: Spin and Quantum Statistics
... understood, mathematically, on the basis of the Schrödinger-Pauli equation. We do not understand how crystalline or quasi-crystalline order can be derived as a consequence of equilibrium quantum statistical mechanics. All this shows how little we understand about ‘emergent behavior’ of many-particl ...
... understood, mathematically, on the basis of the Schrödinger-Pauli equation. We do not understand how crystalline or quasi-crystalline order can be derived as a consequence of equilibrium quantum statistical mechanics. All this shows how little we understand about ‘emergent behavior’ of many-particl ...
physical world
... For example, the universal law of gravitation proposed by Newton is an assumption or hypothesis, which he proposed out of his ingenuity. Before him, there were several observations, experiments and data, on the motion of planets around the sun, motion of the moon around the earth, pendulums, bodies ...
... For example, the universal law of gravitation proposed by Newton is an assumption or hypothesis, which he proposed out of his ingenuity. Before him, there were several observations, experiments and data, on the motion of planets around the sun, motion of the moon around the earth, pendulums, bodies ...
Exercises in Statistical Mechanics ====== [A] Ensemble Theory - classical gases
... (b) Derive the density distribution as function of the distance r from the axis for an ideal classical gas at temperature T (effects of gravitation are negligible). A12. N monomeric units are arranged along a straight line to form a chain molecule. Each unit can be either in a state α (with length a ...
... (b) Derive the density distribution as function of the distance r from the axis for an ideal classical gas at temperature T (effects of gravitation are negligible). A12. N monomeric units are arranged along a straight line to form a chain molecule. Each unit can be either in a state α (with length a ...
Ehrenfest theorem, Galilean invariance and nonlinear Schr\" odinger
... of a lagrangian that is a real scalar dependent on a complex wave function and independent of spatial coordinates except through the wave function and its derivatives. We also assumed that there do not appear derivatives of higher order, although this is not an essential ingredient. Both eqs.(19,21) ...
... of a lagrangian that is a real scalar dependent on a complex wave function and independent of spatial coordinates except through the wave function and its derivatives. We also assumed that there do not appear derivatives of higher order, although this is not an essential ingredient. Both eqs.(19,21) ...
GCOE13_5
... • The bare Higgs mass becomes close to zero at the string scale. It implies that SUSY is restored at the string scale. Actually there are many string vacua in which SUSY is spontaneously broken at the string scale. • The Higgs self coupling also becomes close to zero at the string scale. It indicate ...
... • The bare Higgs mass becomes close to zero at the string scale. It implies that SUSY is restored at the string scale. Actually there are many string vacua in which SUSY is spontaneously broken at the string scale. • The Higgs self coupling also becomes close to zero at the string scale. It indicate ...
chapter13
... • Only ideal systems oscillate indefinitely • In real systems, friction retards the motion • Friction reduces the total energy of the system and the oscillation is said to be damped ...
... • Only ideal systems oscillate indefinitely • In real systems, friction retards the motion • Friction reduces the total energy of the system and the oscillation is said to be damped ...

![Assemblage: Exercises in Statistical Mechanics ====== [A] Ensemble Theory - classical gases](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008930193_1-b370c417d56cac9a0859542b76e2a6e4-300x300.png)







![Exercises in Statistical Mechanics ====== [A] Ensemble Theory - classical gases](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008930185_1-59cc607a5cbfa43d1c480bd3c23f15ec-300x300.png)