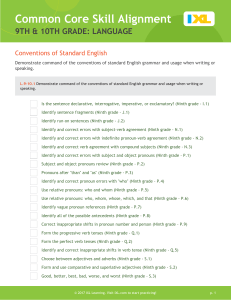
Common Core Skill Alignment
... Misplaced modifiers with pictures (Ninth grade - T.7) Select the misplaced or dangling modifier (Ninth grade - T.8) Are the modifiers used correctly? (Ninth grade - T.9) Is the sentence declarative, interrogative, imperative, or exclamatory? (Tenth grade - H.1) Identify sentence fragments (Tenth gra ...
... Misplaced modifiers with pictures (Ninth grade - T.7) Select the misplaced or dangling modifier (Ninth grade - T.8) Are the modifiers used correctly? (Ninth grade - T.9) Is the sentence declarative, interrogative, imperative, or exclamatory? (Tenth grade - H.1) Identify sentence fragments (Tenth gra ...
How weak and how definite are Weak Definites?
... that the understood value of the definite varies based on the value of another argument (typically the subject) in the sentence. Adopting this perspective, it is of course only responsible to point out that there are plenty of examples where definites receive co-varying interpretations, but which ar ...
... that the understood value of the definite varies based on the value of another argument (typically the subject) in the sentence. Adopting this perspective, it is of course only responsible to point out that there are plenty of examples where definites receive co-varying interpretations, but which ar ...
Partitives A workshop at SLE 43
... • ‘Dedicated’ partitive case: Baltic Finnic, Basque, Oceanian, Russian (to some extent) • Cases that have some partitive-like functions: Hungarian (ablative); most Indo-European languages (genitive) • Languages with partitive articles: French, Italian. • Other types and/or other languages? ...
... • ‘Dedicated’ partitive case: Baltic Finnic, Basque, Oceanian, Russian (to some extent) • Cases that have some partitive-like functions: Hungarian (ablative); most Indo-European languages (genitive) • Languages with partitive articles: French, Italian. • Other types and/or other languages? ...
primary argument case-marking in baltic and finnic
... genitive (-n) and locative cases (adessive -llA, ablative -ltA and allative -lle) may be used to mark agents: these usually have a more or less transparent adverbial background. The term accusative is not unproblematic in Finnic: first of all, no distinct accusative marker is used with plural NPs. ...
... genitive (-n) and locative cases (adessive -llA, ablative -ltA and allative -lle) may be used to mark agents: these usually have a more or less transparent adverbial background. The term accusative is not unproblematic in Finnic: first of all, no distinct accusative marker is used with plural NPs. ...
Stress in simple words
... Two – syllable adjectives are stressed according to the same rules: lovely /lΛvli/, even /i:vn/, hollow /holəu/, divine /divain/, correct /kərekt/, alive /əliv/. There are exceptions; for example, honest /onist/, perfect /pə:fikt/, /pə:fekt/, both of which end with strong syllables but are stressed ...
... Two – syllable adjectives are stressed according to the same rules: lovely /lΛvli/, even /i:vn/, hollow /holəu/, divine /divain/, correct /kərekt/, alive /əliv/. There are exceptions; for example, honest /onist/, perfect /pə:fikt/, /pə:fekt/, both of which end with strong syllables but are stressed ...
African A m erican Vernac ular En glish Lingu istics Daniel K ie s
... consonant cluster deletion operates only when both consonants are identical in voice. The clusters [mp], [nt], and [lt] have one voiced and one voiceless consonant; therefore, they do not delete. ...
... consonant cluster deletion operates only when both consonants are identical in voice. The clusters [mp], [nt], and [lt] have one voiced and one voiceless consonant; therefore, they do not delete. ...
Level Three
... 3. gerunds, infinitives and participial adjectives 4. passive voice (tenses and with modal auxiliaries) 5. adjective clauses (who, whom, which, that, and markerless) 6. noun clauses, used as objects and as complements of adjectives 7. comparatives, equatives, and superlatives 8. questions: Y/N, WH, ...
... 3. gerunds, infinitives and participial adjectives 4. passive voice (tenses and with modal auxiliaries) 5. adjective clauses (who, whom, which, that, and markerless) 6. noun clauses, used as objects and as complements of adjectives 7. comparatives, equatives, and superlatives 8. questions: Y/N, WH, ...