GAC 2.0 ANALOG GALVANOMETER CONTROLLER OPERATOR`S
... architecture of the GAC 2.0 requires that a bipolar (±DC Voltage) be supplied to it and is connected to directly to the output amplifier. The GAC 2.0 has onboard regulators to make all other necessary voltages. A mating connector is typically provided. The mating five-circuit plug is an AMP 6400456- ...
... architecture of the GAC 2.0 requires that a bipolar (±DC Voltage) be supplied to it and is connected to directly to the output amplifier. The GAC 2.0 has onboard regulators to make all other necessary voltages. A mating connector is typically provided. The mating five-circuit plug is an AMP 6400456- ...
Resistance in series and parallel
... 4. Now returning to the circuit, move the ammeter to the position between the first and second resistor, close the switch, and record the current. To move the ammeter, it is usually best to completely disconnect it from the circuit, and then put a wire in the place where the ammeter was previously l ...
... 4. Now returning to the circuit, move the ammeter to the position between the first and second resistor, close the switch, and record the current. To move the ammeter, it is usually best to completely disconnect it from the circuit, and then put a wire in the place where the ammeter was previously l ...
Hand-Drawn Circuit Diagrams for all circuits that are to
... Background: Before doing this experiment, students should be able to Measure inductance using a commercial impedance bridge. Do a transient (time dependent) simulation of RC, RL and RLC circuits using Capture/PSpice Do an AC sweep (frequency dependent) simulation of RC, RL and RLC circuits usi ...
... Background: Before doing this experiment, students should be able to Measure inductance using a commercial impedance bridge. Do a transient (time dependent) simulation of RC, RL and RLC circuits using Capture/PSpice Do an AC sweep (frequency dependent) simulation of RC, RL and RLC circuits usi ...
presentation
... Measuring Resistance • When the VOM is used to measure resistance, what actually is measured is a small current applied to the component. • There are 5 ranges. An out of resistance reading will be indicated by a single “1” digit. Remember k means multiply the reading by 1000. • Operating voltages s ...
... Measuring Resistance • When the VOM is used to measure resistance, what actually is measured is a small current applied to the component. • There are 5 ranges. An out of resistance reading will be indicated by a single “1” digit. Remember k means multiply the reading by 1000. • Operating voltages s ...
Packet 13: Electric Circuits
... By the time we finish the labs and related materials in this unit, you should be able to: 1. Define electric potential difference (voltage), electric current, and electrical resistance and the relationship between them. 2. Differentiate between AC and DC and describe how electrons move in a DC and i ...
... By the time we finish the labs and related materials in this unit, you should be able to: 1. Define electric potential difference (voltage), electric current, and electrical resistance and the relationship between them. 2. Differentiate between AC and DC and describe how electrons move in a DC and i ...
Physics 3204: Current Electricity Notes
... (ii) What is the voltage across resistor 2? • Find total current using ohm's law • Use series rule to determine current through 1 • Use ohm's law to determine voltage across 1 • Use parallel rule to determine voltage across 2 (iii) Will the fuse blow? • Fuses blow when max current is reached • Since ...
... (ii) What is the voltage across resistor 2? • Find total current using ohm's law • Use series rule to determine current through 1 • Use ohm's law to determine voltage across 1 • Use parallel rule to determine voltage across 2 (iii) Will the fuse blow? • Fuses blow when max current is reached • Since ...
Catalog Number 22-204A 50,000 OHMS/VOLT MULTITESTER with
... (V-A/2 —V-2-A) effectively doubles the number of AC and DC scales available. This means you can obtain meter readings in the upper half of the scale, resulting in consistent accuracy. An "OFF" position is provided to insure meter protection during transit. The sensitive 15 µA meter movement with 41/ ...
... (V-A/2 —V-2-A) effectively doubles the number of AC and DC scales available. This means you can obtain meter readings in the upper half of the scale, resulting in consistent accuracy. An "OFF" position is provided to insure meter protection during transit. The sensitive 15 µA meter movement with 41/ ...
Lab1: DC Resistive Measurements
... To use the DMM as a voltmeter to measure voltage, insert a red wire in the jack labeled V and a black wire in the jack labeled COM. Set the meter knob to the voltage setting. Voltmeters have very high resistance that typically exceeds 1 MΩ, so when making voltage measurements, be sure the voltmeter ...
... To use the DMM as a voltmeter to measure voltage, insert a red wire in the jack labeled V and a black wire in the jack labeled COM. Set the meter knob to the voltage setting. Voltmeters have very high resistance that typically exceeds 1 MΩ, so when making voltage measurements, be sure the voltmeter ...
Demagnetisation of CT cores under exposure of operating currents
... was significantly reduced from the value established through the magnetisation. This was a first finding, but further measurements with longer exposure time of the nominal current showed the same result, the residual magnetism did not drop further. Consequently, the exposure time was reduced until a ...
... was significantly reduced from the value established through the magnetisation. This was a first finding, but further measurements with longer exposure time of the nominal current showed the same result, the residual magnetism did not drop further. Consequently, the exposure time was reduced until a ...
current electrycity type 1
... Q.17 A part of a circuit is shown in figure. Here reading of ammeter is 5 ampere and voltmeter is 96V & voltmeter resistance is 480 ohm. Then find the resistance R Q.18 An accumulator of emf 2 Volt and negligible internal resistance is connected across a uniform wire of length 10m and resistance 30 ...
... Q.17 A part of a circuit is shown in figure. Here reading of ammeter is 5 ampere and voltmeter is 96V & voltmeter resistance is 480 ohm. Then find the resistance R Q.18 An accumulator of emf 2 Volt and negligible internal resistance is connected across a uniform wire of length 10m and resistance 30 ...
Directcurrent Circuits
... 6) A hot lightbulb has a much higher resistance 7) A light bulb usually fails just when switched on because the resistance is small and the current high, and thus the power delivered high (P=I2R) In the demos shown in this lecture, all lightbulbs have the same resistance if at the same temperatur ...
... 6) A hot lightbulb has a much higher resistance 7) A light bulb usually fails just when switched on because the resistance is small and the current high, and thus the power delivered high (P=I2R) In the demos shown in this lecture, all lightbulbs have the same resistance if at the same temperatur ...
Code - Dr. Jaafar Jantan
... Magnetic field lines of permanent magnets Magnetic force that a magnetic field exerts on a moving charges Motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field Motion of charges in magnetic & electric fields Mass spectrometer & velocity selectors Force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field ...
... Magnetic field lines of permanent magnets Magnetic force that a magnetic field exerts on a moving charges Motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field Motion of charges in magnetic & electric fields Mass spectrometer & velocity selectors Force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field ...
Most Often Asked Questions About Current and Voltage Transformers
... With 50A flowing in the primary conductor, the CT secondary reading is 5A. Five amperes into the meter gives full-scale deflection. Thus, the meter reading is correct. ...
... With 50A flowing in the primary conductor, the CT secondary reading is 5A. Five amperes into the meter gives full-scale deflection. Thus, the meter reading is correct. ...
x0001 - My School Portfolio
... F: Attitudes in Science Research: You have experimented with magnets in class, but scientist sometime need to use very powerful magnets. But a powerful magnet has a problem, how can the magnet be turned off and on? In 1820, a Danish physicist Hans Christian Oersted, discovered that there was a relat ...
... F: Attitudes in Science Research: You have experimented with magnets in class, but scientist sometime need to use very powerful magnets. But a powerful magnet has a problem, how can the magnet be turned off and on? In 1820, a Danish physicist Hans Christian Oersted, discovered that there was a relat ...
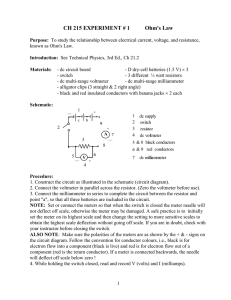
CH 215 EXPERIMENT # 1 Ohm`s Law
... 1. Construct the circuit as illustrated in the schematic (circuit diagram). 2. Connect the voltmeter in parallel across the resistor. (Zero the voltmeter before use). 3. Connect the milliammeter in series to complete the circuit between the resistor and point "a", so that all three batteries are inc ...
... 1. Construct the circuit as illustrated in the schematic (circuit diagram). 2. Connect the voltmeter in parallel across the resistor. (Zero the voltmeter before use). 3. Connect the milliammeter in series to complete the circuit between the resistor and point "a", so that all three batteries are inc ...
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current through its coil in a magnetic field.Galvanometers were the first instruments used to detect and measure electric currents. Sensitive galvanometers were used to detect signals from long submarine cables, and to discover the electrical activity of the heart and brain. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals. Initially a laboratory instrument relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electrotechnology. A type of galvanometer that records measurements permanently is the chart recorder. The term has expanded to include use of the same mechanism in recording, positioning, and servomechanism equipment.