Protein kinase CK2: a newcomer in the `druggable kinome`
... molecules par excellence, whose biological activity can be turned off easily and precisely by compounds that block the catalytic site. All eukaryotic serine/threonine- and tyrosinespecific protein kinases belong to the largest single family of enzymes (the so-called ‘kinome’) numbering over 500 and ...
... molecules par excellence, whose biological activity can be turned off easily and precisely by compounds that block the catalytic site. All eukaryotic serine/threonine- and tyrosinespecific protein kinases belong to the largest single family of enzymes (the so-called ‘kinome’) numbering over 500 and ...
Fes Kinase - Cell Signaling Technology
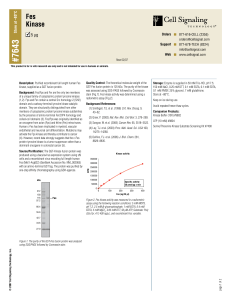
... Background: Fes/Fps and Fer are the only two members of a unique family of cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinases (1,2). Fps and Fer contain a central Src homology-2 (SH2) domain and a carboxy-terminal tyrosine kinase catalytic domain. They are structurally distinguished from other members of cytoplas ...
... Background: Fes/Fps and Fer are the only two members of a unique family of cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinases (1,2). Fps and Fer contain a central Src homology-2 (SH2) domain and a carboxy-terminal tyrosine kinase catalytic domain. They are structurally distinguished from other members of cytoplas ...
lecture3
... low pH mercurials (such as mercuric chloride) urea or by gentle heating. Desensitisation causes dissociation of the ntive enzyme into its component sub-units and this prevents interaction between the regulator and catalytic sites. Unlike most enzymes, many allosteric enzymes undergo reversible inact ...
... low pH mercurials (such as mercuric chloride) urea or by gentle heating. Desensitisation causes dissociation of the ntive enzyme into its component sub-units and this prevents interaction between the regulator and catalytic sites. Unlike most enzymes, many allosteric enzymes undergo reversible inact ...
C-Raf

RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase also known as proto-oncogene c-RAF or simply c-Raf or even Raf-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RAF1 gene. The c-Raf protein is part of the ERK1/2 pathway as a MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAP3K) that functions downstream of the Ras subfamily of membrane associated GTPases. C-Raf is a member of the Raf kinase family of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases, from the TKL (Tyrosine-kinase-like) group of kinases.