Gonadotropin-releasing hormone
... pancreas and in the intestine where it inhibits the secretion of a variety of other hormones.. ...
... pancreas and in the intestine where it inhibits the secretion of a variety of other hormones.. ...
Steroid and Thyroid Hormones
... •dihydrotestosterone (DHT) – but most of conversion of testosterone to DHT occurs outside the testes • estradiol – a small amount of testosteron is also converted into estradiol by aromatization – inhibits testosteron synthesis ...
... •dihydrotestosterone (DHT) – but most of conversion of testosterone to DHT occurs outside the testes • estradiol – a small amount of testosteron is also converted into estradiol by aromatization – inhibits testosteron synthesis ...
File - Anatomy & Physiology
... • The cells, tissues, and organs are called endocrine glands • They are ductless • They use the bloodstream • They secrete hormones • There are also similar glands called paracrine and autocrine glands that are quasi-endocrine • Other glands that secrete substances are the exocrine glands • They hav ...
... • The cells, tissues, and organs are called endocrine glands • They are ductless • They use the bloodstream • They secrete hormones • There are also similar glands called paracrine and autocrine glands that are quasi-endocrine • Other glands that secrete substances are the exocrine glands • They hav ...
Chapter 16 - apsubiology.org
... causes Na+ and Cl- reabsorption into the blood plasma, by targeting the kidney, and causes K+ excretion into the urine water is conserved passively because it follows NaCl movement ...
... causes Na+ and Cl- reabsorption into the blood plasma, by targeting the kidney, and causes K+ excretion into the urine water is conserved passively because it follows NaCl movement ...
Chapter 26 - Scranton Prep Biology
... To understand how the pancreascontrolsblood sugar,you need to rememberonly two things: (1) the pancreasmakes two hormones, insulin and glucagon, and (2) diabetics have high blood sugar, so many of them take insulin. Given these two facts, you can figure everything elseout: If diabeticshave to take i ...
... To understand how the pancreascontrolsblood sugar,you need to rememberonly two things: (1) the pancreasmakes two hormones, insulin and glucagon, and (2) diabetics have high blood sugar, so many of them take insulin. Given these two facts, you can figure everything elseout: If diabeticshave to take i ...
care of the clients
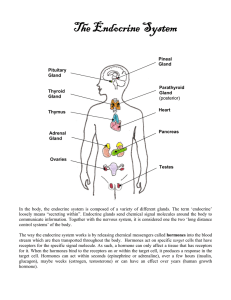
... The endocrine glands: these include the hypothalamus, the anterior and posterior pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, pineal, adrenal cortex/medulla, the gonads (ovary and testes) and the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. The hormones released by the glands can be classified as amines, polypeptides ...
... The endocrine glands: these include the hypothalamus, the anterior and posterior pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, pineal, adrenal cortex/medulla, the gonads (ovary and testes) and the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. The hormones released by the glands can be classified as amines, polypeptides ...
Endocrine System Notes 1
... glucose in take of the cells. A deficiency in this hormone results in diabetes mellitus. Insulin regulates the blood sugar levels by stimulating cells to take in glucose. It also stimulates the synthesis of protein and fat storage. The adrenal medulla is the gland behind the fight-orflight reaction. ...
... glucose in take of the cells. A deficiency in this hormone results in diabetes mellitus. Insulin regulates the blood sugar levels by stimulating cells to take in glucose. It also stimulates the synthesis of protein and fat storage. The adrenal medulla is the gland behind the fight-orflight reaction. ...
Name: Period: ______ Ch 9: The Endocrine System Objectives
... membrane ________________. The hormone does not enter the ________. The binding sets off a series of __________________ that activates an enzyme. The enzyme _________________ a reaction that produces a ________________ __________________ molecule. The molecule oversees additional intracellular _____ ...
... membrane ________________. The hormone does not enter the ________. The binding sets off a series of __________________ that activates an enzyme. The enzyme _________________ a reaction that produces a ________________ __________________ molecule. The molecule oversees additional intracellular _____ ...
Learning Objectives
... Chemical Signals and Their Modes of Action 5. List the three major classes of molecules that function as hormones in vertebrates. 6. Name the three key events involved in signaling by vertebrate hormones. 7. Explain what changes may be triggered by a signal transduction pathway initiated by the bind ...
... Chemical Signals and Their Modes of Action 5. List the three major classes of molecules that function as hormones in vertebrates. 6. Name the three key events involved in signaling by vertebrate hormones. 7. Explain what changes may be triggered by a signal transduction pathway initiated by the bind ...
Get Your Blood and Urine Tested
... Get Your Blood and Urine Tested The following are the basic and advanced tests I'd like you to get for the beta program. Basic Diabesity Testing NOTE: The abnormal levels noted are based on people who are not taking cholesterol or diabetes medications. If you are on medication, the numbers may look ...
... Get Your Blood and Urine Tested The following are the basic and advanced tests I'd like you to get for the beta program. Basic Diabesity Testing NOTE: The abnormal levels noted are based on people who are not taking cholesterol or diabetes medications. If you are on medication, the numbers may look ...
Endocrine System
... – zona glomerulosa (outer) – zona fasciculata (middle) – zona reticularis (inner) ...
... – zona glomerulosa (outer) – zona fasciculata (middle) – zona reticularis (inner) ...
The Endocrine System
... control BSL (blood sugar level). • Ovaries – produces hormones that control female characteristics and menstrual cycle. • Testes – produces a hormone that control male characteristics and sperm production. ...
... control BSL (blood sugar level). • Ovaries – produces hormones that control female characteristics and menstrual cycle. • Testes – produces a hormone that control male characteristics and sperm production. ...
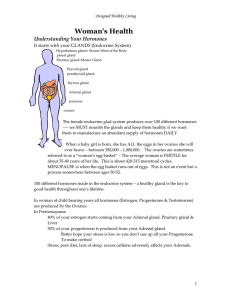
Understanding Your Hormones
... temperature, normal sleep patterns and balancing one’s moods and sense of well being. Menopausal women are concerned about taking HRT (hormone replacement therapy) in light of recent research. Scientific studies suggest that along with a healthy diet & lifestyle, consuming phytoestrogens will help r ...
... temperature, normal sleep patterns and balancing one’s moods and sense of well being. Menopausal women are concerned about taking HRT (hormone replacement therapy) in light of recent research. Scientific studies suggest that along with a healthy diet & lifestyle, consuming phytoestrogens will help r ...
The Endocrine System
... only do humans make DMT themselves in their pineal glands, i.e., we have our own endogenous supply, but it is also ubiquitous in many plants. DMT is believed to be released during birth and also during neardeath experiences. It is also thought to play a role in facilitating the visual aspects of dre ...
... only do humans make DMT themselves in their pineal glands, i.e., we have our own endogenous supply, but it is also ubiquitous in many plants. DMT is believed to be released during birth and also during neardeath experiences. It is also thought to play a role in facilitating the visual aspects of dre ...
The Endocrine System
... are unable to obtain glucose from the blood. This results in a high glucose level in the blood • There are two types of diabetes: Type I and Type II. – Type I occurs when immune cells attack and destroy the islet of Langerhans cells. – Type II occurs when cells don’t have sufficient insulin levels o ...
... are unable to obtain glucose from the blood. This results in a high glucose level in the blood • There are two types of diabetes: Type I and Type II. – Type I occurs when immune cells attack and destroy the islet of Langerhans cells. – Type II occurs when cells don’t have sufficient insulin levels o ...
45 year old woman with facial swelling and hypokalemia
... Eyes: No change in vision. ENT: No thirst. +Facial swelling. Respiratory: No shortness of breath, cough. Cardiovascular: No chest pain, palpitations. +leg swelling. Gastrointestinal: No nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea. ...
... Eyes: No change in vision. ENT: No thirst. +Facial swelling. Respiratory: No shortness of breath, cough. Cardiovascular: No chest pain, palpitations. +leg swelling. Gastrointestinal: No nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea. ...
pediatric endocrinology services
... 21-hydroxylase Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol ...
... 21-hydroxylase Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol ...
Central Adrenal Insufficiency - Children`s Oncology Group Long
... What are the symptoms of central adrenal insufficiency? Under normal circumstances, there may be no symptoms at all, or there may be mild symptoms, such as fatigue, weakness, poor appetite, or dizziness. However, under stressful circumstances, such as fever, infection, surgery, or injury, symptoms m ...
... What are the symptoms of central adrenal insufficiency? Under normal circumstances, there may be no symptoms at all, or there may be mild symptoms, such as fatigue, weakness, poor appetite, or dizziness. However, under stressful circumstances, such as fever, infection, surgery, or injury, symptoms m ...
the muscular system
... These are the male glands and are found in the groin, in the scrotum. The testes produce the hormone testosterone responsible for male sexual characteristics and for the development of secondary sexual characteristics such as the deepening of the voice and beard growth. ...
... These are the male glands and are found in the groin, in the scrotum. The testes produce the hormone testosterone responsible for male sexual characteristics and for the development of secondary sexual characteristics such as the deepening of the voice and beard growth. ...
Chapter 17 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... – zona glomerulosa (outer) – zona fasciculata (middle) – zona reticularis (inner) ...
... – zona glomerulosa (outer) – zona fasciculata (middle) – zona reticularis (inner) ...
As a doctor,what you should know to treat your patient??
... endometrium has cyclic bleeding under the effects of ovarian hormone,which is accompanied by the fibrous tissues hyperplasia,and forms purple-brown spots,finally develops different size purpleblue nodes. • When it occersin the ovary (usually lateral ) there may be brown emplastic dated blood just li ...
... endometrium has cyclic bleeding under the effects of ovarian hormone,which is accompanied by the fibrous tissues hyperplasia,and forms purple-brown spots,finally develops different size purpleblue nodes. • When it occersin the ovary (usually lateral ) there may be brown emplastic dated blood just li ...
drugstore athlete
... huskier FloJo ran 10.49 and 21.34, times that no runner since has even come close to equalling. In other words, at the age of twenty-eight—when most athletes are beginning their decline—Griffith Joyner transformed herself in one season from a career-long better-than-average sprinter to the fastest f ...
... huskier FloJo ran 10.49 and 21.34, times that no runner since has even come close to equalling. In other words, at the age of twenty-eight—when most athletes are beginning their decline—Griffith Joyner transformed herself in one season from a career-long better-than-average sprinter to the fastest f ...
Dr. John Brimhall`s Formula Insight
... The HPA axis is a major thoroughfare between the brain and endocrine system; it must be maintained and balanced to help the body cope with acute and chronic stressors. The hypothalamus is assigned the task of controlling body temperature, fluid balance, appetite, and thirst. This “master” gland send ...
... The HPA axis is a major thoroughfare between the brain and endocrine system; it must be maintained and balanced to help the body cope with acute and chronic stressors. The hypothalamus is assigned the task of controlling body temperature, fluid balance, appetite, and thirst. This “master” gland send ...