Article 3 The Geography of Poverty and Wealth
... productivity. Of the major food grains— wheat, maize and rice—wheat grows only in temperate climates, and maize and rice crops are generally more productive in temperate and subtropical climates than in tropical zones. On average, a hectare of land in the tropics yields 2.3 metric tons of maize, whe ...
... productivity. Of the major food grains— wheat, maize and rice—wheat grows only in temperate climates, and maize and rice crops are generally more productive in temperate and subtropical climates than in tropical zones. On average, a hectare of land in the tropics yields 2.3 metric tons of maize, whe ...
Chapter 19 CENTRAL ASIA
... still widely used. • Literacy rates are high except in Afghanistan, and health care spending overall is low, except in Georgia. • Family life is a mix of traditional and modern influences, depending on rural or urban location. • Under Soviet control, women enjoyed more equal rights than in many coun ...
... still widely used. • Literacy rates are high except in Afghanistan, and health care spending overall is low, except in Georgia. • Family life is a mix of traditional and modern influences, depending on rural or urban location. • Under Soviet control, women enjoyed more equal rights than in many coun ...
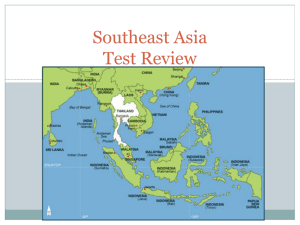
Human Geography of Southeast Asia
... • The 11 countries of Southeast Asia can be divided into two areas: the mainland in the west and the island archipelagoes in the east. • Due to its position along the Pacific Ocean within the Ring of Fire, most of Southeast Asia is mountainous, has active volcanoes, and is prone to earthquakes…The R ...
... • The 11 countries of Southeast Asia can be divided into two areas: the mainland in the west and the island archipelagoes in the east. • Due to its position along the Pacific Ocean within the Ring of Fire, most of Southeast Asia is mountainous, has active volcanoes, and is prone to earthquakes…The R ...
Geography Vocabulary
... 18. Topography - The physical features of a place or region. (Ex; mountains, river valleys, deserts, plains, savannas, plateaus, forests) 19. Plateaus – An elevated, level landform. 20. Plains – Flat treeless land region, that is usually suitable for farming. Generally at a low elevation 21. Savanna ...
... 18. Topography - The physical features of a place or region. (Ex; mountains, river valleys, deserts, plains, savannas, plateaus, forests) 19. Plateaus – An elevated, level landform. 20. Plains – Flat treeless land region, that is usually suitable for farming. Generally at a low elevation 21. Savanna ...
File
... Monsoon Rains Monsoon rains are heaviest in eastern South Asia. When the rains sweep over the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta, the Himalaya block them from moving north. As a result, the rains move west to the Ganges Plain, bringing ...
... Monsoon Rains Monsoon rains are heaviest in eastern South Asia. When the rains sweep over the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta, the Himalaya block them from moving north. As a result, the rains move west to the Ganges Plain, bringing ...
chapter 7 - Classroom Websites
... component of the earth’s climate. Wind transports nutrients from one place to another and can also transport pollutants. Because of wind, everything we do affects some other part of the biosphere. A. Weather is a local area’s short-term physical conditions such as temperature and precipitation. Aver ...
... component of the earth’s climate. Wind transports nutrients from one place to another and can also transport pollutants. Because of wind, everything we do affects some other part of the biosphere. A. Weather is a local area’s short-term physical conditions such as temperature and precipitation. Aver ...
Chapter 5: Climate and Terrestrial Biodiversity
... A. Deserts have little precipitation and little vegetation and are found in tropical, temperate, and polar regions. Deserts cover about 30% of the earth’s land surface, mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The largest ones are found in the interior of continents. Others form because of the ra ...
... A. Deserts have little precipitation and little vegetation and are found in tropical, temperate, and polar regions. Deserts cover about 30% of the earth’s land surface, mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The largest ones are found in the interior of continents. Others form because of the ra ...
The Geography of Poverty and Wealth
... times greater. In contrast, the "tropical-far" category is the poorest, with a per capita GNP only about one third of the world average. Interpreting the Patterns In our research we have examined three major ways in which geography affects economic development. First, as Adam Smith noted, economies ...
... times greater. In contrast, the "tropical-far" category is the poorest, with a per capita GNP only about one third of the world average. Interpreting the Patterns In our research we have examined three major ways in which geography affects economic development. First, as Adam Smith noted, economies ...
The Geography of Poverty and Wealth
... In particular, we have tried to formulate new strategies that would help nations in tropical zones raise their agricultural productivity and reduce the prevalence of diseases such as malaria. The Geographical Divide The best single indicator of prosperity is gross national product (GNP) per capita ...
... In particular, we have tried to formulate new strategies that would help nations in tropical zones raise their agricultural productivity and reduce the prevalence of diseases such as malaria. The Geographical Divide The best single indicator of prosperity is gross national product (GNP) per capita ...
South, Southeast, and East Asia
... – China and Japan have been rivals from time to time – East Asia has experienced colonization, and has seen both internal and international conflict – Japan is extremely wealthy, but poverty may be found in parts of the region – East Asia is one of the core areas of the world economy and an emerging ...
... – China and Japan have been rivals from time to time – East Asia has experienced colonization, and has seen both internal and international conflict – Japan is extremely wealthy, but poverty may be found in parts of the region – East Asia is one of the core areas of the world economy and an emerging ...
Chapter 7 Climate and Biodiversity
... average precipitation are the two major factors that determine climate of a region, together with the related factors of latitude and elevation. 1. Climate refers to long term general patters of atmospheric conditions. B. Global air circulation is affected by the uneven heating of the earth’s surfac ...
... average precipitation are the two major factors that determine climate of a region, together with the related factors of latitude and elevation. 1. Climate refers to long term general patters of atmospheric conditions. B. Global air circulation is affected by the uneven heating of the earth’s surfac ...
apes study guide
... The location of biomes is determined by climate. There are three major types of climate: tropical, polar and temperate. These determine the three major biomes: forests, grasslands and deserts. When climate changes, there is a concomitant shift in biome location. 7-1 What factors influence climate? A ...
... The location of biomes is determined by climate. There are three major types of climate: tropical, polar and temperate. These determine the three major biomes: forests, grasslands and deserts. When climate changes, there is a concomitant shift in biome location. 7-1 What factors influence climate? A ...
Climate - MRMWILLIS
... Imagine you are a zoologist hired to design a camel and a deer exhibit for your community's new zoo. Describe the differences between a deer and a camel. Where and in what kind of climate are you most likely to find these animals? What would you have to provide for each of these animals so they woul ...
... Imagine you are a zoologist hired to design a camel and a deer exhibit for your community's new zoo. Describe the differences between a deer and a camel. Where and in what kind of climate are you most likely to find these animals? What would you have to provide for each of these animals so they woul ...
Tropical North Queensland
... mountains and crystal clear streams and rivers combine to make Tropical North Queensland the destination of choice for millions of visitors every year. The capital of the region is Cairns, one of Australia’s fastest-growing regional centres. Living Here Cairns has all the facilities of a major city, ...
... mountains and crystal clear streams and rivers combine to make Tropical North Queensland the destination of choice for millions of visitors every year. The capital of the region is Cairns, one of Australia’s fastest-growing regional centres. Living Here Cairns has all the facilities of a major city, ...
Tierra del Fuego
... The Andes Mountains The diverse physical and human geographies of Latin America—from the peaks of the Andean range to the low, moist floors of the rainforests— create physical barriers to overcome. Before the completion of the Panama Canal in 1914, economies located in the Andes Mountain region were ...
... The Andes Mountains The diverse physical and human geographies of Latin America—from the peaks of the Andean range to the low, moist floors of the rainforests— create physical barriers to overcome. Before the completion of the Panama Canal in 1914, economies located in the Andes Mountain region were ...
South, Southeast, and East Asia
... A. Zones of latitude - Part of Asia is in the low latitudes and part of it is in the middle latitudes. B. Elevation - Mountainous regions in Asia have colder climates. C. Topography - Mountains block rainfall causing deserts on one side. ...
... A. Zones of latitude - Part of Asia is in the low latitudes and part of it is in the middle latitudes. B. Elevation - Mountainous regions in Asia have colder climates. C. Topography - Mountains block rainfall causing deserts on one side. ...
Temperate forest
... Seasonal rainfall Tropical rain forests get 200-400 cm of rainfall per year. Complex ecosystem, has more plant and animal species than all the other biomes put together. Competition among plants for light. Upper canopy of solitary tall trees, can be 50-60m tall. Lower story canopy is continuous. Man ...
... Seasonal rainfall Tropical rain forests get 200-400 cm of rainfall per year. Complex ecosystem, has more plant and animal species than all the other biomes put together. Competition among plants for light. Upper canopy of solitary tall trees, can be 50-60m tall. Lower story canopy is continuous. Man ...
Geography_Vocabulary_
... Mutual assistance or reliance between two or more counties for goods or services they cannot provide for themselves. (US depends on Middle Eastern oil) ...
... Mutual assistance or reliance between two or more counties for goods or services they cannot provide for themselves. (US depends on Middle Eastern oil) ...
South, Southeast, and East Asia
... precipitation. South Asia gets rain from the monsoons but the Himalaya Mountains block the rain from entering Western China. Most of Western China and Mongolia are in a rain shadow. ...
... precipitation. South Asia gets rain from the monsoons but the Himalaya Mountains block the rain from entering Western China. Most of Western China and Mongolia are in a rain shadow. ...
asia_phys geog PPT - Mr. Byvik Civics and Economics
... precipitation. South Asia gets rain from the monsoons but the Himalaya Mountains block the rain from entering Western China. Most of Western China and Mongolia are in a rain shadow. ...
... precipitation. South Asia gets rain from the monsoons but the Himalaya Mountains block the rain from entering Western China. Most of Western China and Mongolia are in a rain shadow. ...