Covalent Bonding - whitburnscience
... Many atoms can be found as ions. An ion is an atom that has gained or lost an electron. Atoms gain or lose electrons to get full outer shells and increase their stability. The alkali metals produce a charge of one positive and would be written as X+. So Sodium would be written as Na+. While Magnesiu ...
... Many atoms can be found as ions. An ion is an atom that has gained or lost an electron. Atoms gain or lose electrons to get full outer shells and increase their stability. The alkali metals produce a charge of one positive and would be written as X+. So Sodium would be written as Na+. While Magnesiu ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion
... reactions with Lewis acids The product is formed by loss of a proton, which is replaced by bromine FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from ...
... reactions with Lewis acids The product is formed by loss of a proton, which is replaced by bromine FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion
... reactions with Lewis acids The product is formed by loss of a proton, which is replaced by bromine FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from ...
... reactions with Lewis acids The product is formed by loss of a proton, which is replaced by bromine FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from ...
3-3 More bonding.pptx
... Bonding in tetrahedral C • Hybridized atomic orbitals (sp3) give rise to strong directed bonds. – Giving rise to high mp/decomposiKon temperature – because these bonds have to be broken to melt diamo ...
... Bonding in tetrahedral C • Hybridized atomic orbitals (sp3) give rise to strong directed bonds. – Giving rise to high mp/decomposiKon temperature – because these bonds have to be broken to melt diamo ...
Stoichiometry – AP - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... I can write a balanced chemical equation and predict the amount of product formed from a given mass of reactant or the amount of reactant required to produce a desired amount of product. I can identify limiting reactants, and calculate the amount of product formed when given the amounts of all t ...
... I can write a balanced chemical equation and predict the amount of product formed from a given mass of reactant or the amount of reactant required to produce a desired amount of product. I can identify limiting reactants, and calculate the amount of product formed when given the amounts of all t ...
Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and
... Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and Molecular Structure This chapter deals with two additional approaches chemists use to describe chemical bonding: valence-shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory and hybrid orbitals (valence bonding). Lewis dot structures give us limite ...
... Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and Molecular Structure This chapter deals with two additional approaches chemists use to describe chemical bonding: valence-shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory and hybrid orbitals (valence bonding). Lewis dot structures give us limite ...
Chapter 20 Amines-part 2
... t Coupling with phenol occurs best in slightly alkaline solution l Generates a phenoxideion that couples more rapidly l If the solution is too alkaline, a nonreactive diazohydroxide ...
... t Coupling with phenol occurs best in slightly alkaline solution l Generates a phenoxideion that couples more rapidly l If the solution is too alkaline, a nonreactive diazohydroxide ...
Molecular Orbitals and Molecular Structure
... previously met the familiar homologous series of alkanes, alkenes, cycloalkanes and alkynes. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons which fit the general formula CnH-2n+2. This means that every carbon atom in an alkane molecule will have 4 single covalent bonds and as we have previously studied have the ...
... previously met the familiar homologous series of alkanes, alkenes, cycloalkanes and alkynes. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons which fit the general formula CnH-2n+2. This means that every carbon atom in an alkane molecule will have 4 single covalent bonds and as we have previously studied have the ...
problems - chem.msu.su
... (cm), or diffusion current Imax (A), that are proportional to the concentration of the unknown ion, and by the potential at the midpoint of the wave E1/2 (half-wave potential) depending on the nature of the analyte. 1. A weighed amount of PbCl2 was dissolved in 100 mL (V0) of 1M KNO3 solution (the s ...
... (cm), or diffusion current Imax (A), that are proportional to the concentration of the unknown ion, and by the potential at the midpoint of the wave E1/2 (half-wave potential) depending on the nature of the analyte. 1. A weighed amount of PbCl2 was dissolved in 100 mL (V0) of 1M KNO3 solution (the s ...
Chapter 3
... ◦ the products are more stable (lower in energy) than the reactants. ◦ Just because they are exothermic doesn’t mean that alkene addition reactions occur rapidly. ◦ Reaction rate depends on the activation energy. ◦ Many alkene addition reactions require a catalyst. ...
... ◦ the products are more stable (lower in energy) than the reactants. ◦ Just because they are exothermic doesn’t mean that alkene addition reactions occur rapidly. ◦ Reaction rate depends on the activation energy. ◦ Many alkene addition reactions require a catalyst. ...
Questions - Scheikundeolympiade
... The exam paper consists of 29 numbered pages in addition to this cover page and two appendix pages containing Fundamental Constants, useful expressions and conversion factors, and the Periodic Table of the Elements. Furthermore, you are provided with 5 yellow sheets of scratch paper, a pen and a sci ...
... The exam paper consists of 29 numbered pages in addition to this cover page and two appendix pages containing Fundamental Constants, useful expressions and conversion factors, and the Periodic Table of the Elements. Furthermore, you are provided with 5 yellow sheets of scratch paper, a pen and a sci ...
CHEMISTRY SAMPLE PAPER - I
... 18. In order to wash clothes with water containing dissolved calcium hydrogencarbonate, which cleaning agent will you prefer and why: soaps or synthetic detergents? Give one advantage of soaps over ...
... 18. In order to wash clothes with water containing dissolved calcium hydrogencarbonate, which cleaning agent will you prefer and why: soaps or synthetic detergents? Give one advantage of soaps over ...
Remodeling of the natural product fumagillol
... regioselectivity), while 4 could be obtained with Zn(OTf)2 in 76% yield (9:76 regioselectivity). Bis-epoxide opening, and in particular, catalyst-controlled regioselectivity, proved to be quite general (Table 1). A variety of electron-rich and electron-deficient anilines produced either heterocyclic ...
... regioselectivity), while 4 could be obtained with Zn(OTf)2 in 76% yield (9:76 regioselectivity). Bis-epoxide opening, and in particular, catalyst-controlled regioselectivity, proved to be quite general (Table 1). A variety of electron-rich and electron-deficient anilines produced either heterocyclic ...
0922089
... At its fourteenth session, the ADN Safety Committee, recalling that, under 8.2.2.7.2.3 of the Regulations annexed to ADN, the ADN Administrative Committee was required to prepare a catalogue of questions for the ADN examinations, decided that the item should be put on the agenda for future sessions, ...
... At its fourteenth session, the ADN Safety Committee, recalling that, under 8.2.2.7.2.3 of the Regulations annexed to ADN, the ADN Administrative Committee was required to prepare a catalogue of questions for the ADN examinations, decided that the item should be put on the agenda for future sessions, ...
(Organic Chemistry II) Pahlavan
... this point. Carefully add 5 drops of 85 % phosphoric acid. Swirl the flask continuously for about five minutes. Set up a warm water bath. Clamp the flask in a beaker of water. Heat the water on a hot plate to about 70 – 80 oC, stirring the liquid in the flask occasionally. Keep the ...
... this point. Carefully add 5 drops of 85 % phosphoric acid. Swirl the flask continuously for about five minutes. Set up a warm water bath. Clamp the flask in a beaker of water. Heat the water on a hot plate to about 70 – 80 oC, stirring the liquid in the flask occasionally. Keep the ...
Chapter 3
... The assembly of individual molecular units driven by intermolecular interactions represents the central scope of supramolecular chemistry.1 Its principles can be applied in the solid state to the formation of supramolecular networks. These networks can be mono dimensional 1D, 2D or 3D and this depen ...
... The assembly of individual molecular units driven by intermolecular interactions represents the central scope of supramolecular chemistry.1 Its principles can be applied in the solid state to the formation of supramolecular networks. These networks can be mono dimensional 1D, 2D or 3D and this depen ...
Name: Northwest Vista College Chem 1311
... Reaction B: Products are at a higher energy content than reactants. 250 kJ are required to activate the reaction. A total of 100 kJ are absorbed by the reaction. It is endothermic. 2. Choose one of the hypothetical reactions in the diagrams above and write a general thermochemical equation for it us ...
... Reaction B: Products are at a higher energy content than reactants. 250 kJ are required to activate the reaction. A total of 100 kJ are absorbed by the reaction. It is endothermic. 2. Choose one of the hypothetical reactions in the diagrams above and write a general thermochemical equation for it us ...
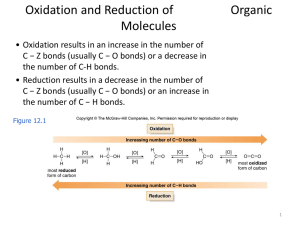
Oxidation and Reduction of Organic Molecules
... • The number of degrees of unsaturation lost = the number of bonds. • The number of degrees of unsaturation remaining in the product = the number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule co ...
... • The number of degrees of unsaturation lost = the number of bonds. • The number of degrees of unsaturation remaining in the product = the number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule co ...