1 2 - UMSONPatho
... Regulation of Cortisol Synthesis and Secretion Description • Pharmacologic steroids produce a negative feedback effect on the hypothalamus and pituitary. – CRH and ACTH are decreased to zero – Over time, the adrenal gland becomes less able to produce cortisol. ...
... Regulation of Cortisol Synthesis and Secretion Description • Pharmacologic steroids produce a negative feedback effect on the hypothalamus and pituitary. – CRH and ACTH are decreased to zero – Over time, the adrenal gland becomes less able to produce cortisol. ...
A deficiency of growth hormone can also cause people to put on fat
... Dr Kearney explains: ‘If you’ve got too much thyroid hormone, it’s as if you’re buzzing. You can be slightly irritable, wired, sweaty and the pulse rate tends to be fast.’ Other symptoms can include gabbled speech, prominent, sticking-out eyes (caused by antibodies in the bloodstream affecting the m ...
... Dr Kearney explains: ‘If you’ve got too much thyroid hormone, it’s as if you’re buzzing. You can be slightly irritable, wired, sweaty and the pulse rate tends to be fast.’ Other symptoms can include gabbled speech, prominent, sticking-out eyes (caused by antibodies in the bloodstream affecting the m ...
Endocrine Assignment Hyperthyroid and Diabetes Mellitus Type I
... metabolism, heat intolerance, and increased tissue sensitivity to sympathetic stimulation. (Jones & Huether, 2006). Discussion Question: What would you see for signs and symptoms of hyperthyroid? Most signs and symptoms are the same for all hyperthyroidisms; except infiltrative ophthalmopathy and de ...
... metabolism, heat intolerance, and increased tissue sensitivity to sympathetic stimulation. (Jones & Huether, 2006). Discussion Question: What would you see for signs and symptoms of hyperthyroid? Most signs and symptoms are the same for all hyperthyroidisms; except infiltrative ophthalmopathy and de ...
investigations in uveitis
... • Diseases like PAN ,MPO or Wegener's Granulomatosis can very rarely cause retinal vessel inflammation. • These diseases primarily affect sclera and adnexa. • Manifestations are secondary to the associated renal induced hypertension (PAN,MPO). • Direct infiltration of retina and optic nerve in case ...
... • Diseases like PAN ,MPO or Wegener's Granulomatosis can very rarely cause retinal vessel inflammation. • These diseases primarily affect sclera and adnexa. • Manifestations are secondary to the associated renal induced hypertension (PAN,MPO). • Direct infiltration of retina and optic nerve in case ...
Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder
... Identify and discuss the organs of the endocrine and metabolic systems and their function(s) Discuss common illnesses involving the endocrine and metabolic systems ...
... Identify and discuss the organs of the endocrine and metabolic systems and their function(s) Discuss common illnesses involving the endocrine and metabolic systems ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... always feels cold. Her heart rate is slow and blood pressure is low due to both indirect and direct effects of missing thyroid hormones. Inadequate thyroxine causes an indirect decrease in adrenergic stimulation of the heart and blood vessels (dilation) but also causes a direct decrease of thyroxine ...
... always feels cold. Her heart rate is slow and blood pressure is low due to both indirect and direct effects of missing thyroid hormones. Inadequate thyroxine causes an indirect decrease in adrenergic stimulation of the heart and blood vessels (dilation) but also causes a direct decrease of thyroxine ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... always feels cold. Her heart rate is slow and blood pressure is low due to both indirect and direct effects of missing thyroid hormones. Inadequate thyroxine causes an indirect decrease in adrenergic stimulation of the heart and blood vessels (dilation) but also causes a direct decrease of thyroxine ...
... always feels cold. Her heart rate is slow and blood pressure is low due to both indirect and direct effects of missing thyroid hormones. Inadequate thyroxine causes an indirect decrease in adrenergic stimulation of the heart and blood vessels (dilation) but also causes a direct decrease of thyroxine ...
Pathology Chapter 24 p1107-1130 [4-20
... Almost all cases of Grave’s have thyroid-stimulating Ig, and they’re specific for Grave’s disease, unlike the other 2 Ig’s seen o Thyroid-growth stimulating Ig- also targets the TSH receptor and causes proliferation of the follicle epithelium o TSH-binding inhibitor Ig- bind and inhibit TSH, and c ...
... Almost all cases of Grave’s have thyroid-stimulating Ig, and they’re specific for Grave’s disease, unlike the other 2 Ig’s seen o Thyroid-growth stimulating Ig- also targets the TSH receptor and causes proliferation of the follicle epithelium o TSH-binding inhibitor Ig- bind and inhibit TSH, and c ...
estrogen receptors in human thyroid gland
... thyroid stimulating hormone receptors and their therapeutic importance in thyroid neoplasm.18 In fact, detection of ER in thyroid has been the object of various studies. Table-3 summarizes the different studies, which have been carried out for the determination of ER. In most studies chemical method ...
... thyroid stimulating hormone receptors and their therapeutic importance in thyroid neoplasm.18 In fact, detection of ER in thyroid has been the object of various studies. Table-3 summarizes the different studies, which have been carried out for the determination of ER. In most studies chemical method ...
power point Link
... Diseases of the Endocrine System If there are problems with one or more glands in the endocrine system, organs won’t function properly. Diseases of the endocrine system can develop when either too much or too little of a hormone is produced. ...
... Diseases of the Endocrine System If there are problems with one or more glands in the endocrine system, organs won’t function properly. Diseases of the endocrine system can develop when either too much or too little of a hormone is produced. ...
Drug List - Grand Saline ISD
... levothyroxine Dispensing Issues Warning! • Can be cardiotoxic; report any of the following: – Chest pain, increased pulse, palpitations, heat intolerance, excessive sweating ...
... levothyroxine Dispensing Issues Warning! • Can be cardiotoxic; report any of the following: – Chest pain, increased pulse, palpitations, heat intolerance, excessive sweating ...
AHS I
... 6. Which two pituitary hormones act on the ovaries and the testes? A. ACTH and TSH B. FSH and LH C. LH and ACTH 7. Which anterior pituitary lobe hormone is responsible for the development of breasts tissue and stimulates the production of milk after childbirth? A. Prolactin (PRL) B. Luteinizing hor ...
... 6. Which two pituitary hormones act on the ovaries and the testes? A. ACTH and TSH B. FSH and LH C. LH and ACTH 7. Which anterior pituitary lobe hormone is responsible for the development of breasts tissue and stimulates the production of milk after childbirth? A. Prolactin (PRL) B. Luteinizing hor ...
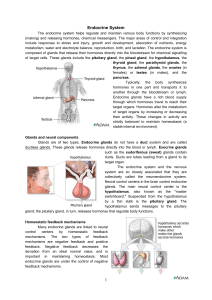
Endocrine System
... terminals until they are released into the blood vascular network surrounding the posterior pituitary gland. ADH acts upon the kidney tubules to help maintain a constant level of body water. This level is accomplished by increasing the water reabsorption amount when body water levels are low. Oxytoc ...
... terminals until they are released into the blood vascular network surrounding the posterior pituitary gland. ADH acts upon the kidney tubules to help maintain a constant level of body water. This level is accomplished by increasing the water reabsorption amount when body water levels are low. Oxytoc ...
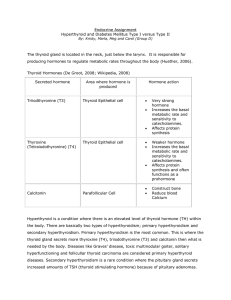
Thyroid hormones
... • Production of TSH by the pituitary is controlled by a stimulatory effect of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) of the hypothalamus by negative feedback from circulating free T3 & free T4. • Accordingly, the hypothalamus (via TRH), sets the level of thyroid hormones production required physiologic ...
... • Production of TSH by the pituitary is controlled by a stimulatory effect of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) of the hypothalamus by negative feedback from circulating free T3 & free T4. • Accordingly, the hypothalamus (via TRH), sets the level of thyroid hormones production required physiologic ...
Pituitary Agents. Thyroid and Antithyroid Agents. Antidiabe
... levothyroxine Dispensing Issues Warning! • Can be cardiotoxic; report any of the following: – Chest pain, increased pulse, palpitations, heat intolerance, excessive sweating ...
... levothyroxine Dispensing Issues Warning! • Can be cardiotoxic; report any of the following: – Chest pain, increased pulse, palpitations, heat intolerance, excessive sweating ...
General Surgery Rotation Expectations
... thyroid function. Describe the impact of aging on the thyroid hormone synthetic pathway and thyroid function. Outline appropriate thyroid function testing for the following clinical scenarios, including interpretation of predicted test results :Thyroid nodule, Goiter, Hyperthyroidism & ...
... thyroid function. Describe the impact of aging on the thyroid hormone synthetic pathway and thyroid function. Outline appropriate thyroid function testing for the following clinical scenarios, including interpretation of predicted test results :Thyroid nodule, Goiter, Hyperthyroidism & ...
the endocrine system
... Adrenal glands - influence the way your body uses energy, they also release a hormone called adrenaline when you are under stress Hypothalamus - part of your brain that controls hormone production by releasing different chemicals to the pituitary gland Ovaries - produce estrogen and progesterone in ...
... Adrenal glands - influence the way your body uses energy, they also release a hormone called adrenaline when you are under stress Hypothalamus - part of your brain that controls hormone production by releasing different chemicals to the pituitary gland Ovaries - produce estrogen and progesterone in ...
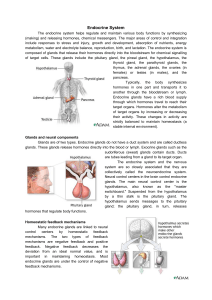
Endocrine System
... do not require continuous adjustment. In positive feedback mechanisms, the original stimulus is promoted rather than negated. Positive feedback increases the deviation from an ideal normal value. Unlike negative feedback that maintains hormone levels within narrow ranges, positive feedback is rarely ...
... do not require continuous adjustment. In positive feedback mechanisms, the original stimulus is promoted rather than negated. Positive feedback increases the deviation from an ideal normal value. Unlike negative feedback that maintains hormone levels within narrow ranges, positive feedback is rarely ...
PITUITARY GLAND: POSTERIOR LOBE
... 1. In puberty: stimulate axillary/pubic hair growth/growth spurt 2. Insignificant effect in males after puberty 3. In females: libido and converted into estrogens ...
... 1. In puberty: stimulate axillary/pubic hair growth/growth spurt 2. Insignificant effect in males after puberty 3. In females: libido and converted into estrogens ...
Endocrine Pathology
... It results from presence of autoantibodies to TSH receptors cause their activation and stimulate thyroid hormone secretion causing hyperthyroidism. These antibodies are called thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI: stimulate thyroxin -T4 synthesis). TGI lead to gland hyperplasia and ...
... It results from presence of autoantibodies to TSH receptors cause their activation and stimulate thyroid hormone secretion causing hyperthyroidism. These antibodies are called thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI: stimulate thyroxin -T4 synthesis). TGI lead to gland hyperplasia and ...
Document
... A blood chemistry profile, including electrolytes, provides information about your pet’s liver, kidneys, and pancreas as well as other functions of the body, such as blood sugar and hydration. A complete blood count (CBC) can identify infection, inflammation, and anemia. ...
... A blood chemistry profile, including electrolytes, provides information about your pet’s liver, kidneys, and pancreas as well as other functions of the body, such as blood sugar and hydration. A complete blood count (CBC) can identify infection, inflammation, and anemia. ...
The_endocrine_system
... Disorders of the Thyroid Hypothyroidism- not enough thyroxine or I-3 produced. Cretinism- infants and children, stunted growth, abnormal bone formation, retarded mental development, low body temperature. • If not corrected within the first month of birth permanent mental retardation will occur. Myx ...
... Disorders of the Thyroid Hypothyroidism- not enough thyroxine or I-3 produced. Cretinism- infants and children, stunted growth, abnormal bone formation, retarded mental development, low body temperature. • If not corrected within the first month of birth permanent mental retardation will occur. Myx ...
3 - Austin Community College
... Relates the increased frequency of autoantibodies and increased immune system deficiency to age. Mutation or loss of immune regulatory powers results in the condition in which ...
... Relates the increased frequency of autoantibodies and increased immune system deficiency to age. Mutation or loss of immune regulatory powers results in the condition in which ...
Parathyroidectomy - Meridian Surgery Center
... 1. Bleeding – this is a problem that could happen any time the skin is cut. A blood transfusion is rare. 2. Infection – we take special care to prevent an infection, but it is always a possibility. An infection may require prolonged hospitalization and treatment to resolve. 3. Reactions to medicatio ...
... 1. Bleeding – this is a problem that could happen any time the skin is cut. A blood transfusion is rare. 2. Infection – we take special care to prevent an infection, but it is always a possibility. An infection may require prolonged hospitalization and treatment to resolve. 3. Reactions to medicatio ...
Graves' disease

Graves' disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter and Flajani-Basedow-Graves disease, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in hyperthyroidism and an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, and weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye problems such as bulging, a condition known as Graves' ophthalmopathy. About 25% to 80% of people develop eye problems.The exact cause is unclear; however, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. A person is more likely to be affected if they have a family member with the disease. If one twin is affected there is a 30% chance the other twin will also have the disease. The onset of disease may be triggered by stress, infection, or giving birth. Those with other autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis are more likely to be affected. Smoking increases the risk of disease and may make the eye problems worse. The disorder results from an antibody, called thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI), that has a similar effect to thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). These antibodies cause the thyroid gland to produce excess thyroid hormone. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms with blood tests and radioiodine uptake used to confirm the disease. Typically blood tests show a raised T3 and T4, low TSH, increased radioiodine uptake in all areas of the thyroid, and TSI antibodies.There are three treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. Eye problems may require additional treatments.Graves' disease occurs in about 0.5% of people. It occurs about 7.5 times more often in women than men. Often it starts between the ages of forty and sixty. It is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism in the United States (about 50% to 80% of cases). The condition is named after Robert Graves who described it in 1835. A number of prior descriptions also exist.