Charges and Fields - Part I
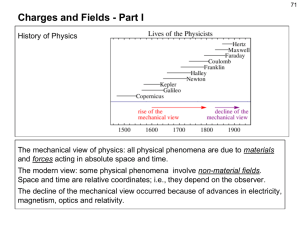
... and forces acting in absolute space and time. The modern view: some physical phenomena involve non-material fields. Space and time are relative coordinates; i.e., they depend on the observer. The decline of the mechanical view occurred because of advances in electricity, magnetism, optics and relati ...
... and forces acting in absolute space and time. The modern view: some physical phenomena involve non-material fields. Space and time are relative coordinates; i.e., they depend on the observer. The decline of the mechanical view occurred because of advances in electricity, magnetism, optics and relati ...
CnErCS2
... 300000 km/sec. Such an object is called a ‘black hole’. Presumably light from such an object could not escape to be seen by a distant observer, so that it would not appear at all and be perceived as a ‘black hole’. This conception was developed within the framework of GRT, but contains a logical err ...
... 300000 km/sec. Such an object is called a ‘black hole’. Presumably light from such an object could not escape to be seen by a distant observer, so that it would not appear at all and be perceived as a ‘black hole’. This conception was developed within the framework of GRT, but contains a logical err ...
Document
... Replace each circle with a coil of 10, 100 or more turns, carrying the same current: the attraction or repulsion increase by an appropriate factor. In fact, each coil acts very much like a magnet with magnetic poles at each end (an "electromagnet"). Ampere guessed that each atom of iron contained a ...
... Replace each circle with a coil of 10, 100 or more turns, carrying the same current: the attraction or repulsion increase by an appropriate factor. In fact, each coil acts very much like a magnet with magnetic poles at each end (an "electromagnet"). Ampere guessed that each atom of iron contained a ...
Relativity Presentation
... 4. If time is strange, what about space? 5. Faster than light? Momentum, Energy and E = mc² This sequence includes all of the points in the SD, but orders them in a more historically logical way. ...
... 4. If time is strange, what about space? 5. Faster than light? Momentum, Energy and E = mc² This sequence includes all of the points in the SD, but orders them in a more historically logical way. ...
Explosion at the Shipyard, N.F.G
... Lieutenant Junior Grade, U.S.N. Albert Einstein is seated before five senior officers at a Judge Advocate General Board of Inquiry. It has been convened at Pearl Harbor Naval Shipyard. Lt. J.G. Einstein is the defendant and the Board is about to issue it’s verdict. The charges are very serious. It s ...
... Lieutenant Junior Grade, U.S.N. Albert Einstein is seated before five senior officers at a Judge Advocate General Board of Inquiry. It has been convened at Pearl Harbor Naval Shipyard. Lt. J.G. Einstein is the defendant and the Board is about to issue it’s verdict. The charges are very serious. It s ...
YEAR 2: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM JULIA YEOMANS
... 9. A straight conducting wire of circular cross section and radius a has resistance R and carries a current I. Find the value and direction of the Poynting vector at a distance r from the centre of the wire. Hence show that: (a) the total power crossing the surface of the wire is I 2 R. (b) the ener ...
... 9. A straight conducting wire of circular cross section and radius a has resistance R and carries a current I. Find the value and direction of the Poynting vector at a distance r from the centre of the wire. Hence show that: (a) the total power crossing the surface of the wire is I 2 R. (b) the ener ...
SR 1 1 Special relativity, 1 Newton and Maxwell We have seen that
... and vz′ , with v′y = vy and vz′ = vz , but with v′x = vx − V . Back to Maxwell. Maxwell says that an accelerating charge generates electromagnetic radiation that travels at speed c in all directions. But if two Newtonian observers are moving relative to one another, then only one of them can observe ...
... and vz′ , with v′y = vy and vz′ = vz , but with v′x = vx − V . Back to Maxwell. Maxwell says that an accelerating charge generates electromagnetic radiation that travels at speed c in all directions. But if two Newtonian observers are moving relative to one another, then only one of them can observe ...
PHYSICS COURSE SYLLABUS Lucy C. Laney High School School
... c. Determine equivalent resistances in series and parallel circuits. d. Determine the relationship between moving electric charges and magnetic fields. SP6. The student will describe the corrections to Newtonian physics given by quantum mechanics and relativity when matter is very small, moving fast ...
... c. Determine equivalent resistances in series and parallel circuits. d. Determine the relationship between moving electric charges and magnetic fields. SP6. The student will describe the corrections to Newtonian physics given by quantum mechanics and relativity when matter is very small, moving fast ...
Chapter Three: Propagation of light waves Dr.Muayyed Jabar Zoory
... called displacement current. Thus this equation means that a magnetic field is generated by a time-varying electric field. ...
... called displacement current. Thus this equation means that a magnetic field is generated by a time-varying electric field. ...
CHAPTER 1: The Birth of Modern Physics
... Light propagates as a wave of concentric circles from the point of origin Explained reflection and refraction ...
... Light propagates as a wave of concentric circles from the point of origin Explained reflection and refraction ...
Chapter 34. Electromagnetic Induction
... where V is the velocity of frame S' relative to frame S and where the fields are measured at the same point in space by experimenters at rest in each reference frame. NOTE: These equations are only valid if V << c. ...
... where V is the velocity of frame S' relative to frame S and where the fields are measured at the same point in space by experimenters at rest in each reference frame. NOTE: These equations are only valid if V << c. ...
The Meaning of the Maxwell Field Equations
... the curl of the vector potential is associated with energy of rotational motion. This distinction between the electric and magnetic fields is far more vital than any formal mathematical analogies between them. To complete the derivation of the field equations, we require only one further condition. ...
... the curl of the vector potential is associated with energy of rotational motion. This distinction between the electric and magnetic fields is far more vital than any formal mathematical analogies between them. To complete the derivation of the field equations, we require only one further condition. ...
Phy107Fall06Lect15 - UW High Energy Physics
... – He used the waves to form an interference pattern and calculated the wavelength – From v = f , v was found – v was very close to 3 x 108 m/s, the known speed of light • This provided evidence in support of Maxwell’s ...
... – He used the waves to form an interference pattern and calculated the wavelength – From v = f , v was found – v was very close to 3 x 108 m/s, the known speed of light • This provided evidence in support of Maxwell’s ...
Fall 2003 Digression: on the constancy of c.
... invents a “magnetic” force to explain the attraction between test charge and current-carrying wire. But the “magnetic” force is present only when current is flowing. It is not valid to talk about a separate “magnetic” force. You must talk about the “electromagnetic” force. ...
... invents a “magnetic” force to explain the attraction between test charge and current-carrying wire. But the “magnetic” force is present only when current is flowing. It is not valid to talk about a separate “magnetic” force. You must talk about the “electromagnetic” force. ...
JKDoranPaper - FSU High Energy Physics
... The theory of special relativity makes two postulates (Prosper, Krane). The first is that the laws of physics are the same for all non-accelerating observers, or observers moving in an inertial frame of reference. This means that it is impossible to verify whether you or your surroundings are moving ...
... The theory of special relativity makes two postulates (Prosper, Krane). The first is that the laws of physics are the same for all non-accelerating observers, or observers moving in an inertial frame of reference. This means that it is impossible to verify whether you or your surroundings are moving ...
Time in physics

Time in physics is defined by its measurement: time is what a clock reads. In classical, non-relativistic physics it is a scalar quantity and, like length, mass, and charge, is usually described as a fundamental quantity. Time can be combined mathematically with other physical quantities to derive other concepts such as motion, kinetic energy and time-dependent fields. Timekeeping is a complex of technological and scientific issues, and part of the foundation of recordkeeping.