Optical Electronic Spectroscopy 2
... “collisional deactivation” (molecules hitting each other), which causes quenching of phosphorescence signal ...
... “collisional deactivation” (molecules hitting each other), which causes quenching of phosphorescence signal ...
Chapter 12
... they can be time consuming to draw, and they do not show the spatial relationships of the atoms well. For example, the Lewis structure of butyl ethyl ether seems to indicate that the bond angles around each carbon atom are either 90° or 180° and that the carbon atoms lie in a straight line. In contr ...
... they can be time consuming to draw, and they do not show the spatial relationships of the atoms well. For example, the Lewis structure of butyl ethyl ether seems to indicate that the bond angles around each carbon atom are either 90° or 180° and that the carbon atoms lie in a straight line. In contr ...
CHE-05 Organic Chemistry
... in the Programme Guide that we sent you after your enrolment. A weightage of 30 percent, as you are aware, has been earmarked for continuous evaluation, which would consist of two tutor-marked assignments for this course. These assignments are provided in this booklet. Assignment-01 is based on Bloc ...
... in the Programme Guide that we sent you after your enrolment. A weightage of 30 percent, as you are aware, has been earmarked for continuous evaluation, which would consist of two tutor-marked assignments for this course. These assignments are provided in this booklet. Assignment-01 is based on Bloc ...
B.Sc. Industrial Chemistry
... B.Sc. Industrial Chemistry The course on B.Sc. Industrial Chemistry was introduced in the University of Delhi in 1984 and since then this course has undergone many changes and has become more comprehensive and relevant. The importance of industrial chemistry hardly needs any emphasis. It basically ...
... B.Sc. Industrial Chemistry The course on B.Sc. Industrial Chemistry was introduced in the University of Delhi in 1984 and since then this course has undergone many changes and has become more comprehensive and relevant. The importance of industrial chemistry hardly needs any emphasis. It basically ...
atomic number - geraldinescience
... Valence Electrons and Periodic Properties, continued • When an atom has 8 valence electrons, it is considered stable, or chemically unreactive. Unreactive atoms do not easily lose or gain electrons. • Elements whose atoms have only one, two, or three valence electrons tend to lose electrons easily. ...
... Valence Electrons and Periodic Properties, continued • When an atom has 8 valence electrons, it is considered stable, or chemically unreactive. Unreactive atoms do not easily lose or gain electrons. • Elements whose atoms have only one, two, or three valence electrons tend to lose electrons easily. ...
SAMPLE PAPER Class - XII SUBJECT
... Ferric hydroxide sol gets coagulated on addition of sodium chloride solution (b) Cottrell’s smoke precipitator is fitted at the mouth of the chimney used in factories. (c) Physical adsorption is multilayered, while chemisorption is monolayered. Q.17. Nitro group increases the reactivity of chloroben ...
... Ferric hydroxide sol gets coagulated on addition of sodium chloride solution (b) Cottrell’s smoke precipitator is fitted at the mouth of the chimney used in factories. (c) Physical adsorption is multilayered, while chemisorption is monolayered. Q.17. Nitro group increases the reactivity of chloroben ...
Solvent effects on excited state relaxation phenomena
... generally a redshift of the spectra on increasing solvent polarity, because excited state dipole moments are more often larger than in the ground state. Specific interactions could ifluence the energy of the inital and final state of an electronic transition in the same or in opposite way, causing t ...
... generally a redshift of the spectra on increasing solvent polarity, because excited state dipole moments are more often larger than in the ground state. Specific interactions could ifluence the energy of the inital and final state of an electronic transition in the same or in opposite way, causing t ...
File
... as a unit. Energy is stored in chemical bonds. To break bonds, energy must be added. When bonds form, energy is released. All chemical reactions involve changes in energy. Energy is either produced or absorbed during a chemical reaction. For example, the burning of wood is a chemical reaction (see F ...
... as a unit. Energy is stored in chemical bonds. To break bonds, energy must be added. When bonds form, energy is released. All chemical reactions involve changes in energy. Energy is either produced or absorbed during a chemical reaction. For example, the burning of wood is a chemical reaction (see F ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... Example (needs to be a double replacement reaction) AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl + NaNO3 1. this is the full balanced equation 2. next, write it as an ionic equation by splitting the compounds into their ions: Ag1+ + NO31- + Na1+ + Cl1- AgCl + Na1+ + NO31Note that the AgCl did not ionize, because it is a “ ...
... Example (needs to be a double replacement reaction) AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl + NaNO3 1. this is the full balanced equation 2. next, write it as an ionic equation by splitting the compounds into their ions: Ag1+ + NO31- + Na1+ + Cl1- AgCl + Na1+ + NO31Note that the AgCl did not ionize, because it is a “ ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Enzymes aren’t used up Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
... Enzymes aren’t used up Enzymes are not changed by the reaction used only temporarily re-used again for the same reaction with other molecules very little enzyme needed to help in many reactions ...
Covalent Bonding
... covalent bond • Two shared pairs of electrons is a double covalent bond. • Three shared pairs of electrons is a triple covalent bond. ...
... covalent bond • Two shared pairs of electrons is a double covalent bond. • Three shared pairs of electrons is a triple covalent bond. ...
Chapter 2 - people.vcu.edu
... I can guarantee that at some point you will be asked to circle the functional groups on a large molecule and state what class of compound each functional group makes the molecule. ...
... I can guarantee that at some point you will be asked to circle the functional groups on a large molecule and state what class of compound each functional group makes the molecule. ...
Research Achievements
... molecules with high energy and long lifetimes, which are capable of undergoing inner-sphere atom transfer reactions. Che, Gray and Roundhill are the pioneers in the development of a molecular photocatalyst, [Pt2(P2O5H2)4]4−, which can catalyze light-induced cleavage of C-H bonds of hydrocarbons with ...
... molecules with high energy and long lifetimes, which are capable of undergoing inner-sphere atom transfer reactions. Che, Gray and Roundhill are the pioneers in the development of a molecular photocatalyst, [Pt2(P2O5H2)4]4−, which can catalyze light-induced cleavage of C-H bonds of hydrocarbons with ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... Example (needs to be a double replacement reaction) AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl + NaNO3 1. this is the full balanced equation 2. next, write it as an ionic equation by splitting the compounds into their ions: Ag1+ + NO31- + Na1+ + Cl1- AgCl + Na1+ + NO31Note that the AgCl did not ionize, because it is a “ ...
... Example (needs to be a double replacement reaction) AgNO3 + NaCl AgCl + NaNO3 1. this is the full balanced equation 2. next, write it as an ionic equation by splitting the compounds into their ions: Ag1+ + NO31- + Na1+ + Cl1- AgCl + Na1+ + NO31Note that the AgCl did not ionize, because it is a “ ...
COURSES SCHEME & SYLLABUS
... Course Objective: To impart advanced knowledge of aromaticity, stereochemistry of organic compounds, pericyclic and photochemical reactions. Stereochemistry: Conformational analysis of Cycloalkanes and Decalins, Effect of conformation on reactivity, Conformation of sugars, Steric-strain due to unavo ...
... Course Objective: To impart advanced knowledge of aromaticity, stereochemistry of organic compounds, pericyclic and photochemical reactions. Stereochemistry: Conformational analysis of Cycloalkanes and Decalins, Effect of conformation on reactivity, Conformation of sugars, Steric-strain due to unavo ...
Equivalent weight
... •Equivalent weight (also known as gram equivalent) is a term which has been used in several contexts in chemistry. •In its most general usage, it is the mass of one equivalent, that is the mass of a given substance which will: •supply or react with one mole of hydrogen ions(H+) in an acid–base react ...
... •Equivalent weight (also known as gram equivalent) is a term which has been used in several contexts in chemistry. •In its most general usage, it is the mass of one equivalent, that is the mass of a given substance which will: •supply or react with one mole of hydrogen ions(H+) in an acid–base react ...
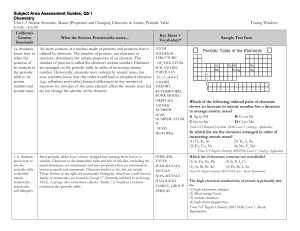
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... element from Group 2 will most often combine with two atoms of an element from Group 17 (e.g., MgCl2) because Group 2 elements have two electrons available for bonding, and Group 17 elements have only one electron position open in the outermost energy level. (Note that some periodic tables indicate ...
... element from Group 2 will most often combine with two atoms of an element from Group 17 (e.g., MgCl2) because Group 2 elements have two electrons available for bonding, and Group 17 elements have only one electron position open in the outermost energy level. (Note that some periodic tables indicate ...
Barnard Castle School Chemistry Department
... compound contains a fixed number of atoms of each kind, and has a formula to show how many of each atom is used. Be familiar with the names and symbols of the 1st 20 elements in the Periodic Table (ie. H, He, B, Be …….to Ca). Compounds have very different properties to the elements from which they a ...
... compound contains a fixed number of atoms of each kind, and has a formula to show how many of each atom is used. Be familiar with the names and symbols of the 1st 20 elements in the Periodic Table (ie. H, He, B, Be …….to Ca). Compounds have very different properties to the elements from which they a ...
physical setting chemistry
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
AS CHECKLISTS File
... Describe the combustion of alkanes, leading to their use as fuels in industry, in the home and in transport. Explain using equations the incomplete combustion of alkanes in a limited supply of oxygen and outline the potential dangers arising from production of CO in the home and from car use. Descri ...
... Describe the combustion of alkanes, leading to their use as fuels in industry, in the home and in transport. Explain using equations the incomplete combustion of alkanes in a limited supply of oxygen and outline the potential dangers arising from production of CO in the home and from car use. Descri ...
Spring 2001 - TAMU Chemistry
... The atomic radius of oxygen is smaller than the ionic radius of the oxide anion. A lithium cation is smaller than a lithium atom. The first ionization energy of helium is greater than that of neon. ...
... The atomic radius of oxygen is smaller than the ionic radius of the oxide anion. A lithium cation is smaller than a lithium atom. The first ionization energy of helium is greater than that of neon. ...