I. DEFINITIONS THE DEGLUTITION PROCESS 2) Peristalsis
... When food get into the stomach, gentle contraction of the stomach wall mix the bolus with the gastric juice forming a thin fluid called the chyme. The muscular wall of the stomach is stronger in the pyloric region, and the peristalsis waves here force several milliliters of chyme into the duodenum t ...
... When food get into the stomach, gentle contraction of the stomach wall mix the bolus with the gastric juice forming a thin fluid called the chyme. The muscular wall of the stomach is stronger in the pyloric region, and the peristalsis waves here force several milliliters of chyme into the duodenum t ...
Mouth - Wsimg.com
... absorb (including undigested material) -Absorption of water Rectum (short term storage which holds feces before it is expelled). ...
... absorb (including undigested material) -Absorption of water Rectum (short term storage which holds feces before it is expelled). ...
Islamic University
... ( )2 6- The spermatic cord contains? a- spermatic artery, spermatic vein, spermatic nerve, ductus deferens, epididymis b- spermatic artery, spermatic vein, spermatic nerve, seminal vesicle c- spermatic artery, spermatic vein, spermatic nerve, epididymis d- ovarian artery, ovarian vein, ovarian nerve ...
... ( )2 6- The spermatic cord contains? a- spermatic artery, spermatic vein, spermatic nerve, ductus deferens, epididymis b- spermatic artery, spermatic vein, spermatic nerve, seminal vesicle c- spermatic artery, spermatic vein, spermatic nerve, epididymis d- ovarian artery, ovarian vein, ovarian nerve ...
Gastric Secretions
... Bile is a yellowish, green liquid and is secreted continuously by the hepatic cells It contains water, bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, and electrolytes. Bile salts the most numerous and the only substance to have a digestive function Hepatic cell use cholesterol to produce bile salts and in ...
... Bile is a yellowish, green liquid and is secreted continuously by the hepatic cells It contains water, bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, and electrolytes. Bile salts the most numerous and the only substance to have a digestive function Hepatic cell use cholesterol to produce bile salts and in ...
Ch25-Digestive-System
... 1. Location– anterior/posterior (circle one) to the greater curvature of the stomach 2. Dimension– 12-15 cm long & 2.5 cm thick 3. Functions– both endocrine (1%; insulin + glucagon) and exocrine gland (99%; secretes pancreatic juice) – Pancreatic juice: alkaline mixture of water, enzymes, zymogens, ...
... 1. Location– anterior/posterior (circle one) to the greater curvature of the stomach 2. Dimension– 12-15 cm long & 2.5 cm thick 3. Functions– both endocrine (1%; insulin + glucagon) and exocrine gland (99%; secretes pancreatic juice) – Pancreatic juice: alkaline mixture of water, enzymes, zymogens, ...
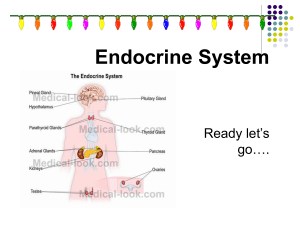
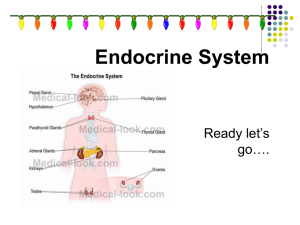
Laboratory Exercise 17: Anatomy of the Endocrine System
... Pancreas Location, Shape and Parts: Pancreas is a flat tail-like organ, located dorsal to the greater curvature of the stomach retroperitoneal. It is classified as both an endocrine and an exocrine gland. The exocrine part predominates in the form of circular groups of cells, the acini, which produc ...
... Pancreas Location, Shape and Parts: Pancreas is a flat tail-like organ, located dorsal to the greater curvature of the stomach retroperitoneal. It is classified as both an endocrine and an exocrine gland. The exocrine part predominates in the form of circular groups of cells, the acini, which produc ...
Chapter 24
... undigested parts of food most water reabsorbed in small intestine but large intestine also important in water reabsorption ...
... undigested parts of food most water reabsorbed in small intestine but large intestine also important in water reabsorption ...
Mechanical digestion – the breakdown of food
... the stomach to have a high acidity which kills most of the bacteria present in food. It also activates the enzyme pepsin. • Pepsin begins digesting protein in the stomach by breaking it down into peptides. ...
... the stomach to have a high acidity which kills most of the bacteria present in food. It also activates the enzyme pepsin. • Pepsin begins digesting protein in the stomach by breaking it down into peptides. ...
Document
... A. When blood sugar is high, ___________________ is released to convert glucose into ____________________________ B. When blood sugar is low, ____________________ is released to convert glycogen into ____________________________ C. Produces other enzymes for breakdown of nutrients ...
... A. When blood sugar is high, ___________________ is released to convert glucose into ____________________________ B. When blood sugar is low, ____________________ is released to convert glycogen into ____________________________ C. Produces other enzymes for breakdown of nutrients ...
Digestive System
... molecules that can be absorbed by the body in one long tube from mouth to anus ...
... molecules that can be absorbed by the body in one long tube from mouth to anus ...
TEST CH 9 THE ENODCRINE SYSTEM
... 4. Individuals with ______________ diabetes mellitus may often control their disease by diet and exercise. 5. Individuals with ______________ diabetes mellitus normally have to take insulin shots to control their diabetes. 6. Hypothyroidism in children may lead to ___________________. 7. ___________ ...
... 4. Individuals with ______________ diabetes mellitus may often control their disease by diet and exercise. 5. Individuals with ______________ diabetes mellitus normally have to take insulin shots to control their diabetes. 6. Hypothyroidism in children may lead to ___________________. 7. ___________ ...
Digestion - WordPress.com
... breakdown of starch to maltose Lipase, to break down lipids to fatty acids and glycerol Trypsinogen, precursor of the protease trypsin ...
... breakdown of starch to maltose Lipase, to break down lipids to fatty acids and glycerol Trypsinogen, precursor of the protease trypsin ...
The DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART 2
... general circulation. It screens blood reaching it in the hepatic portal system so that its composition when it leaves will be close to normal for the body. Furthermore, this homeostatic mechanism works both ways. When, for example, the concentration of glucose in the blood drops between meals, the ...
... general circulation. It screens blood reaching it in the hepatic portal system so that its composition when it leaves will be close to normal for the body. Furthermore, this homeostatic mechanism works both ways. When, for example, the concentration of glucose in the blood drops between meals, the ...
Notes: Digestion
... - Stored in the gall bladder; secretes bile into duodenum to… Job of bile: - M: emulsify fat; breaks fat globs into smaller globlets 3. Stores and releases sugars to keep blood sugar levels at homeostasis - See your endocrine notes = Negative feedback loop of glucose levels in the blood! b) Pancreas ...
... - Stored in the gall bladder; secretes bile into duodenum to… Job of bile: - M: emulsify fat; breaks fat globs into smaller globlets 3. Stores and releases sugars to keep blood sugar levels at homeostasis - See your endocrine notes = Negative feedback loop of glucose levels in the blood! b) Pancreas ...
Chapter 18: Nutrients and Digestion
... duodenum, where most of the digestion takes place Bile is released from your liver, and breaks up the large fat particles Pancreas releases another solution that breaks down carbohydrates, proteins and fats Pancreas also produces insulin, which always glucose to pass from your bloodstream into ...
... duodenum, where most of the digestion takes place Bile is released from your liver, and breaks up the large fat particles Pancreas releases another solution that breaks down carbohydrates, proteins and fats Pancreas also produces insulin, which always glucose to pass from your bloodstream into ...
EMBRYOLOGY Mid-Gut
... It takes origin from 2 pancreatic Buds (from the endodermal lining of the Duodenum),these buds are one dorsal & one ventral buds.The dorsal pancreatic bud grows in to the mesoduodenum & forms the tail,body & the major part of the head of the pancrease.It also give the major part of the main panci ...
... It takes origin from 2 pancreatic Buds (from the endodermal lining of the Duodenum),these buds are one dorsal & one ventral buds.The dorsal pancreatic bud grows in to the mesoduodenum & forms the tail,body & the major part of the head of the pancrease.It also give the major part of the main panci ...
the digestive system - people.vcu.edu
... PANCREAS AND OTHER ORGANS MUCOUS SECRETIONS PROTECT THE DIGESTIVE TRACT ACID IS SECRETED IN THE STOMACH THERE ARE OTHER SECRETIONS OF IMPORTANCE ...
... PANCREAS AND OTHER ORGANS MUCOUS SECRETIONS PROTECT THE DIGESTIVE TRACT ACID IS SECRETED IN THE STOMACH THERE ARE OTHER SECRETIONS OF IMPORTANCE ...
AP Digestive System Guided Notes
... Regulates the composition of _______________________ (amounts of sugar, also known as glucose, protein, and the fat that enters the bloodstream.) Removes ______________________________ from the blood. Processes the nutrients absorbed by the intestines during digestion, converts them into forms ...
... Regulates the composition of _______________________ (amounts of sugar, also known as glucose, protein, and the fat that enters the bloodstream.) Removes ______________________________ from the blood. Processes the nutrients absorbed by the intestines during digestion, converts them into forms ...
45.1-45.2 - Wild about Bio
... Insulin and Glucagon: Control of Blood Glucose • Insulin (decreases blood glucose) and glucagon (increases blood glucose) are antagonistic hormones that help maintain glucose homeostasis • The pancreas has clusters of endocrine cells called pancreatic islets with alpha cells that produce glucagon a ...
... Insulin and Glucagon: Control of Blood Glucose • Insulin (decreases blood glucose) and glucagon (increases blood glucose) are antagonistic hormones that help maintain glucose homeostasis • The pancreas has clusters of endocrine cells called pancreatic islets with alpha cells that produce glucagon a ...
Pancreas

The pancreas /ˈpæŋkriəs/ is a glandular organ in the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. It is an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide which circulate in the blood. The pancreas is also a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. These enzymes help to further break down the carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids in the chyme.