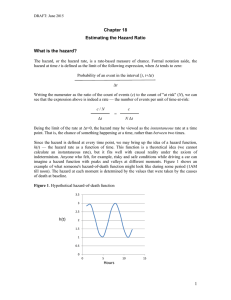
The Impact of Sample Reduction on PCA-based Feature Mykola Pechenizkiy Seppo Puuronen
... The essential drawback of all the methods that just assign weights to individual features is their insensitivity to interacting or correlated features. Also, in many cases some features are useful on one example set but useless or even misleading in another. That is why the transformation of the giv ...
... The essential drawback of all the methods that just assign weights to individual features is their insensitivity to interacting or correlated features. Also, in many cases some features are useful on one example set but useless or even misleading in another. That is why the transformation of the giv ...
Knowledge-Driven Business Intelligence Systems: Part II
... chromosome selection and formulate the problem effectively. Thus genetic algorithms should be considered at present more as an instrument for scientific research rather than as a tool for generic practical data analysis, for instance, in finance. ...
... chromosome selection and formulate the problem effectively. Thus genetic algorithms should be considered at present more as an instrument for scientific research rather than as a tool for generic practical data analysis, for instance, in finance. ...
Challenge
... Lesson Learned from Watson (1): scalable knowledge model building method “The Watson program is already a breakthrough technology in AI. For many years it had been largely assumed that for a computer to go beyond search and really be able to perform complex human language tasks it needed to do on ...
... Lesson Learned from Watson (1): scalable knowledge model building method “The Watson program is already a breakthrough technology in AI. For many years it had been largely assumed that for a computer to go beyond search and really be able to perform complex human language tasks it needed to do on ...
Modeling Linear Functions
... In a scatterplot, you can see patterns, trends, relationships, and even the occasional extraordinary value sitting apart from the others. • This figure shows a positive association between the year since 1900 and the % of people ...
... In a scatterplot, you can see patterns, trends, relationships, and even the occasional extraordinary value sitting apart from the others. • This figure shows a positive association between the year since 1900 and the % of people ...
Design and analysis of clinical correlative studies
... (approach) the number of malignant cells will be compared between CR vs. nonCR, and between those who are progression-free at 2 years vs. those who are not, using Wilcoxon rank-sum tests with one-sided Type I error of 10%. (sample) We expect that blood samples will be collected in approximately 9 ...
... (approach) the number of malignant cells will be compared between CR vs. nonCR, and between those who are progression-free at 2 years vs. those who are not, using Wilcoxon rank-sum tests with one-sided Type I error of 10%. (sample) We expect that blood samples will be collected in approximately 9 ...
Normal Distribution
... Teachers were told that certain children (chosen randomly) were expected to be intellectual “growth spurters,” based on the Harvard Test of Inflected Acquisition (a test that didn’t actually exist). These children were ...
... Teachers were told that certain children (chosen randomly) were expected to be intellectual “growth spurters,” based on the Harvard Test of Inflected Acquisition (a test that didn’t actually exist). These children were ...
pdf (paper) - Pascal Hitzler
... Usability of Linked Data is significantly hampered by the fact that it is still very raw data in the sense that it contains many mistakes and omissions, and cannot distinguish between different points of view [24]. In order to leverage logic-based methods mediated by ontology reasoning, data would b ...
... Usability of Linked Data is significantly hampered by the fact that it is still very raw data in the sense that it contains many mistakes and omissions, and cannot distinguish between different points of view [24]. In order to leverage logic-based methods mediated by ontology reasoning, data would b ...
Time series

A time series is a sequence of data points, typically consisting of successive measurements made over a time interval. Examples of time series are ocean tides, counts of sunspots, and the daily closing value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. Time series are very frequently plotted via line charts. Time series are used in statistics, signal processing, pattern recognition, econometrics, mathematical finance, weather forecasting, intelligent transport and trajectory forecasting, earthquake prediction, electroencephalography, control engineering, astronomy, communications engineering, and largely in any domain of applied science and engineering which involves temporal measurements.Time series analysis comprises methods for analyzing time series data in order to extract meaningful statistics and other characteristics of the data. Time series forecasting is the use of a model to predict future values based on previously observed values. While regression analysis is often employed in such a way as to test theories that the current values of one or more independent time series affect the current value of another time series, this type of analysis of time series is not called ""time series analysis"", which focuses on comparing values of a single time series or multiple dependent time series at different points in time.Time series data have a natural temporal ordering. This makes time series analysis distinct from cross-sectional studies, in which there is no natural ordering of the observations (e.g. explaining people's wages by reference to their respective education levels, where the individuals' data could be entered in any order). Time series analysis is also distinct from spatial data analysis where the observations typically relate to geographical locations (e.g. accounting for house prices by the location as well as the intrinsic characteristics of the houses). A stochastic model for a time series will generally reflect the fact that observations close together in time will be more closely related than observations further apart. In addition, time series models will often make use of the natural one-way ordering of time so that values for a given period will be expressed as deriving in some way from past values, rather than from future values (see time reversibility.)Time series analysis can be applied to real-valued, continuous data, discrete numeric data, or discrete symbolic data (i.e. sequences of characters, such as letters and words in the English language.).