Embryological origin for autism
... the cranial nerve motor nuclei are forming cannot be tested from the existing anatomical literature. We prepared and examined serial sections from the brainstem of a n autistic patient for evidence of abnormalities in cranial nerve nuclei. A theoretical embryological argument against a brainstem inj ...
... the cranial nerve motor nuclei are forming cannot be tested from the existing anatomical literature. We prepared and examined serial sections from the brainstem of a n autistic patient for evidence of abnormalities in cranial nerve nuclei. A theoretical embryological argument against a brainstem inj ...
Thyroid gland II
... on the thyrotrop cells, more than on the anterior hypothalamus (site of release of TRH). • The feedback mechanism controlling thyroid gland activity act mainly on the ant pituitary. ...
... on the thyrotrop cells, more than on the anterior hypothalamus (site of release of TRH). • The feedback mechanism controlling thyroid gland activity act mainly on the ant pituitary. ...
Module 8
... are released to descend down the pituitary stalk to the pituitary gland where they stimulate the release of pituitary hormones. While the pituitary gland is known as the ‘master’ endocrine gland, both of the lobes are under the control of the hypothalamus; the anterior pituitary receives its signals ...
... are released to descend down the pituitary stalk to the pituitary gland where they stimulate the release of pituitary hormones. While the pituitary gland is known as the ‘master’ endocrine gland, both of the lobes are under the control of the hypothalamus; the anterior pituitary receives its signals ...
Lecture 4_Circulation of blood and its regulation. Features of
... Effects of thyroid hormones Thyroid hormones increase transmission process in ribosome and nucleus of cells. Intracellular enzymes are stimulated due to increasing protein synthesis. Also increases glucose absorption and uptake of glucose by cells, increases glycolisis and gluconeogenesis. ...
... Effects of thyroid hormones Thyroid hormones increase transmission process in ribosome and nucleus of cells. Intracellular enzymes are stimulated due to increasing protein synthesis. Also increases glucose absorption and uptake of glucose by cells, increases glycolisis and gluconeogenesis. ...
Active potential of contractive heart cells Phases of active potential 0
... Effects of thyroid hormones Thyroid hormones increase transmission process in ribosome and nucleus of cells. Intracellular enzymes are stimulated due to increasing protein synthesis. Also increases glucose absorption and uptake of glucose by cells, increases glycolisis and gluconeogenesis. In ...
... Effects of thyroid hormones Thyroid hormones increase transmission process in ribosome and nucleus of cells. Intracellular enzymes are stimulated due to increasing protein synthesis. Also increases glucose absorption and uptake of glucose by cells, increases glycolisis and gluconeogenesis. In ...
+ 63 days (62-64)
... 1. Amino acid derivatives; dopamine, catecholamines, thyroid hormone 2. Small neuropeptides; GnRH, TRH, somatostatin, vasopression 3. Large proteins; LH, FSH, insulin, parathyroid hormone 4. Steroid hormones; oestrogen, progesterone, testosterone, cortisol 5. Vitamin derivatives; retinoids ...
... 1. Amino acid derivatives; dopamine, catecholamines, thyroid hormone 2. Small neuropeptides; GnRH, TRH, somatostatin, vasopression 3. Large proteins; LH, FSH, insulin, parathyroid hormone 4. Steroid hormones; oestrogen, progesterone, testosterone, cortisol 5. Vitamin derivatives; retinoids ...
File - Kevin Morrison`s e
... Increase risk of health factors that lead to heart disease High blood pressure, obese, and diabetes ...
... Increase risk of health factors that lead to heart disease High blood pressure, obese, and diabetes ...
... memory, increased body fat, lipid abnormalities and insulin resistance. {JClin Endocrinol Met. 95(5): 1621-34.) Growth hormone deficiency is also appreciated to be a factor in increased mortality from cardiovascular disease. {Lancet. 1990 Aug;8710(4):285-8....[G]rowth hormone replacement can provide ...
Renal system
... which convey senses of pain and temperature 133. Upper motor neurons are descending (motor) pathways having their cell bodies in the brain 134. Lower motor neurons are descending (motor) pathways having their cell bodies in anterior horn of spinal cord 135. Direct upper motor neurons are anterior an ...
... which convey senses of pain and temperature 133. Upper motor neurons are descending (motor) pathways having their cell bodies in the brain 134. Lower motor neurons are descending (motor) pathways having their cell bodies in anterior horn of spinal cord 135. Direct upper motor neurons are anterior an ...
Somatic regions Limbic These functionally distinct
... 4) There are motor neurons located in the midbrain. What movements do those motor neurons control? (These direct outputs of the midbrain are not a subject of much discussion in the chapter.) 5) At the base of the midbrain (ventral side) one finds a fiber bundle that shows great differences in rela ...
... 4) There are motor neurons located in the midbrain. What movements do those motor neurons control? (These direct outputs of the midbrain are not a subject of much discussion in the chapter.) 5) At the base of the midbrain (ventral side) one finds a fiber bundle that shows great differences in rela ...
Healthy Hair - HormoneBalance.org
... Healthy Hair Hair loss in post-menopausal and peri-menopausal women is most likely related to declining hormone levels. Estrogen, testosterone and thyroid deficiency are not only associated with hair loss, but also hair changes. Hair may become finer, loosing body, wave and shine. It becomes dry and ...
... Healthy Hair Hair loss in post-menopausal and peri-menopausal women is most likely related to declining hormone levels. Estrogen, testosterone and thyroid deficiency are not only associated with hair loss, but also hair changes. Hair may become finer, loosing body, wave and shine. It becomes dry and ...
THYROID FUNCTION IN ME – IS THERE A MAJOR DIAGNOSTIC
... Therapeutic replacement of thyroid hormones in deficient individuals by T4 (thyroxine) and not by the more active metabolite (T3) is usually chosen to imitate the physiological situation. The aim is to restore normal levels of thyroxine and (by negative feedback to the pituitary gland) to reduce ass ...
... Therapeutic replacement of thyroid hormones in deficient individuals by T4 (thyroxine) and not by the more active metabolite (T3) is usually chosen to imitate the physiological situation. The aim is to restore normal levels of thyroxine and (by negative feedback to the pituitary gland) to reduce ass ...
Chapter 10 Quiz Show
... Which of the following is a result of pancreatic beta cell activation? a. increased breakdown of glycogen to glucose in liver and skeletal muscle b. increased amino acid absorption and protein synthesis c. increased breakdown of fats to fatty acids in adipose tissue d. decreased rate of glucose util ...
... Which of the following is a result of pancreatic beta cell activation? a. increased breakdown of glycogen to glucose in liver and skeletal muscle b. increased amino acid absorption and protein synthesis c. increased breakdown of fats to fatty acids in adipose tissue d. decreased rate of glucose util ...
The organisation of the stress response, and its relevance to
... [7]. Once the stress response is activated, behavioral and physiological changes lead the way for the organism to adjust homeostasis within the body, and increase its chances for survival [8]. It is in times of sustained or repeated activation that the stress response may alter [7]. Due to the intri ...
... [7]. Once the stress response is activated, behavioral and physiological changes lead the way for the organism to adjust homeostasis within the body, and increase its chances for survival [8]. It is in times of sustained or repeated activation that the stress response may alter [7]. Due to the intri ...
Effect of Adrenalectomy on Miniature Inhibitory Postsynaptic
... The setpoint of HPA activity is not only determined by the humoral feedback via corticosterone but also by neuronal signals integrated in the PVN. The PVN receives excitatory inputs from several brain areas, such as the amygdala (Feldman and Weidenfeld 1998), the dorsomedial hypothalamus (Morin et a ...
... The setpoint of HPA activity is not only determined by the humoral feedback via corticosterone but also by neuronal signals integrated in the PVN. The PVN receives excitatory inputs from several brain areas, such as the amygdala (Feldman and Weidenfeld 1998), the dorsomedial hypothalamus (Morin et a ...
changes of thyroid hormones in different physiological periods in
... from Figure 1, while in each physiological period there is decrease in T3 and T4 levels along with an increase in environmental temperature, there is increase in T3 and T4 levels as the environmental temperature decreases. The environmental temperature, being the most important external factor in re ...
... from Figure 1, while in each physiological period there is decrease in T3 and T4 levels along with an increase in environmental temperature, there is increase in T3 and T4 levels as the environmental temperature decreases. The environmental temperature, being the most important external factor in re ...
The Nervous System, cont
... behavior and of the outer reaches of what is possible for this organ. – Includes the study of the biological foundations of consciousness, perception, memory, emotion, and ...
... behavior and of the outer reaches of what is possible for this organ. – Includes the study of the biological foundations of consciousness, perception, memory, emotion, and ...
Natural Hormone Replacement Therapy
... Hormones Parts of our integrated neuro-endocrine-immune system Travel via blood to all cells Control cells’ proliferation, differentiation, protein synthesis, metabolic rate, etc. The most powerful molecules in biology Optimal levels and effects are essential for health and quality of life ...
... Hormones Parts of our integrated neuro-endocrine-immune system Travel via blood to all cells Control cells’ proliferation, differentiation, protein synthesis, metabolic rate, etc. The most powerful molecules in biology Optimal levels and effects are essential for health and quality of life ...
Derived copy of The Thyroid Gland
... of the thyroid gland is the more common cause of low blood levels of thyroid hormones. Called hypothyroidism, the condition is characterized by a low metabolic rate, weight gain, cold extremities, constipation, reduced libido, menstrual irregularities, and reduced mental activity. In contrast, hyper ...
... of the thyroid gland is the more common cause of low blood levels of thyroid hormones. Called hypothyroidism, the condition is characterized by a low metabolic rate, weight gain, cold extremities, constipation, reduced libido, menstrual irregularities, and reduced mental activity. In contrast, hyper ...
Blog post 1 - WordPress.com
... the hormones released during the acute response and the factors that can have a positive or negative effect. It is believed that the cortisol to testosterone ratio should be at an appropriate level during the acute phase (Tuner et, al., 2010). If cortisol is too high for a long period of time this m ...
... the hormones released during the acute response and the factors that can have a positive or negative effect. It is believed that the cortisol to testosterone ratio should be at an appropriate level during the acute phase (Tuner et, al., 2010). If cortisol is too high for a long period of time this m ...
The Endocrine System
... glands are known as the ductless glands. Despite the fact that hormones in the blood reach all parts of the body, only certain tissues respond. The tissue that is influenced by a specific hormone is called the target tissue. The cells that make up this tissue have specific receptors on their membranes ...
... glands are known as the ductless glands. Despite the fact that hormones in the blood reach all parts of the body, only certain tissues respond. The tissue that is influenced by a specific hormone is called the target tissue. The cells that make up this tissue have specific receptors on their membranes ...
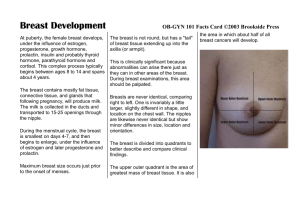
Breast Development
... Breast Development At puberty, the female breast develops, under the influence of estrogen, progesterone, growth hormone, prolactin, insulin and probably thyroid hormone, parathyroid hormone and cortisol. This complex process typically begins between ages 8 to 14 and spans about 4 years. The breast ...
... Breast Development At puberty, the female breast develops, under the influence of estrogen, progesterone, growth hormone, prolactin, insulin and probably thyroid hormone, parathyroid hormone and cortisol. This complex process typically begins between ages 8 to 14 and spans about 4 years. The breast ...
Anti-Thyroid2009-06-17 13:26379 KB
... ● Critical for nervous, skeletal and reproductive tissues ● Its effects depend on pituitary synthesis + potentiation of the secretion and action of growth hormone ● Inadequate secretion in early life: irreversible mental tetardation (cretinisim) and dwarfism or congenital cretinism ● Effect on growt ...
... ● Critical for nervous, skeletal and reproductive tissues ● Its effects depend on pituitary synthesis + potentiation of the secretion and action of growth hormone ● Inadequate secretion in early life: irreversible mental tetardation (cretinisim) and dwarfism or congenital cretinism ● Effect on growt ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.