Optimal energy transition and taxation of non
... tighten it over time so that we let the economy develop while giving the firms increasingly higher incentive to substitute the renewables? Or should we tax very high and loosen it over time so that we initially stimulate the use of renewables? In this paper, we approach these classical questions fro ...
... tighten it over time so that we let the economy develop while giving the firms increasingly higher incentive to substitute the renewables? Or should we tax very high and loosen it over time so that we initially stimulate the use of renewables? In this paper, we approach these classical questions fro ...
2014/21
... Energy transition refers to the process in which the economy substitutes renewable resources for non-renewables over time and eventually approaches a green, zero-carbon state. What matters for energy transition is not only the current level of policy measures but also their planned time paths. When ...
... Energy transition refers to the process in which the economy substitutes renewable resources for non-renewables over time and eventually approaches a green, zero-carbon state. What matters for energy transition is not only the current level of policy measures but also their planned time paths. When ...
Analysis of selected concepts on Resource Management
... For many years, environmental policy has focused on resolving the most urgent problems as regards environmental pollution, to a large extent by focusing on end-of-pipe technologies. More and more, the public and policy makers are also directing attention to the need for reducing resource use and its ...
... For many years, environmental policy has focused on resolving the most urgent problems as regards environmental pollution, to a large extent by focusing on end-of-pipe technologies. More and more, the public and policy makers are also directing attention to the need for reducing resource use and its ...
Lobbying, Trade and Resource Conversion
... Despite the prevalence of this link between rent-seeking, corruption and government land use policy, the existing literature in economics has failed to examine the consequences of special interest lobbying pressures on agricultural land conversion. There is a varied and growing literature that exami ...
... Despite the prevalence of this link between rent-seeking, corruption and government land use policy, the existing literature in economics has failed to examine the consequences of special interest lobbying pressures on agricultural land conversion. There is a varied and growing literature that exami ...
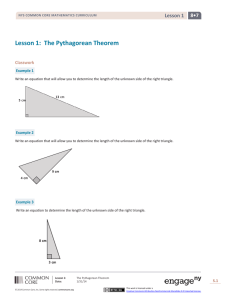
Lesson 1: The Pythagorean Theorem 8•7 Lesson 1
... The number is represented on the number line shown below. Each new line is a magnification of the interval shown above it. For example, the first line is the unit from 0 to 1 divided into 10 equal parts, or tenths. The second line is the interval from 0.8 to 0.9 divided into ten equal parts, or hund ...
... The number is represented on the number line shown below. Each new line is a magnification of the interval shown above it. For example, the first line is the unit from 0 to 1 divided into 10 equal parts, or tenths. The second line is the interval from 0.8 to 0.9 divided into ten equal parts, or hund ...
Chapter 15 "Non-renewable resources
... depleted in a market economy. As you would expect from the analysis in Chapters 5 and 11, the extraction path in competitive market economies will, under certain circumstances, be socially optimal. It is usually argued that one of these circumstances is that resource markets are competitive. We inve ...
... depleted in a market economy. As you would expect from the analysis in Chapters 5 and 11, the extraction path in competitive market economies will, under certain circumstances, be socially optimal. It is usually argued that one of these circumstances is that resource markets are competitive. We inve ...
Environmental and Resource Economics - Research portal
... assumed to care predominantly about human welfare. In recent times, however, these two perspectives are increasingly converging. For example, for many environmental management problems, economists frequently consider ecological functions, or “services”, to be important arguments in welfare functions ...
... assumed to care predominantly about human welfare. In recent times, however, these two perspectives are increasingly converging. For example, for many environmental management problems, economists frequently consider ecological functions, or “services”, to be important arguments in welfare functions ...
Economics of Natural Resources
... • Renewable Resources: are differentiated from depletable resources primarily by the fact that natural replenishment augments the flow of renewable resources at a non-negligible rate. Examples include: solar energy, water, cereal grains, forest, fish, animals etc. ...
... • Renewable Resources: are differentiated from depletable resources primarily by the fact that natural replenishment augments the flow of renewable resources at a non-negligible rate. Examples include: solar energy, water, cereal grains, forest, fish, animals etc. ...
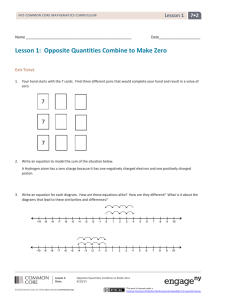
Lesson 1: Opposite Quantities Combine to Make Zero 7•2 Lesson 1
... A hand of six integer cards has one matching set of two or more cards. If the matching set of cards is removed from the hand, the score of the hand will increase by six. What are the possible values of these matching cards? Explain. Write an equation using multiplication showing how the matching car ...
... A hand of six integer cards has one matching set of two or more cards. If the matching set of cards is removed from the hand, the score of the hand will increase by six. What are the possible values of these matching cards? Explain. Write an equation using multiplication showing how the matching car ...
externalities (new window)
... The opportunity cost is the deadweight loss that arises from overproduction with a negative externality or underproduction with a positive externality. But, there are also costs to internalizing an externality. Sometimes the costs of internalizing the externality are greater than the cost of the ext ...
... The opportunity cost is the deadweight loss that arises from overproduction with a negative externality or underproduction with a positive externality. But, there are also costs to internalizing an externality. Sometimes the costs of internalizing the externality are greater than the cost of the ext ...
Chapter 15 PowerPoint document
... This is a considerably simpler, yet more specialised, case than that investigated in Chapter 14 where utility derived from consumption goods, obtained through a production function with a natural resource, physical capital (and, implicitly, labour) as inputs. Although doing this pushes the productio ...
... This is a considerably simpler, yet more specialised, case than that investigated in Chapter 14 where utility derived from consumption goods, obtained through a production function with a natural resource, physical capital (and, implicitly, labour) as inputs. Although doing this pushes the productio ...
externality
... A firm that starts a project (e.g., to produce industrial robot) could develop a new technology / generate an innovation in production techniques so as to improve the initial project. Such an improvement could benefit the firm but also the society as a whole, because such knowledge will accumulate a ...
... A firm that starts a project (e.g., to produce industrial robot) could develop a new technology / generate an innovation in production techniques so as to improve the initial project. Such an improvement could benefit the firm but also the society as a whole, because such knowledge will accumulate a ...
externalities1 (new window)
... Many people mistakenly believe that resources are more likely to be conserved for the future and less likely to be depleted if they are owned in common than if they are private property. In fact, quite the opposite is true. If one person conserves on current use of a common property resource, that p ...
... Many people mistakenly believe that resources are more likely to be conserved for the future and less likely to be depleted if they are owned in common than if they are private property. In fact, quite the opposite is true. If one person conserves on current use of a common property resource, that p ...
10. Externalities
... They are used to fight environmental pollution. They allow the voluntary transfer of the rights to pollute from one firm to the other. In fact: a market for pollution rights is created. A firm that faces low cost to reduce her own pollution will prefer to sell her rights to pollute to a firm that fa ...
... They are used to fight environmental pollution. They allow the voluntary transfer of the rights to pollute from one firm to the other. In fact: a market for pollution rights is created. A firm that faces low cost to reduce her own pollution will prefer to sell her rights to pollute to a firm that fa ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TRADE, TRAGEDY, AND THE COMMONS Brian R. Copeland
... We develop a theory where an existing government regulates the use of a renewable resource by a set of agents who have a right to harvest. The resource could be a fishery, forest stock, aquifer, etc., and we assume it is local and therefore contained within one country. The government sets rules li ...
... We develop a theory where an existing government regulates the use of a renewable resource by a set of agents who have a right to harvest. The resource could be a fishery, forest stock, aquifer, etc., and we assume it is local and therefore contained within one country. The government sets rules li ...
Trade, Tragedy, and the Commons
... We develop a theory where an existing government regulates the use of a renewable resource by a set of agents who have a right to harvest. The resource could be a fishery, forest stock, aquifer, etc., and we assume it is local and therefore contained within one country. The government sets rules li ...
... We develop a theory where an existing government regulates the use of a renewable resource by a set of agents who have a right to harvest. The resource could be a fishery, forest stock, aquifer, etc., and we assume it is local and therefore contained within one country. The government sets rules li ...
PPT Market Failure - QSI International School of Shenzhen
... production (MSC). As a result, the free market will provide a quantity of the good which is less than the socially optimal quantity. ...
... production (MSC). As a result, the free market will provide a quantity of the good which is less than the socially optimal quantity. ...
An Artificially Scarce Good
... • If the measure doesn’t pass, your vote would not have changed the outcome. Either way, by not voting—by freeriding on those who do vote—you save $10. • The result is that when a large group of people share a common political interest, they are likely to exert too little effort promoting their caus ...
... • If the measure doesn’t pass, your vote would not have changed the outcome. Either way, by not voting—by freeriding on those who do vote—you save $10. • The result is that when a large group of people share a common political interest, they are likely to exert too little effort promoting their caus ...
Krugman`s Chapter 20 PPT - Public Goods and Common Resources
... social benefit equals the marginal cost of providing the good. Like a positive externality, marginal social benefit is greater than any one individual’s marginal benefit, so no individual is willing to provide the efficient quantity. 5. One rationale for the presence of government is that it allows ...
... social benefit equals the marginal cost of providing the good. Like a positive externality, marginal social benefit is greater than any one individual’s marginal benefit, so no individual is willing to provide the efficient quantity. 5. One rationale for the presence of government is that it allows ...
public good - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Copyright © 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ...
... Copyright © 2008 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ...
Econ 201 Week 5_6 Economics of the Public Sector
... (ocean, old days pasture land) Natural Monopoly – excludable but non-rival (protecting another house – MC is small) ...
... (ocean, old days pasture land) Natural Monopoly – excludable but non-rival (protecting another house – MC is small) ...
Guiding Principles for Integrated Ecosystem
... profits and jobs in logging and log-transporting. Therefore, existing tenure arrangements fail to meet Firey’s basic requirements for sustainability. The institutional fiction embedded in existing tenure arrangements also creates a false sense of opportunism for aspiring entrepreneurs in First Natio ...
... profits and jobs in logging and log-transporting. Therefore, existing tenure arrangements fail to meet Firey’s basic requirements for sustainability. The institutional fiction embedded in existing tenure arrangements also creates a false sense of opportunism for aspiring entrepreneurs in First Natio ...
Microeconomics Topic 9: “Explain externalities and
... the commons had no incentive to reduce their use of the commons in order to preserve some grass for tomorrow and next week, because someone else could bring in livestock to graze in the meantime. Anything preserved for the future by one person would not necessarily be available to that person in the ...
... the commons had no incentive to reduce their use of the commons in order to preserve some grass for tomorrow and next week, because someone else could bring in livestock to graze in the meantime. Anything preserved for the future by one person would not necessarily be available to that person in the ...
Government and the Market
... (ocean, old days pasture land) Natural Monopoly – excludable but non-rival (protecting another house – MC is small) ...
... (ocean, old days pasture land) Natural Monopoly – excludable but non-rival (protecting another house – MC is small) ...
Tragedy of the commons

The tragedy of the commons is a term, probably coined originally by William Forster Lloyd and later used by Garrett Hardin, to denote a situation where individuals acting independently and rationally according to each's self-interest behave contrary to the best interests of the whole group by depleting some common resource. The concept was based upon an essay written in 1833 by Lloyd, the Victorian economist, on the effects of unregulated grazing on common land and made widely-known by an article written by Hardin in 1968.""Commons"" in this sense has come to mean such resources as atmosphere, oceans, rivers, fish stocks, an office refrigerator, energy or any other shared resource which is not formally regulated, not common land in its agricultural sense.The tragedy of the commons concept is often cited in connection with sustainable development, meshing economic growth and environmental protection, as well as in the debate over global warming. It has also been used in analyzing behavior in the fields of economics, evolutionary psychology, anthropology, game theory, politics, taxation, and sociology. However the concept, as originally developed, has also received criticism for not taking into account the many other factors operating to enforce or agree on regulation in this scenario.