the Main-Group Metals - McQuarrie General Chemistry
... construction of aircraft and missiles and in the manufacture of engine blocks and other parts for high-performance vehicles. Due to its light weight and good electrical properties, magnesium is also used in various electronic devices, such as laptop computers. Like the alkali metals, the alkaline-ea ...
... construction of aircraft and missiles and in the manufacture of engine blocks and other parts for high-performance vehicles. Due to its light weight and good electrical properties, magnesium is also used in various electronic devices, such as laptop computers. Like the alkali metals, the alkaline-ea ...
Atoms, Electrons and Periodicity test - A
... Explain why the first ionisation energy of B is less than that of Be. ...
... Explain why the first ionisation energy of B is less than that of Be. ...
Frac Makeup and PPC Treatment
... Obtaining the needed water to makeup frac water, with subsequent disposal of the flowback water, presents a significant problem for gas production firms. In many areas, the amount of suitable water needed for formulation of frac water is just not available. The best solution to this combined wastewa ...
... Obtaining the needed water to makeup frac water, with subsequent disposal of the flowback water, presents a significant problem for gas production firms. In many areas, the amount of suitable water needed for formulation of frac water is just not available. The best solution to this combined wastewa ...
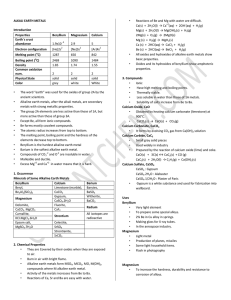
ALKALI EARTH METALS Introduction Properties Beryllium
... The word “earth” was used for the oxides of group 2A by the ancient scientists. Alkaline earth metals, after the alkali metals, are secondary metals with strong metallic properties. The group 2A elements are less active than those of 1A, but more active than those of group 3A. Except Be, all form io ...
... The word “earth” was used for the oxides of group 2A by the ancient scientists. Alkaline earth metals, after the alkali metals, are secondary metals with strong metallic properties. The group 2A elements are less active than those of 1A, but more active than those of group 3A. Except Be, all form io ...
Alkaline earth metals
... All In the second row Don’t occur as free elements Most commonly are found occurring as the carbonates, phosphates silicates, and sulfates Atoms loose 2 electrons Most are insoluble or slightly soluble Very Reactive ...
... All In the second row Don’t occur as free elements Most commonly are found occurring as the carbonates, phosphates silicates, and sulfates Atoms loose 2 electrons Most are insoluble or slightly soluble Very Reactive ...
Strontium

Strontium (/ˈstrɒntiəm/ STRON-tee-əm) is a chemical element with symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. The metal turns yellow when it is exposed to air. Strontium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of its two neighbors calcium and barium. It occurs naturally in the minerals celestine, putnisite and strontianite. While natural strontium is stable, the synthetic 90Sr isotope is present in radioactive fallout and has a half-life of 28.90 years.Both strontium and strontianite are named after Strontian, a village in Scotland near which the mineral was discovered in 1790 by Adair Crawford and William Cruickshank. The production of sugar from sugar beet was in the 19th century its largest application (see strontian process). At the peak of production of television cathode ray tubes, up to 75 percent of U.S. strontium consumption was used to make the faceplate glass. With the displacement of cathode ray tubes by other display methods in television sets consumption of strontium has dramatically declined.