Mirror Neuron System in Monkey: A Computational Modeling
... Mirror neurons within a monkey's premotor area F5 fire not only when the monkey performs a certain class of actions but also when the monkey observes another monkey (or the experimenter) perform a similar action. It has thus been argued that these neurons are crucial for understanding of actions by ...
... Mirror neurons within a monkey's premotor area F5 fire not only when the monkey performs a certain class of actions but also when the monkey observes another monkey (or the experimenter) perform a similar action. It has thus been argued that these neurons are crucial for understanding of actions by ...
Gerenciamento Autônomo de Redes na Internet do
... network controlling mechanisms. Deploying such autonomous and rational entities in the network can improve its behavior in the presence of very dynamic and complex control scenarios. Unfortunately, building agent-based mechanisms for networks is not an easy task. The main difficulty is to create con ...
... network controlling mechanisms. Deploying such autonomous and rational entities in the network can improve its behavior in the presence of very dynamic and complex control scenarios. Unfortunately, building agent-based mechanisms for networks is not an easy task. The main difficulty is to create con ...
(Statistical) Relational Learning
... How to deal with millions of interrelated research papers ? How to accumulate general knowledge automatically from the Web ? How to deal with billions of shared users’ perceptions stored at massive scale ? How to realize the vision of social search? Kristian Kersting (Statistical) Relational Learnin ...
... How to deal with millions of interrelated research papers ? How to accumulate general knowledge automatically from the Web ? How to deal with billions of shared users’ perceptions stored at massive scale ? How to realize the vision of social search? Kristian Kersting (Statistical) Relational Learnin ...
Package `FCNN4R`
... mlp_gradij computes gradients of network outputs, i.e the derivatives of outputs w.r.t. active weights, at given data row. The derivatives of outputs are placed in subsequent columns of the returned matrix. Scaled by the output errors and averaged they give the same as gradi(input, output, i). This ...
... mlp_gradij computes gradients of network outputs, i.e the derivatives of outputs w.r.t. active weights, at given data row. The derivatives of outputs are placed in subsequent columns of the returned matrix. Scaled by the output errors and averaged they give the same as gradi(input, output, i). This ...
A computational model of action selection in the basal ganglia. I. A
... the resolution of con¯icts between functional units that are physically separated within the brain but are in competition for behavioural expression. Stated informally, it is the problem of how we decide `what to do next'. This situation is particularly acute if several such units are competing for ...
... the resolution of con¯icts between functional units that are physically separated within the brain but are in competition for behavioural expression. Stated informally, it is the problem of how we decide `what to do next'. This situation is particularly acute if several such units are competing for ...
Neural Preprocessing and Control of Reactive Walking
... Research in the domain of biologically inspired walking machines has focused for the most part on the mechanical designs and locomotion control. Although some of this research has been concentrated on the generation of a reactive behavior of walking machines, it has been restricted only to a few of ...
... Research in the domain of biologically inspired walking machines has focused for the most part on the mechanical designs and locomotion control. Although some of this research has been concentrated on the generation of a reactive behavior of walking machines, it has been restricted only to a few of ...
Neurally Plausible Model of Robot Reaching Inspired by Infant
... A two-layer neural network is in the core of the GHA algorithm. In this example, the output layer that captures the principal components can have up to 4 nodes. The output nodes with dashed line could be the two least significant components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... A two-layer neural network is in the core of the GHA algorithm. In this example, the output layer that captures the principal components can have up to 4 nodes. The output nodes with dashed line could be the two least significant components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Laminar Selectivity of the Cholinergic Suppression of Synaptic
... CA1 by input from the entorhinal cortex. The recall ofthese associations could be tested by inducing activity in region CA3 alone and evaluating how closely the activity spreading into region CA1 resembled the activity previously provided by input from the entorhinal cortex. Most previous models of ...
... CA1 by input from the entorhinal cortex. The recall ofthese associations could be tested by inducing activity in region CA3 alone and evaluating how closely the activity spreading into region CA1 resembled the activity previously provided by input from the entorhinal cortex. Most previous models of ...
Techniques to solve AI problems
... bestnode is a goal node. If so, exist and report a solution (either bestnode if all we want is the node or the path that has been created between the initial state and bestnode if we are interested in the path.) Otherwise, generate the successors of bestnode but do not set bestnode to point to them ...
... bestnode is a goal node. If so, exist and report a solution (either bestnode if all we want is the node or the path that has been created between the initial state and bestnode if we are interested in the path.) Otherwise, generate the successors of bestnode but do not set bestnode to point to them ...
Cognon Neural Model Software Verification and
... Little is known yet about how the brain can recognize arbitrary sensory patterns within milliseconds using neural spikes to communicate information between neurons. In a typical brain there are several layers of neurons, with each neuron axon connecting to ∼ 104 synapses of neurons in an adjacent la ...
... Little is known yet about how the brain can recognize arbitrary sensory patterns within milliseconds using neural spikes to communicate information between neurons. In a typical brain there are several layers of neurons, with each neuron axon connecting to ∼ 104 synapses of neurons in an adjacent la ...
Aalborg Universitet Learning dynamic Bayesian networks with mixed variables Bøttcher, Susanne Gammelgaard
... is conditional Gaussian (CG) and show how to learn the parameters and structure of the DBN when data is complete. Further we present an automated method for specifying prior parameter distributions for the parameters in a DBN. These methods are simple extensions of the ones used for ordinary Bayesia ...
... is conditional Gaussian (CG) and show how to learn the parameters and structure of the DBN when data is complete. Further we present an automated method for specifying prior parameter distributions for the parameters in a DBN. These methods are simple extensions of the ones used for ordinary Bayesia ...
Organization of Cortical and Thalamic Input to Pyramidal Neurons in
... Stereotactic injections. Animal protocols were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees at Janelia Farm Research Campus and Northwestern University. Experimental procedures were similar to previous studies (Petreanu et al., 2009; Mao et al., 2011). C57BL/6 mice of either sex (Charles ...
... Stereotactic injections. Animal protocols were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees at Janelia Farm Research Campus and Northwestern University. Experimental procedures were similar to previous studies (Petreanu et al., 2009; Mao et al., 2011). C57BL/6 mice of either sex (Charles ...
Mechanisms of excitability in the central and peripheral nervous
... The work in this thesis concerns mechanisms of excitability of neurons. Specifically, it deals with how neurons respond to input, and how their response is controlled by ion channels and other active components of the neuron. I have studied excitability in two systems of the nervous system, the hipp ...
... The work in this thesis concerns mechanisms of excitability of neurons. Specifically, it deals with how neurons respond to input, and how their response is controlled by ion channels and other active components of the neuron. I have studied excitability in two systems of the nervous system, the hipp ...
6 Learning in Multiagent Systems
... an extended view of ML that captures not only single-agent learning but also multiagent learning can lead to an improved understanding of the general principles underlying learning in both computational and natural systems. The first reason is grounded in the insight that multiagent systems typicall ...
... an extended view of ML that captures not only single-agent learning but also multiagent learning can lead to an improved understanding of the general principles underlying learning in both computational and natural systems. The first reason is grounded in the insight that multiagent systems typicall ...
6 Learning in Multiagent Systems
... an extended view of ML that captures not only single-agent learning but also multiagent learning can lead to an improved understanding of the general principles underlying learning in both computational and natural systems. The first reason is grounded in the insight that multiagent systems typicall ...
... an extended view of ML that captures not only single-agent learning but also multiagent learning can lead to an improved understanding of the general principles underlying learning in both computational and natural systems. The first reason is grounded in the insight that multiagent systems typicall ...
An efficient approach for finding the MPE in belief networks
... some algorithms directly evaluating belief networks [1]. An improvement is to translate the minimal-cost proof problems into 0-1 programming problems, and solve them by using simplex combined with branch and bound techniques (24, 25, 1]. Although the new tech nique outperformed the best-first sear ...
... some algorithms directly evaluating belief networks [1]. An improvement is to translate the minimal-cost proof problems into 0-1 programming problems, and solve them by using simplex combined with branch and bound techniques (24, 25, 1]. Although the new tech nique outperformed the best-first sear ...
2015 Cosyne Program
... and theoretical/computational approaches to problems in systems neuroscience. To encourage interdisciplinary interactions, the main meeting is arranged in a single track. A set of invited talks are selected by the Executive Committee and Organizing Committee, and additional talks and posters are sel ...
... and theoretical/computational approaches to problems in systems neuroscience. To encourage interdisciplinary interactions, the main meeting is arranged in a single track. A set of invited talks are selected by the Executive Committee and Organizing Committee, and additional talks and posters are sel ...
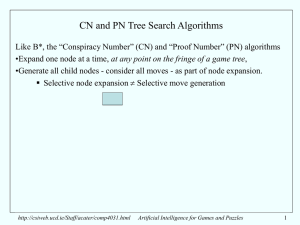
ppt
... • needs no conspiracy to achieve its current value V0, (which must be the current value of at least one of the children) • can achieve any greater value that any of its child nodes may achieve only when all its child nodes have achieved at least that value • its ascending bounds sequence {V0, V1 … V ...
... • needs no conspiracy to achieve its current value V0, (which must be the current value of at least one of the children) • can achieve any greater value that any of its child nodes may achieve only when all its child nodes have achieved at least that value • its ascending bounds sequence {V0, V1 … V ...
Catastrophic interference
Catastrophic Interference, also known as catastrophic forgetting, is the tendency of a artificial neural network to completely and abruptly forget previously learned information upon learning new information. Neural networks are an important part of the network approach and connectionist approach to cognitive science. These networks use computer simulations to try and model human behaviours, such as memory and learning. Catastrophic interference is an important issue to consider when creating connectionist models of memory. It was originally brought to the attention of the scientific community by research from McCloskey and Cohen (1989), and Ractcliff (1990). It is a radical manifestation of the ‘sensitivity-stability’ dilemma or the ‘stability-plasticity’ dilemma. Specifically, these problems refer to the issue of being able to make an artificial neural network that is sensitive to, but not disrupted by, new information. Lookup tables and connectionist networks lie on the opposite sides of the stability plasticity spectrum. The former remains completely stable in the presence of new information but lacks the ability to generalize, i.e. infer general principles, from new inputs. On the other hand, connectionst networks like the standard backpropagation network are very sensitive to new information and can generalize on new inputs. Backpropagation models can be considered good models of human memory insofar as they mirror the human ability to generalize but these networks often exhibit less stability than human memory. Notably, these backpropagation networks are susceptible to catastrophic interference. This is considered an issue when attempting to model human memory because, unlike these networks, humans typically do not show catastrophic forgetting. Thus, the issue of catastrophic interference must be eradicated from these backpropagation models in order to enhance the plausibility as models of human memory.