Graves Disease Booklet
... What is the thyroid, and why is it important? The thyroid is an endocrine gland that plays a key role in regulating growth, development, and normal function of the body.1 It is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck. The thyroid can affect your heart rate, your emotional state, y ...
... What is the thyroid, and why is it important? The thyroid is an endocrine gland that plays a key role in regulating growth, development, and normal function of the body.1 It is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck. The thyroid can affect your heart rate, your emotional state, y ...
Theories of Autoimmunity
... hormones (TSH) •The binding of TSH to a receptor on thyroid cells activates adenylate cyclase and stimulates the synthesis of two thyroid hormones: thyroxine and triiodothyronine •A person with Grave’s Disease makes auto-antibodies to the receptor for TSH. The binding of these auto-antibodies to the ...
... hormones (TSH) •The binding of TSH to a receptor on thyroid cells activates adenylate cyclase and stimulates the synthesis of two thyroid hormones: thyroxine and triiodothyronine •A person with Grave’s Disease makes auto-antibodies to the receptor for TSH. The binding of these auto-antibodies to the ...
TEAR DEFICIENCY (Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca)
... • Diminish outflow – punctal plugs (refer to College Guidance on the ‘use of punctum plugs and intracanalicular occlusion’) • Reduce evaporation – lid hygiene for Meibomian dysfunction (hot compress and massage, lid cleaning with swabs or cotton buds) • Advise avoidance of factors that aggravate sym ...
... • Diminish outflow – punctal plugs (refer to College Guidance on the ‘use of punctum plugs and intracanalicular occlusion’) • Reduce evaporation – lid hygiene for Meibomian dysfunction (hot compress and massage, lid cleaning with swabs or cotton buds) • Advise avoidance of factors that aggravate sym ...
Endocrine System
... of gametes & stimulates ovaries to produce estrogen - releases Luteinizing Hormone (LH) = stimulates ovulation & stimulates testicles to produce testosterone -releases Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) = stimulates adrenal glands -releases Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) = stimulates release of t ...
... of gametes & stimulates ovaries to produce estrogen - releases Luteinizing Hormone (LH) = stimulates ovulation & stimulates testicles to produce testosterone -releases Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) = stimulates adrenal glands -releases Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) = stimulates release of t ...
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Nicolas
... Thyroid Stimulating Hormone on the thyroid causing a release of T3 and T4 into the blood. As this occurs, the anterior pituitary is measuring levels of T3 and T4 and halts the production of TRH and TSH when levels of T3 and T4 are homeostatic. Clearly, each hormone plays an important role in proper ...
... Thyroid Stimulating Hormone on the thyroid causing a release of T3 and T4 into the blood. As this occurs, the anterior pituitary is measuring levels of T3 and T4 and halts the production of TRH and TSH when levels of T3 and T4 are homeostatic. Clearly, each hormone plays an important role in proper ...
Laboratory Values
... Anatomy: endocrine gland (alpha cells: glucagon, beta cells: insulin), secretes directly into the systemic circulation Physiology: glucose is regulated within a relatively narrow range (in part) by the effects of insulin which drives the uptake of glucose into cells and glucagon which stimulates the ...
... Anatomy: endocrine gland (alpha cells: glucagon, beta cells: insulin), secretes directly into the systemic circulation Physiology: glucose is regulated within a relatively narrow range (in part) by the effects of insulin which drives the uptake of glucose into cells and glucagon which stimulates the ...
Endocrine System Lecture
... metabolism, how cells use glucose and oxygen to produce heat/energy; controls levels of calcium in the blood; stimulates physical and mental growth • Calcitonin – accelerates storage of calcium in bones and lowers blood calcium levels; 99% of calcium in the body is stored in bones, necessary for blo ...
... metabolism, how cells use glucose and oxygen to produce heat/energy; controls levels of calcium in the blood; stimulates physical and mental growth • Calcitonin – accelerates storage of calcium in bones and lowers blood calcium levels; 99% of calcium in the body is stored in bones, necessary for blo ...
The Endocrine System - An Overview
... situated in the front of your neck, just below the Adams Apple. ...
... situated in the front of your neck, just below the Adams Apple. ...
Endocrine System Worksheet Key
... , ÿnctions. Use the terms in the word box to label the diagram and identify the gland to which each hormone (in the box at the bottom) is associated. ...
... , ÿnctions. Use the terms in the word box to label the diagram and identify the gland to which each hormone (in the box at the bottom) is associated. ...
The Endocrine System - An Overview
... neck, just below the Adams Apple. The thyroid gland produces two main hormones which are very important for growth and development. One is called thyroxine (T4) and the other is called triiodothyronine (T3). T4 is converted to T3 in the body’s cells and tissues. T3 is an active hormone and is needed ...
... neck, just below the Adams Apple. The thyroid gland produces two main hormones which are very important for growth and development. One is called thyroxine (T4) and the other is called triiodothyronine (T3). T4 is converted to T3 in the body’s cells and tissues. T3 is an active hormone and is needed ...
Using Cutting Edge Accurate Identification of the GI Microbiota in the
... “Zonulin, a protein that modulates intestinal permeability, is upregulated in several autoimmune diseases and is involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diabetes. Zonulin upregulation seems to precede the onset of the disease, providing a possible link between increased intestinal permeability, ...
... “Zonulin, a protein that modulates intestinal permeability, is upregulated in several autoimmune diseases and is involved in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diabetes. Zonulin upregulation seems to precede the onset of the disease, providing a possible link between increased intestinal permeability, ...
Ectopic_Hormone_Syndromes
... active, and cases associated with thyrotoxicosis can be due to autoimmune stimulation of the normal thyroid gland ...
... active, and cases associated with thyrotoxicosis can be due to autoimmune stimulation of the normal thyroid gland ...
Document
... how you care for yourself? Are there any specific treatments you would not use to treat this condition? ...
... how you care for yourself? Are there any specific treatments you would not use to treat this condition? ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Thyroid and steroid hormones cross the cell membrane and bind to INTRACELLULAR receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus The hormone- receptor complex triggers activation or inactivation of specific genes Synthesis of new protein alters cellular ...
... Thyroid and steroid hormones cross the cell membrane and bind to INTRACELLULAR receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus The hormone- receptor complex triggers activation or inactivation of specific genes Synthesis of new protein alters cellular ...
Endocrine
... Graves disease is a chronic immune system disorder affecting the thyroid gland that results in overproduction of thyroid hormones. Symptoms: Weakness/ fatigue Unexplained weight loss Muscle cramps Anxiety Irregular heartbeats Heat sensitivity Fine hand coordination difficulties Skin ...
... Graves disease is a chronic immune system disorder affecting the thyroid gland that results in overproduction of thyroid hormones. Symptoms: Weakness/ fatigue Unexplained weight loss Muscle cramps Anxiety Irregular heartbeats Heat sensitivity Fine hand coordination difficulties Skin ...
Endocrine System
... • Hyposecretion of this hormone causes diabetes insipidus, treated by replacement doses of ADH ...
... • Hyposecretion of this hormone causes diabetes insipidus, treated by replacement doses of ADH ...
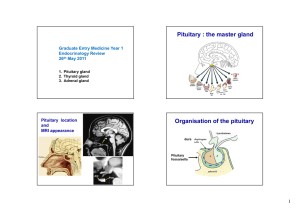
Pituitary : the master gland Organisation of the pituitary
... stimulates long bone and tissue growth ...
... stimulates long bone and tissue growth ...
Endocrinology Regulation of Posterior pituitary hormones and
... b) Normal development of NS, especially CNS(brain); Shows large effect in children without thyroid at birth. ...
... b) Normal development of NS, especially CNS(brain); Shows large effect in children without thyroid at birth. ...
Graves' disease

Graves' disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter and Flajani-Basedow-Graves disease, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in hyperthyroidism and an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, and weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye problems such as bulging, a condition known as Graves' ophthalmopathy. About 25% to 80% of people develop eye problems.The exact cause is unclear; however, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. A person is more likely to be affected if they have a family member with the disease. If one twin is affected there is a 30% chance the other twin will also have the disease. The onset of disease may be triggered by stress, infection, or giving birth. Those with other autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis are more likely to be affected. Smoking increases the risk of disease and may make the eye problems worse. The disorder results from an antibody, called thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI), that has a similar effect to thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). These antibodies cause the thyroid gland to produce excess thyroid hormone. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms with blood tests and radioiodine uptake used to confirm the disease. Typically blood tests show a raised T3 and T4, low TSH, increased radioiodine uptake in all areas of the thyroid, and TSI antibodies.There are three treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. Eye problems may require additional treatments.Graves' disease occurs in about 0.5% of people. It occurs about 7.5 times more often in women than men. Often it starts between the ages of forty and sixty. It is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism in the United States (about 50% to 80% of cases). The condition is named after Robert Graves who described it in 1835. A number of prior descriptions also exist.