Chapters Study Guide
... 2. Limiting reactant problems (aka calculate theoretical yield) “In the reaction CaC2 + 2H2O C2H2 + Ca(OH)2, 64 g H2O is reacted with 64 g CaC2. CaC2. Which is the excess reactant, which is limiting? What is the theoretical yield of C 2H2 ? ...
... 2. Limiting reactant problems (aka calculate theoretical yield) “In the reaction CaC2 + 2H2O C2H2 + Ca(OH)2, 64 g H2O is reacted with 64 g CaC2. CaC2. Which is the excess reactant, which is limiting? What is the theoretical yield of C 2H2 ? ...
Lesson 2: Electrolytes
... Bases release hydroxide ions in solution (water). The water already contains a mixture of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. H2O →2H+1 + OHTherefore in a basic solution there will be both hydrogen and hydroxide ions. However there will be more hydroxide ions. The pH of bases is greater than 7 ...
... Bases release hydroxide ions in solution (water). The water already contains a mixture of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. H2O →2H+1 + OHTherefore in a basic solution there will be both hydrogen and hydroxide ions. However there will be more hydroxide ions. The pH of bases is greater than 7 ...
Solutions Powerpoint
... Solubility is a physical property that gives the grams of solute that will dissolve in a solvent (usually water) at a given temperature and pressure. ...
... Solubility is a physical property that gives the grams of solute that will dissolve in a solvent (usually water) at a given temperature and pressure. ...
An assessment of excess carbon dioxide partial pressures in natural
... Studies of dissolved carbon dioxide in natural waters provide an important indicator of their biological productivity and sewage contamination. This is because dissolved carbon dioxide provides an indication of the balance between photosynthesis and respiration by biota, both within the water column ...
... Studies of dissolved carbon dioxide in natural waters provide an important indicator of their biological productivity and sewage contamination. This is because dissolved carbon dioxide provides an indication of the balance between photosynthesis and respiration by biota, both within the water column ...
Mineral Formation
... 1. Kevin Walsh, modified by CK-12 Foundation. Granite is formed from magma, and contains quartz, feldspar, and biotite. CC BY 2.0 2. Rebecca Calhoun. Crystals form when water evaporates. CC BY-NC 3.0 3. Flickr:Zengame. Tufa towers in Mono Lake. CC BY 2.0 4. Image copyright Phon Promwisate, 2014. Pic ...
... 1. Kevin Walsh, modified by CK-12 Foundation. Granite is formed from magma, and contains quartz, feldspar, and biotite. CC BY 2.0 2. Rebecca Calhoun. Crystals form when water evaporates. CC BY-NC 3.0 3. Flickr:Zengame. Tufa towers in Mono Lake. CC BY 2.0 4. Image copyright Phon Promwisate, 2014. Pic ...
WS Molarity PPMs
... grams of solution 1. What is the concentration (in ppm), of 5.0 x 10-5g chlorine molecules in 100g of pool water? ...
... grams of solution 1. What is the concentration (in ppm), of 5.0 x 10-5g chlorine molecules in 100g of pool water? ...
Acidity Test Kit Alkalinity Test Kit 9
... Alkalinity is the quantitative capacity of a water sample to neutralize an acid to a set pH. This measurement is very important in determining the corrosive characteristics of water due primarily to hydroxide, carbonate, and bicarbonate ions. Other sources of alkalinity can be from anions that can b ...
... Alkalinity is the quantitative capacity of a water sample to neutralize an acid to a set pH. This measurement is very important in determining the corrosive characteristics of water due primarily to hydroxide, carbonate, and bicarbonate ions. Other sources of alkalinity can be from anions that can b ...
ELEMENTS
... and mercuric oxide through an electric current. That electric current passed through an electrolyte. The name “Calcium” comes from the Latin base word, “calcis,” which means “lime.” ...
... and mercuric oxide through an electric current. That electric current passed through an electrolyte. The name “Calcium” comes from the Latin base word, “calcis,” which means “lime.” ...
WS-11-1
... 17. Although A1(OH)3 is insoluble in water, NaOH is very soluble. Explain in terms of lattice energies. ...
... 17. Although A1(OH)3 is insoluble in water, NaOH is very soluble. Explain in terms of lattice energies. ...
Minerals - Ms. Banjavcic`s Science
... (O) and usually one or more other elements. Since silicon and oxygen are the two most abundant elements in Earth’s crust, these two elements alone combine to form the basic building blocks of most minerals. ...
... (O) and usually one or more other elements. Since silicon and oxygen are the two most abundant elements in Earth’s crust, these two elements alone combine to form the basic building blocks of most minerals. ...
Nature of Acids and Bases
... Answer the questions below by circling the number of the correct response 1. In the reversible reaction, 2H2O º H3O+ + OH–, showing the ionization of water, which of the following is true? (1) The forward reaction forming ions from water is favored. (2) The concentration of ions in pure water is hig ...
... Answer the questions below by circling the number of the correct response 1. In the reversible reaction, 2H2O º H3O+ + OH–, showing the ionization of water, which of the following is true? (1) The forward reaction forming ions from water is favored. (2) The concentration of ions in pure water is hig ...
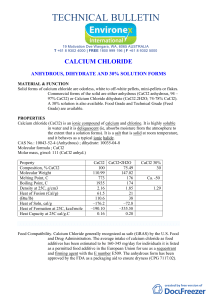
technical bulletin
... avoid inhalation. Dry calcium chloride reacts exothermically when exposed to water. Burns can result in the mouth and esophagus if humans or other animals ingest dry calcium chloride pellets. Ecology: It promotes algae and higher plant growth. Chloride ions are also required for normal cellular oper ...
... avoid inhalation. Dry calcium chloride reacts exothermically when exposed to water. Burns can result in the mouth and esophagus if humans or other animals ingest dry calcium chloride pellets. Ecology: It promotes algae and higher plant growth. Chloride ions are also required for normal cellular oper ...
Unit 1 Matter and Change HOMEWORK
... 16. In the following reaction: 2NaN3 decomposes to form 2Na + 3N2. If 500 grams of NaN3 decomposes to form 323.20 grams of N2. How much Na is produced? ____176.8 or 177 _____ g ...
... 16. In the following reaction: 2NaN3 decomposes to form 2Na + 3N2. If 500 grams of NaN3 decomposes to form 323.20 grams of N2. How much Na is produced? ____176.8 or 177 _____ g ...
Fundamental properties of water and Methods of Purification
... size less than 0.1 micron. Colloids containing iron (Fe), aluminium (Al), silica (SiO2) and organics are commonly found in water. ...
... size less than 0.1 micron. Colloids containing iron (Fe), aluminium (Al), silica (SiO2) and organics are commonly found in water. ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... • Compounds that do not dissolve in water or only a small fraction dissolves in water thus producing a small amount of ions. • These cmps include insoluble salts, weak acids and weak bases. • When a solid insoluble salt is added to water, most of it sinks to the bottom of the beaker as a solid. ...
... • Compounds that do not dissolve in water or only a small fraction dissolves in water thus producing a small amount of ions. • These cmps include insoluble salts, weak acids and weak bases. • When a solid insoluble salt is added to water, most of it sinks to the bottom of the beaker as a solid. ...
PDF-Download
... Sediment rocks Limestone (Dolomite) Probably middle earth age The yellow colouring iron oxide limonite is included in the dolomite. 3-4 (according to Mohs's hardness scale 1-10) Lijar / Province Almeria / Spain ...
... Sediment rocks Limestone (Dolomite) Probably middle earth age The yellow colouring iron oxide limonite is included in the dolomite. 3-4 (according to Mohs's hardness scale 1-10) Lijar / Province Almeria / Spain ...
C3.1 The Periodic Table
... State that soapless detergents do not form scum Describe how compounds (such as those of calcium or magnesium) become dissolved in water to make it hard Describe how temporary hard water can be softened, and how this can be used to distinguish between temporary and permanent hard water Explain how h ...
... State that soapless detergents do not form scum Describe how compounds (such as those of calcium or magnesium) become dissolved in water to make it hard Describe how temporary hard water can be softened, and how this can be used to distinguish between temporary and permanent hard water Explain how h ...
scale inhibitors
... Scale is the precipitate that forms on surfaces in contact with water as a result of the precipitation of normally soluble solids that become insoluble as temperature increases. The chemical treatment of water associated with oil and gas includes the application of scale inhibitors, such as phosphon ...
... Scale is the precipitate that forms on surfaces in contact with water as a result of the precipitation of normally soluble solids that become insoluble as temperature increases. The chemical treatment of water associated with oil and gas includes the application of scale inhibitors, such as phosphon ...
Minerals
... • Is formed at or near Earth’s surface, especially when calcium, oxygen, and carbon combine in sea water. • Some ocean animals have calcite shells or other body parts. • Found in caves. ...
... • Is formed at or near Earth’s surface, especially when calcium, oxygen, and carbon combine in sea water. • Some ocean animals have calcite shells or other body parts. • Found in caves. ...
hgms_conoco basic mi..
... The most common use is for making sheet rock wallboard. 3. CALCITE, hardness of 3 Calcium Carbonate: A very common mineral that typically is precipitated by organisms like clams, which use it to make their skeletons. When large amounts of these biological products accumulate and get cemented togethe ...
... The most common use is for making sheet rock wallboard. 3. CALCITE, hardness of 3 Calcium Carbonate: A very common mineral that typically is precipitated by organisms like clams, which use it to make their skeletons. When large amounts of these biological products accumulate and get cemented togethe ...
Intro to Soln Stoich
... If MgCl2 is 0.2 M, what is concentration of Mg2+? Of Cl-? Concentration of Mg2+is 0.2 M and Cl- is 0.4 M ◦ 1:1 ratio of MgCl2 : Mg2+ ◦ 1:2 ratio of MgCl2 : Cl- ...
... If MgCl2 is 0.2 M, what is concentration of Mg2+? Of Cl-? Concentration of Mg2+is 0.2 M and Cl- is 0.4 M ◦ 1:1 ratio of MgCl2 : Mg2+ ◦ 1:2 ratio of MgCl2 : Cl- ...
Why worry about pH
... that measures neutral (7.0) on the pH scale has an equal number of hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions. Water that is low in pH has more hydrogen ions than hydroxyl ions. Though the major cause of acidic well water is the high amount of dissolved carbon dioxide gas (carbonic acid when combined with wate ...
... that measures neutral (7.0) on the pH scale has an equal number of hydrogen ions and hydroxyl ions. Water that is low in pH has more hydrogen ions than hydroxyl ions. Though the major cause of acidic well water is the high amount of dissolved carbon dioxide gas (carbonic acid when combined with wate ...
a mean to learn many words used in everyday English, not
... What you need: materials list Some calcium carbonate from the lab ...
... What you need: materials list Some calcium carbonate from the lab ...
Hard water

Hard water is water that has high mineral content (in contrast with ""soft water""). Hard water is formed when water percolates through deposits of limestone and chalk which are largely made up of calcium and magnesium carbonates. Hard drinking water may have moderate health benefits, but can pose serious problems in industrial settings, where water hardness is monitored to avoid costly breakdowns in boilers, cooling towers, and other equipment that handles water. In domestic settings, hard water is often indicated by a lack of suds formation when soap is agitated in water, and by the formation of limescale in kettles and water heaters. Wherever water hardness is a concern, water softening is commonly used to reduce hard water's adverse effects.