Alg2-Ch3-Sect1_2-Power_Point_Lesson
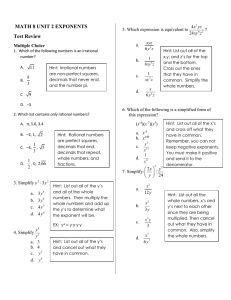
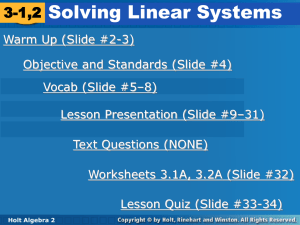
... Example 1A: Solving Linear Systems by Substitution Use variable substitution to solve the system: y= x–1 x+y=7 Step 1: Substitute the equivalent expression for “y” from the first equation in place of “y” in the second equation and solve for “x”. x+y=7 x + (x – 1) = 7 2x – 1 = 7 2x = 8 x=4 ...
... Example 1A: Solving Linear Systems by Substitution Use variable substitution to solve the system: y= x–1 x+y=7 Step 1: Substitute the equivalent expression for “y” from the first equation in place of “y” in the second equation and solve for “x”. x+y=7 x + (x – 1) = 7 2x – 1 = 7 2x = 8 x=4 ...
Operators and Expressions
... odd or even. Write a boolean expression that checks for given integer if it can be divided (without remainder) by 7 and 5 in the same time. Write an expression that calculates rectangle’s area by given width and height. Write an expression that checks for given integer if its third digit (right-to-l ...
... odd or even. Write a boolean expression that checks for given integer if it can be divided (without remainder) by 7 and 5 in the same time. Write an expression that calculates rectangle’s area by given width and height. Write an expression that checks for given integer if its third digit (right-to-l ...
Representation Theory.
... algebra of quaternions H. All these cases occur. E XAMPLE 1.4.3. The trivial representation G → GL1 (R) is irreducible for any G, and EndG = R. E XAMPLE 1.4.4. Let Cn be a cyclic group with n elements (n ≥ 3) and consider its representation in R2 as the group of rotations of a regular n-gon. No line ...
... algebra of quaternions H. All these cases occur. E XAMPLE 1.4.3. The trivial representation G → GL1 (R) is irreducible for any G, and EndG = R. E XAMPLE 1.4.4. Let Cn be a cyclic group with n elements (n ≥ 3) and consider its representation in R2 as the group of rotations of a regular n-gon. No line ...
Linear Algebra - Willmar Public Schools
... a car wash. Without the car wash, gas costs $2.79 per gallon. The car wash is $8.95. What are the possible amounts (in gallons) of gasoline that you can buy if you also get a car wash and can spend at most ...
... a car wash. Without the car wash, gas costs $2.79 per gallon. The car wash is $8.95. What are the possible amounts (in gallons) of gasoline that you can buy if you also get a car wash and can spend at most ...
Document
... Conclusion: A harmonic oscillator driven by a classical force from the ground state is always in a coherent state. We have seen that the coherent state follows basically the equations for the classical eqns for position and momentum. It could be taken as a reproduction of the classical dynamics fro ...
... Conclusion: A harmonic oscillator driven by a classical force from the ground state is always in a coherent state. We have seen that the coherent state follows basically the equations for the classical eqns for position and momentum. It could be taken as a reproduction of the classical dynamics fro ...
quantum states satisfying classical probability constraints
... present examples of such bipartite states. We prove (proposition 2) that the nonseparable Werner state (5 ) is a DSO state for any dimension d ≥ 2 and represents a Bell class state if d ≥ 3. In sections 2.2, 2.3, for an arbitrary bipartite state, we derive (propositions 3, 4) new upper bounds of lin ...
... present examples of such bipartite states. We prove (proposition 2) that the nonseparable Werner state (5 ) is a DSO state for any dimension d ≥ 2 and represents a Bell class state if d ≥ 3. In sections 2.2, 2.3, for an arbitrary bipartite state, we derive (propositions 3, 4) new upper bounds of lin ...
For ULSI workshop. OUR SLIDES not ready. In PPT format.
... • We know, however, from the symbolic output what binary vector values can occur and with what probabilities on the output. • So all possible measurement vectors can be known in advance with their probabilities. • If these values can collapse to the correct output vector (of a non-faulty circuit) th ...
... • We know, however, from the symbolic output what binary vector values can occur and with what probabilities on the output. • So all possible measurement vectors can be known in advance with their probabilities. • If these values can collapse to the correct output vector (of a non-faulty circuit) th ...