Excel and Calculator
... We often want to know the variability of data. Please give me $1000, I will give you… 8% to 9% in a year. Small variability. -50% to 300% in a week. Large variability. Most people prefer certainty to variability. We won’t meet in this classroom next week, and I am not certain where we wi ...
... We often want to know the variability of data. Please give me $1000, I will give you… 8% to 9% in a year. Small variability. -50% to 300% in a week. Large variability. Most people prefer certainty to variability. We won’t meet in this classroom next week, and I am not certain where we wi ...
Lecture Chapter 14
... Central tendency is usually summarized with one of three statistics: the mode, the median, or the mean. For any particular application, one of these statistics may be preferable, but each has a role to play in data analysis. To choose an appropriate measure of central tendency, the analyst must cons ...
... Central tendency is usually summarized with one of three statistics: the mode, the median, or the mean. For any particular application, one of these statistics may be preferable, but each has a role to play in data analysis. To choose an appropriate measure of central tendency, the analyst must cons ...
3. Descriptive statistics
... What is the estimated regression equation? We’ll see later in course the formulas for finding the correlation and the “best fitting” regression equation (with possibly several explanatory variables), but for now, try using software such as SPSS to find the answers. ...
... What is the estimated regression equation? We’ll see later in course the formulas for finding the correlation and the “best fitting” regression equation (with possibly several explanatory variables), but for now, try using software such as SPSS to find the answers. ...
LIST OF QUESTIONS FOR AP EXAM IN STATISTICS Part 1
... 5. Which scales of measurement do you know? 6. What is nominal scale? 7. What is ordinal scale? 8. What is interval scale? 9. What is ratio scale? 10. What are conditions for scale to be ratio scale? 11. What is numerical and non-numerical data? 12. What is qualitative (categorical) data? 13. What i ...
... 5. Which scales of measurement do you know? 6. What is nominal scale? 7. What is ordinal scale? 8. What is interval scale? 9. What is ratio scale? 10. What are conditions for scale to be ratio scale? 11. What is numerical and non-numerical data? 12. What is qualitative (categorical) data? 13. What i ...
frequency distribution
... – Outliers: Values that lie outside the normal range of values, and that may or may not be legitimate – Wild codes: Impossible or invalid codes, like a code of “3” for the variable sex when valid codes are 1 (female) and 2 (male) ...
... – Outliers: Values that lie outside the normal range of values, and that may or may not be legitimate – Wild codes: Impossible or invalid codes, like a code of “3” for the variable sex when valid codes are 1 (female) and 2 (male) ...
Statistics Packet/Project Levels 1-4
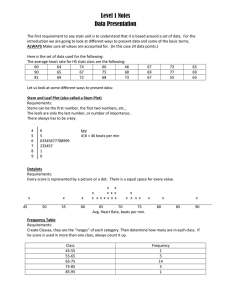
... ALWAYS Make sure all values are accounted for. (In this case 24 data points.) Here is the set of data used for the following: The average heart rate for HS stats class are the following: ...
... ALWAYS Make sure all values are accounted for. (In this case 24 data points.) Here is the set of data used for the following: The average heart rate for HS stats class are the following: ...
Lecture 15
... will be much larger than n, because the deviations of each bin from the shifted smooth curve are larger than i. Likewise, if we change the width, or the amplitude of the curve, either of these ...
... will be much larger than n, because the deviations of each bin from the shifted smooth curve are larger than i. Likewise, if we change the width, or the amplitude of the curve, either of these ...
Standard Deviation
... 正負 2 個標準差, 約可含概 95%的資料 For example, the average height for adult men in the United States is about 70 inches, with a standard deviation of around 3 inches. This means that most men (about 68%, assuming a normal distribution) have a height within 3 inches of the mean (67 inches – 73 inches), while al ...
... 正負 2 個標準差, 約可含概 95%的資料 For example, the average height for adult men in the United States is about 70 inches, with a standard deviation of around 3 inches. This means that most men (about 68%, assuming a normal distribution) have a height within 3 inches of the mean (67 inches – 73 inches), while al ...
Time series

A time series is a sequence of data points, typically consisting of successive measurements made over a time interval. Examples of time series are ocean tides, counts of sunspots, and the daily closing value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. Time series are very frequently plotted via line charts. Time series are used in statistics, signal processing, pattern recognition, econometrics, mathematical finance, weather forecasting, intelligent transport and trajectory forecasting, earthquake prediction, electroencephalography, control engineering, astronomy, communications engineering, and largely in any domain of applied science and engineering which involves temporal measurements.Time series analysis comprises methods for analyzing time series data in order to extract meaningful statistics and other characteristics of the data. Time series forecasting is the use of a model to predict future values based on previously observed values. While regression analysis is often employed in such a way as to test theories that the current values of one or more independent time series affect the current value of another time series, this type of analysis of time series is not called ""time series analysis"", which focuses on comparing values of a single time series or multiple dependent time series at different points in time.Time series data have a natural temporal ordering. This makes time series analysis distinct from cross-sectional studies, in which there is no natural ordering of the observations (e.g. explaining people's wages by reference to their respective education levels, where the individuals' data could be entered in any order). Time series analysis is also distinct from spatial data analysis where the observations typically relate to geographical locations (e.g. accounting for house prices by the location as well as the intrinsic characteristics of the houses). A stochastic model for a time series will generally reflect the fact that observations close together in time will be more closely related than observations further apart. In addition, time series models will often make use of the natural one-way ordering of time so that values for a given period will be expressed as deriving in some way from past values, rather than from future values (see time reversibility.)Time series analysis can be applied to real-valued, continuous data, discrete numeric data, or discrete symbolic data (i.e. sequences of characters, such as letters and words in the English language.).