The Basics of Noise Filtering
... the remaining voltage (noise) after filtering is dependent upon both the frequency and the input voltage. For example, given a particular power filter with a performance curve as defined in Figure 6, an input voltage (noise) of 10 volts at 100kHz is attenuated by –50dB, resulting in a final voltage ...
... the remaining voltage (noise) after filtering is dependent upon both the frequency and the input voltage. For example, given a particular power filter with a performance curve as defined in Figure 6, an input voltage (noise) of 10 volts at 100kHz is attenuated by –50dB, resulting in a final voltage ...
UML1N
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
Turn Ratio
... The turn’s ratio of a transformer therefore defines the transformer as step up or step-down. A stepup transformer is one whose secondary voltage is greater than its primary voltage and a transformer that steps up voltage will step-down current. A step-down transformer is one whose secondary voltage ...
... The turn’s ratio of a transformer therefore defines the transformer as step up or step-down. A stepup transformer is one whose secondary voltage is greater than its primary voltage and a transformer that steps up voltage will step-down current. A step-down transformer is one whose secondary voltage ...
Evaluates: MAX1856 MAX1856 Evaluation Kit SLIC Power Supply General Description
... Note: Exercise caution when measuring the -72V. For instructions on reconfiguring VOUT1 to -48V, see Evaluating -48V Output. ...
... Note: Exercise caution when measuring the -72V. For instructions on reconfiguring VOUT1 to -48V, see Evaluating -48V Output. ...
Cathodic Protection systems
... metal as determined from the reference electrode with the desired level of protection as set by the operator. Amplifies the difference between two levels and sends an electrical signal to the power supply which controls the amount of current delivered to the anodes. ...
... metal as determined from the reference electrode with the desired level of protection as set by the operator. Amplifies the difference between two levels and sends an electrical signal to the power supply which controls the amount of current delivered to the anodes. ...
DSM3 Installation and Quick Start Guide for XM3
... For units in service, backup battery power will not be available during this procedure. DSM3 Series installation and setup is comprised of three basic steps: 1. Installation of the DSM3 Series into the power supply, making front panel connections and verifying operation. 2. Setting Options: the DS ...
... For units in service, backup battery power will not be available during this procedure. DSM3 Series installation and setup is comprised of three basic steps: 1. Installation of the DSM3 Series into the power supply, making front panel connections and verifying operation. 2. Setting Options: the DS ...
Shaker Flashlight - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... Figure 5: Measuring the voltage of the AC circuit The signal is green, and we see that the voltage is alternating between positive and negative as a sine wave. It spends half the time positive, and half the time negative. This means that the current flows in one direction, slows down, flows in the ...
... Figure 5: Measuring the voltage of the AC circuit The signal is green, and we see that the voltage is alternating between positive and negative as a sine wave. It spends half the time positive, and half the time negative. This means that the current flows in one direction, slows down, flows in the ...
Self-excited induction generator research—a survey
... The increasing importance of fuel saving has been responsible for the revival of interest in so-called alternative source of energy. Thus, the drive towards the decentralization of power generation and increasing use of non-conventional energy sources such as wind energy, bio-gas, solar and hydro po ...
... The increasing importance of fuel saving has been responsible for the revival of interest in so-called alternative source of energy. Thus, the drive towards the decentralization of power generation and increasing use of non-conventional energy sources such as wind energy, bio-gas, solar and hydro po ...
chapter 4 pitch control of wind turbine generators
... produced powers, so the rotor speed is kept constant within a narrow band, which is called slip, which is the procentual relation between actual and ...
... produced powers, so the rotor speed is kept constant within a narrow band, which is called slip, which is the procentual relation between actual and ...
LMD18200 3A, 55V H-Bridge 3A, 55V
... shorted motor windings and locked rotors. Under these conditions the inductance of the motor (as well as any series inductance in the VCC supply line) serves to reduce the magnitude of a current surge to a safe level for the LMD18200. Once the device is shut down, the control circuitry will periodic ...
... shorted motor windings and locked rotors. Under these conditions the inductance of the motor (as well as any series inductance in the VCC supply line) serves to reduce the magnitude of a current surge to a safe level for the LMD18200. Once the device is shut down, the control circuitry will periodic ...
Single Phase Transformer© Nafees Ahmed By
... Nafees Ahmed Asstt. Prof. Department of Electrical Engineering DIT, University, Dehradun, Uttarakhand ...
... Nafees Ahmed Asstt. Prof. Department of Electrical Engineering DIT, University, Dehradun, Uttarakhand ...
MP6001 - Monolithic Power System
... see Figure 1. When power is applied, the capacitor at the VCC pin is charged through the VIN pin. When the voltage at the VCC pin crosses 6.0V without fault, the controller is enabled. The VCC pin is then disconnected from the VIN pin and VCC voltage is discharged via the operating current. When VCC ...
... see Figure 1. When power is applied, the capacitor at the VCC pin is charged through the VIN pin. When the voltage at the VCC pin crosses 6.0V without fault, the controller is enabled. The VCC pin is then disconnected from the VIN pin and VCC voltage is discharged via the operating current. When VCC ...
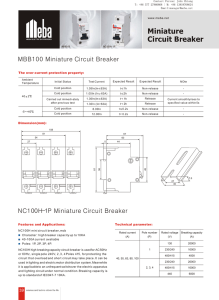
Meba Main switch NC100H 1P 127.26 kB
... NC100H mini circuit breaker, mcb Character: high breaker capacity up to 10KA 40-100A current avaliable Poles: 1P, 2P, 3P, 4P. NC100H high breaking capaci ty circuit breaker is used for AC 50Hz or 60Hz, single pole 240V, 2, 3, 4 Poles 415, for protecting the circuit that overload and short circuit ma ...
... NC100H mini circuit breaker, mcb Character: high breaker capacity up to 10KA 40-100A current avaliable Poles: 1P, 2P, 3P, 4P. NC100H high breaking capaci ty circuit breaker is used for AC 50Hz or 60Hz, single pole 240V, 2, 3, 4 Poles 415, for protecting the circuit that overload and short circuit ma ...
Solid-state NMR training course - New York Structural Biology Center
... No NMR spectroscopists are satisfied with probes’ power handling capabilities.. Bruker WB HXY and HFX probes are spec’d for: 1H/13C/15N: 120kHz@50ms, 50kHz@10ms, 50kHz@10ms in single channel mode. We test the probes with a double cross polarization experiment: 1H/15N 60kHz/50kHz@3ms followed by 1H/1 ...
... No NMR spectroscopists are satisfied with probes’ power handling capabilities.. Bruker WB HXY and HFX probes are spec’d for: 1H/13C/15N: 120kHz@50ms, 50kHz@10ms, 50kHz@10ms in single channel mode. We test the probes with a double cross polarization experiment: 1H/15N 60kHz/50kHz@3ms followed by 1H/1 ...
Commercial Powersines COMEC
... chopping part of each voltage cycle. They have high electric distortion especially with non-linear loads, require over-sized filters, very poor input line harmonics and will not handle surge currents such as motor starting. The second type, Inverter- based, implements various switching and modulatio ...
... chopping part of each voltage cycle. They have high electric distortion especially with non-linear loads, require over-sized filters, very poor input line harmonics and will not handle surge currents such as motor starting. The second type, Inverter- based, implements various switching and modulatio ...
Variable Frequency Drives - a Comparison of VSI versus
... f. An output filter has not been used in the past for any VSI drives. g. The motors for VSI drives are custom built with appropriate motor insulation systems. This usually means a higher voltage insulation system than for a standard utility-fed motor. LCI Drive Design a. The input transformer is se ...
... f. An output filter has not been used in the past for any VSI drives. g. The motors for VSI drives are custom built with appropriate motor insulation systems. This usually means a higher voltage insulation system than for a standard utility-fed motor. LCI Drive Design a. The input transformer is se ...
Attenuators
... An attenuator is a device for introducing a specified loss between a signal source and a matched load without upsetting the impedance relationship necessary for matching. The loss introduced is constant irrespective of frequency; since reactive elements (L or C) vary with frequency, it follows that ...
... An attenuator is a device for introducing a specified loss between a signal source and a matched load without upsetting the impedance relationship necessary for matching. The loss introduced is constant irrespective of frequency; since reactive elements (L or C) vary with frequency, it follows that ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... and Germany [1,2]. A special focus in these requirements is drawn to both the wind turbine fault ride-through capability and the wind turbine grid support capability. Fault ride-through capability addresses primarily the design of the wind turbine controller in such a way that the wind turbine is ab ...
... and Germany [1,2]. A special focus in these requirements is drawn to both the wind turbine fault ride-through capability and the wind turbine grid support capability. Fault ride-through capability addresses primarily the design of the wind turbine controller in such a way that the wind turbine is ab ...
A final decision on temperature control concerned the basic setup... Basic setup
... This section covers the design of the necessary control circuitry (power driver, signal conditioning and acquisition) and the functional characterization of the necessary elements (temperature sensors and Peltier cells). The control algorithm, a proportional-integrative-derivative (PID) method, that ...
... This section covers the design of the necessary control circuitry (power driver, signal conditioning and acquisition) and the functional characterization of the necessary elements (temperature sensors and Peltier cells). The control algorithm, a proportional-integrative-derivative (PID) method, that ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... multi bus power system where series and shunt parameters of transmission lines are lumped separately in the form of series and shunt equivalent. The equivalent network parameters like GVSM, critical voltage, global receiving end voltage etc., are able to sense any type of change in system in accurat ...
... multi bus power system where series and shunt parameters of transmission lines are lumped separately in the form of series and shunt equivalent. The equivalent network parameters like GVSM, critical voltage, global receiving end voltage etc., are able to sense any type of change in system in accurat ...
Drive Solutions for the Global Cement Industry
... Why Use Electrical Variable Frequency Drives? Here are some of the reasons to use electrical medium voltage drives: Increased Reliability Pages 5, 5, 9 Variable speed motor-drive systems are more reliable than traditional mechanical approaches such as using louvers, valves, gears, or turbines to co ...
... Why Use Electrical Variable Frequency Drives? Here are some of the reasons to use electrical medium voltage drives: Increased Reliability Pages 5, 5, 9 Variable speed motor-drive systems are more reliable than traditional mechanical approaches such as using louvers, valves, gears, or turbines to co ...
IRF420-423/IRF820-823 MTP2N45/2N50 N
... IRF420-423/IRF820-823 MTP2N45/2N50 N-Channel Power MOSFETs 3.0A, 450V/500V Description These devices are n-channel, enhancement mode, power MOSFETs designed especially for high speed applications, such as switching power supplies, converters, AC and DC motor controls, relay and solenoid drivers and ...
... IRF420-423/IRF820-823 MTP2N45/2N50 N-Channel Power MOSFETs 3.0A, 450V/500V Description These devices are n-channel, enhancement mode, power MOSFETs designed especially for high speed applications, such as switching power supplies, converters, AC and DC motor controls, relay and solenoid drivers and ...
Frequently Asked Questions
... output (or "secondary") voltage varies only a small amount from minimum to full rated output current. All neon transformers have deliberately poor output voltage regulation made possible by the use magnetic shunts in the transformer. This poor regulation is necessary to limit current in neon tubing. ...
... output (or "secondary") voltage varies only a small amount from minimum to full rated output current. All neon transformers have deliberately poor output voltage regulation made possible by the use magnetic shunts in the transformer. This poor regulation is necessary to limit current in neon tubing. ...
Power engineering

Power engineering, also called power systems engineering, is a subfield of energy engineering that deals with the generation, transmission, distribution and utilization of electric power and the electrical devices connected to such systems including generators, motors and transformers. Although much of the field is concerned with the problems of three-phase AC power – the standard for large-scale power transmission and distribution across the modern world – a significant fraction of the field is concerned with the conversion between AC and DC power and the development of specialized power systems such as those used in aircraft or for electric railway networks. It was a subfield of electrical engineering before the emergence of energy engineering.Electricity became a subject of scientific interest in the late 17th century with the work of William Gilbert. Over the next two centuries a number of important discoveries were made including the incandescent light bulb and the voltaic pile. Probably the greatest discovery with respect to power engineering came from Michael Faraday who in 1831 discovered that a change in magnetic flux induces an electromotive force in a loop of wire—a principle known as electromagnetic induction that helps explain how generators and transformers work.In 1881 two electricians built the world's first power station at Godalming in England. The station employed two waterwheels to produce an alternating current that was used to supply seven Siemens arc lamps at 250 volts and thirty-four incandescent lamps at 40 volts. However supply was intermittent and in 1882 Thomas Edison and his company, The Edison Electric Light Company, developed the first steam-powered electric power station on Pearl Street in New York City. The Pearl Street Station consisted of several generators and initially powered around 3,000 lamps for 59 customers. The power station used direct current and operated at a single voltage. Since the direct current power could not be easily transformed to the higher voltages necessary to minimise power loss during transmission, the possible distance between the generators and load was limited to around half-a-mile (800 m).That same year in London Lucien Gaulard and John Dixon Gibbs demonstrated the first transformer suitable for use in a real power system. The practical value of Gaulard and Gibbs' transformer was demonstrated in 1884 at Turin where the transformer was used to light up forty kilometres (25 miles) of railway from a single alternating current generator. Despite the success of the system, the pair made some fundamental mistakes. Perhaps the most serious was connecting the primaries of the transformers in series so that switching one lamp on or off would affect other lamps further down the line. Following the demonstration George Westinghouse, an American entrepreneur, imported a number of the transformers along with a Siemens generator and set his engineers to experimenting with them in the hopes of improving them for use in a commercial power system.One of Westinghouse's engineers, William Stanley, recognised the problem with connecting transformers in series as opposed to parallel and also realised that making the iron core of a transformer a fully enclosed loop would improve the voltage regulation of the secondary winding. Using this knowledge he built a much improved alternating current power system at Great Barrington, Massachusetts in 1886. In 1885 the Italian physicist and electrical engineer Galileo Ferraris demonstrated an induction motor and in 1887 and 1888 the Serbian-American engineer Nikola Tesla filed a range of patents related to power systems including one for a practical two-phase induction motor which Westinghouse licensed for his AC system.By 1890 the power industry had flourished and power companies had built thousands of power systems (both direct and alternating current) in the United States and Europe – these networks were effectively dedicated to providing electric lighting. During this time a fierce rivalry in the US known as the ""War of Currents"" emerged between Edison and Westinghouse over which form of transmission (direct or alternating current) was superior. In 1891, Westinghouse installed the first major power system that was designed to drive an electric motor and not just provide electric lighting. The installation powered a 100 horsepower (75 kW) synchronous motor at Telluride, Colorado with the motor being started by a Tesla induction motor. On the other side of the Atlantic, Oskar von Miller built a 20 kV 176 km three-phase transmission line from Lauffen am Neckar to Frankfurt am Main for the Electrical Engineering Exhibition in Frankfurt. In 1895, after a protracted decision-making process, the Adams No. 1 generating station at Niagara Falls began transmitting three-phase alternating current power to Buffalo at 11 kV. Following completion of the Niagara Falls project, new power systems increasingly chose alternating current as opposed to direct current for electrical transmission.Although the 1880s and 1890s were seminal decades in the field, developments in power engineering continued throughout the 20th and 21st century. In 1936 the first commercial high-voltage direct current (HVDC) line using mercury-arc valves was built between Schenectady and Mechanicville, New York. HVDC had previously been achieved by installing direct current generators in series (a system known as the Thury system) although this suffered from serious reliability issues. In 1957 Siemens demonstrated the first solid-state rectifier (solid-state rectifiers are now the standard for HVDC systems) however it was not until the early 1970s that this technology was used in commercial power systems. In 1959 Westinghouse demonstrated the first circuit breaker that used SF6 as the interrupting medium. SF6 is a far superior dielectric to air and, in recent times, its use has been extended to produce far more compact switching equipment (known as switchgear) and transformers. Many important developments also came from extending innovations in the ICT field to the power engineering field. For example, the development of computers meant load flow studies could be run more efficiently allowing for much better planning of power systems. Advances in information technology and telecommunication also allowed for much better remote control of the power system's switchgear and generators.