Hormone and Metabolite Changes associated with
... et al., 1996). Leptin increases lipid oxidation and reduces triacylglycerol synthesis. In mammals, the progression of food deprivation generally results in a decrease in leptin within a few days of the cessation of food consumption (Kolaczynski et al., 1996; Mustonen et al., 2005). This in turn supp ...
... et al., 1996). Leptin increases lipid oxidation and reduces triacylglycerol synthesis. In mammals, the progression of food deprivation generally results in a decrease in leptin within a few days of the cessation of food consumption (Kolaczynski et al., 1996; Mustonen et al., 2005). This in turn supp ...
How should we interrogate the hypothalamic-pituitary
... secretion are stimulated by corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) which is secreted in the hypothalamus [1]. These processes are under negative feedback by glucocorticoids. ACTH secretion can be suppressed by exogenous glucocorticoids via this negative feedback mechanism and this represents the most ...
... secretion are stimulated by corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) which is secreted in the hypothalamus [1]. These processes are under negative feedback by glucocorticoids. ACTH secretion can be suppressed by exogenous glucocorticoids via this negative feedback mechanism and this represents the most ...
The thalamus as a putative biomarker in neurodegenerative disorders
... defining the boundaries of the thalamus are as follows: the third ventricle serves as the medial boundary, and the internal capsule separates the thalamus from the basal ganglia laterally; superiorly the thalamus is bound by the lateral ventricle, and inferiorly a number of distinctive structures a ...
... defining the boundaries of the thalamus are as follows: the third ventricle serves as the medial boundary, and the internal capsule separates the thalamus from the basal ganglia laterally; superiorly the thalamus is bound by the lateral ventricle, and inferiorly a number of distinctive structures a ...
Regulation of inhibin/activin subunits and follistatin mRNA
... Frozen tissue was pulverized in liquid nitrogen and then total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent (Gibco BRL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Total RNA was dissolved in RNase-free water and its concentration and purity were determined by optical density measu ...
... Frozen tissue was pulverized in liquid nitrogen and then total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent (Gibco BRL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Total RNA was dissolved in RNase-free water and its concentration and purity were determined by optical density measu ...
Pituitary Drugs
... IM, SC, IV forms, and gel and repository forms Follow directions carefully for administration ...
... IM, SC, IV forms, and gel and repository forms Follow directions carefully for administration ...
Projections of auditory cortex to the medial geniculate body of the cat
... visual system may reveal the basic principles of CT organization. For example, the feline medial geniculate body has three divisions and !12 nuclei (Winer, 1992), some without a precise analogue in the visual thalamus (Stone, 1983). Therefore, it is pertinent to ask how many patterns of CT input exi ...
... visual system may reveal the basic principles of CT organization. For example, the feline medial geniculate body has three divisions and !12 nuclei (Winer, 1992), some without a precise analogue in the visual thalamus (Stone, 1983). Therefore, it is pertinent to ask how many patterns of CT input exi ...
Carbohydrate Overview
... Promotes amino acid synthesis from glucose intermediates Decreases / inhibits glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis ...
... Promotes amino acid synthesis from glucose intermediates Decreases / inhibits glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis ...
Pathology of the thyroid, and parathyroid gland(s)
... tremor, hyperactivity, insomny, emotional lability, anxiety, proximal muscle weakness, loss of muscle Ocular changes: „eyes shut wide” - levator palpebrae sympathetic overdose real exophtalm only in Graves disease GI: hypermotility, malbsorption, diarrhea Bones: osteoporosis due to enhanced resorpti ...
... tremor, hyperactivity, insomny, emotional lability, anxiety, proximal muscle weakness, loss of muscle Ocular changes: „eyes shut wide” - levator palpebrae sympathetic overdose real exophtalm only in Graves disease GI: hypermotility, malbsorption, diarrhea Bones: osteoporosis due to enhanced resorpti ...
Vestibular Signals in the Parasolitary Nucleus
... nucleus solitarius and tractus solitarius. It is located dorsal and lateral to these structures. It extends rostrocaudally for about 2 mm and in its most rostral extent lies wedged between the medial and descending vestibular nuclei (MVN and DVN). Rather than being directly a part of a baroceptive r ...
... nucleus solitarius and tractus solitarius. It is located dorsal and lateral to these structures. It extends rostrocaudally for about 2 mm and in its most rostral extent lies wedged between the medial and descending vestibular nuclei (MVN and DVN). Rather than being directly a part of a baroceptive r ...
Olfactory pathway
... Then to olfactory association cortex (anterior part of parahippocampal gyrus or entorinal area). The primary olfactory area and olfactory association cortex are referred to as the pyriform cortex. It is responsible for the appreciation of olfactory stimuli. ...
... Then to olfactory association cortex (anterior part of parahippocampal gyrus or entorinal area). The primary olfactory area and olfactory association cortex are referred to as the pyriform cortex. It is responsible for the appreciation of olfactory stimuli. ...
The Pathophysiology of Amenorrhea in the Adolescent
... in response to serum levels of gonadal steroids. Secretion of GnRH is also regulated by a number of neurotransmitters, including dopamine, endogenous opioids, norepinephrine, gamma amino butyric acid (GABA), and corticotropin- releasing hormone (CRH). Some of these neurotransmitters (e.g., dopamine) ...
... in response to serum levels of gonadal steroids. Secretion of GnRH is also regulated by a number of neurotransmitters, including dopamine, endogenous opioids, norepinephrine, gamma amino butyric acid (GABA), and corticotropin- releasing hormone (CRH). Some of these neurotransmitters (e.g., dopamine) ...
Herbal Therapeutic Treatments for Hypothyroidism
... Primary hypothyroidism occurs when thyroid hormone levels are lowered and TSH is elevated in the blood; it usually indicates defective thyroid synthesis. Secondary hypothyroidism occurs when both TSH levels and thyroid hormone levels are low. This indicates that the pituitary gland is responsible fo ...
... Primary hypothyroidism occurs when thyroid hormone levels are lowered and TSH is elevated in the blood; it usually indicates defective thyroid synthesis. Secondary hypothyroidism occurs when both TSH levels and thyroid hormone levels are low. This indicates that the pituitary gland is responsible fo ...
Body Mass Index Determines Evoked Growth Hormone (GH
... major negative determinant of evoked GH response to provocative testing. The pathogenesis of GH insufficiency in obesity is unclear. Possible mechanisms include disordered hypothalamic tone and altered somatotrope cell function. A functional compensatory somatotrope response to the complex altered a ...
... major negative determinant of evoked GH response to provocative testing. The pathogenesis of GH insufficiency in obesity is unclear. Possible mechanisms include disordered hypothalamic tone and altered somatotrope cell function. A functional compensatory somatotrope response to the complex altered a ...
Common Endocrine Disorders
... Hyperthyroidism [TSH<0.05] Sick Euthyroid Syndrome [TSH 0.05-0.3] vs Subclinical Hyperthyroidism ...
... Hyperthyroidism [TSH<0.05] Sick Euthyroid Syndrome [TSH 0.05-0.3] vs Subclinical Hyperthyroidism ...
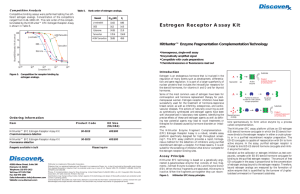
Estrogen Receptor Assay Kit - GE Healthcare Life Sciences
... Figure 5. Competition for receptor binding by estrogen analogs. ...
... Figure 5. Competition for receptor binding by estrogen analogs. ...
Chapter 11 The Endocrine System
... atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH), which stimulates sodium loss from the kidneys • Fat-storing cells secrete leptin, which controls how full or hungry we feel ...
... atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH), which stimulates sodium loss from the kidneys • Fat-storing cells secrete leptin, which controls how full or hungry we feel ...
Chapter 10 Head and Neck Together the head and neck provide the
... Autoimmune antibodies against thyroid gland, often causing hypothyroidism Infants Encephalocele Neural tube defect with protrusions of brain and membranes that cover it through openings in the skull Microcephaly Circumference of head is smaller than normal because brain has not developed properly o ...
... Autoimmune antibodies against thyroid gland, often causing hypothyroidism Infants Encephalocele Neural tube defect with protrusions of brain and membranes that cover it through openings in the skull Microcephaly Circumference of head is smaller than normal because brain has not developed properly o ...
The physiological role of orexin/hypocretin neurons in the regulation
... feeding, thermogenesis, and sleeping. Orexins (also known as hypocretins) were identified as endogenous ligands for two orphan G-protein-coupled receptors in the lateral hypothalamic area. They were initially recognized as regulators of feeding behavior, but they are mainly regarded as key modulators ...
... feeding, thermogenesis, and sleeping. Orexins (also known as hypocretins) were identified as endogenous ligands for two orphan G-protein-coupled receptors in the lateral hypothalamic area. They were initially recognized as regulators of feeding behavior, but they are mainly regarded as key modulators ...
The Evolution of Thyroidal Function in Fishes
... surprisingly therefore, there are many accounts of thyroid activity paralleling reproductive activity (see reviews, especially Gorbman, 1969). So close are these parallels that it is difficult to imagine how the thyroid could have any effect that is not closely related to reproduction. A third and f ...
... surprisingly therefore, there are many accounts of thyroid activity paralleling reproductive activity (see reviews, especially Gorbman, 1969). So close are these parallels that it is difficult to imagine how the thyroid could have any effect that is not closely related to reproduction. A third and f ...
THYROID STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH) ENZYME
... secreted from the anterior pituitary, is generally regarded as the most sensitive indicator available for the diagnosis of primary and secondary (pituitary) hypothyroidism (1,2). Increase in serum concentrations of TSH, which is primarily responsible for the synthesis and release of thyroid hormones ...
... secreted from the anterior pituitary, is generally regarded as the most sensitive indicator available for the diagnosis of primary and secondary (pituitary) hypothyroidism (1,2). Increase in serum concentrations of TSH, which is primarily responsible for the synthesis and release of thyroid hormones ...
doc PHGY311
... Hormones released into the circulation can circulate either freely or bound to carrier proteins, also known as binding proteins. The binding proteins serve as a reservoir for the hormone and prolong the hormone's half-life, the time during which the concentration of a hormone decreases to 50% of its ...
... Hormones released into the circulation can circulate either freely or bound to carrier proteins, also known as binding proteins. The binding proteins serve as a reservoir for the hormone and prolong the hormone's half-life, the time during which the concentration of a hormone decreases to 50% of its ...
Thyroid Hormone Action During Brain Development: More
... maternal thyroxine production during gestation (maternal hypothyroxinemea) greatly increases the risk for neurodevelopmental abnormalities and may lead to a decreased IQ in the progeny (de Escobar et al., 2004). Children can also develop hypothyroidism after birth due to an agenesis or dysgenesis of ...
... maternal thyroxine production during gestation (maternal hypothyroxinemea) greatly increases the risk for neurodevelopmental abnormalities and may lead to a decreased IQ in the progeny (de Escobar et al., 2004). Children can also develop hypothyroidism after birth due to an agenesis or dysgenesis of ...
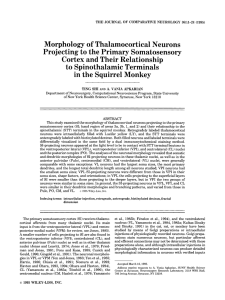
Morphology of Thalamocortical Neurons Projecting
... al., 1993; Apkarian and Shi 1994). Samples of these filled locations of the neurons shown in Figures 2-8 are illuscells and STT terminals were drawn with a camera lucida trated in a schematic diagram of coronal sections of the and a computerized microscope system (Eutectic Electron- thalamus (Fig. 9 ...
... al., 1993; Apkarian and Shi 1994). Samples of these filled locations of the neurons shown in Figures 2-8 are illuscells and STT terminals were drawn with a camera lucida trated in a schematic diagram of coronal sections of the and a computerized microscope system (Eutectic Electron- thalamus (Fig. 9 ...
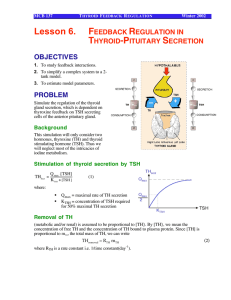
Lesson 6. FEEDBACK REGULATION IN THYROID
... µg/liter. Plot both [TH] and [TSH] and determine their "normal" steady state values. Are they consistent with the data? Note how fast the feedback system operates. Compare with different values of n. [Hint: [TH]ss = 80 µg/l; if you don’t get this, check your parameter values carefully. 2. A patient ...
... µg/liter. Plot both [TH] and [TSH] and determine their "normal" steady state values. Are they consistent with the data? Note how fast the feedback system operates. Compare with different values of n. [Hint: [TH]ss = 80 µg/l; if you don’t get this, check your parameter values carefully. 2. A patient ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.