magnetism - University of South Alabama
... Magnetic Force: y Can either attract or repel y Two kinds of poles: N = north(seeking); S = south(seeking) y All magnets are DIPOLES: always have both poles y POLES: Likes repel, opposites attract y Magnetic (force)field: y Direction to which a small magnetic dipole would align y Traced out by iron ...
... Magnetic Force: y Can either attract or repel y Two kinds of poles: N = north(seeking); S = south(seeking) y All magnets are DIPOLES: always have both poles y POLES: Likes repel, opposites attract y Magnetic (force)field: y Direction to which a small magnetic dipole would align y Traced out by iron ...
Exam 2 Solutions
... the resulting magnetic field 190 m from the bolt in μT? Suppose that the bolt extends far above and below the point of observation. ...
... the resulting magnetic field 190 m from the bolt in μT? Suppose that the bolt extends far above and below the point of observation. ...
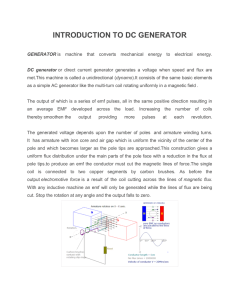
INTRODUCTION TO DC GENERATOR
... It has armature with iron core and air gap which is uniform the vicinity of the center of the pole and which becomes larger as the pole tips are approached.This construction gives a uniform flux distribution under the main parts of the pole face with a reduction in the flux at pole tips.to produce a ...
... It has armature with iron core and air gap which is uniform the vicinity of the center of the pole and which becomes larger as the pole tips are approached.This construction gives a uniform flux distribution under the main parts of the pole face with a reduction in the flux at pole tips.to produce a ...
Electromagnetism Article
... the sound coming out of its speakers. And when someone rings your doorbell, a tiny electromagnet pulls a metal clapper against a bell. Mechanically, an electromagnet is pretty simple. It consists of a conductive wire, usually copper, wrapped around a piece of metal. A current is introduced, eithe ...
... the sound coming out of its speakers. And when someone rings your doorbell, a tiny electromagnet pulls a metal clapper against a bell. Mechanically, an electromagnet is pretty simple. It consists of a conductive wire, usually copper, wrapped around a piece of metal. A current is introduced, eithe ...
Chapter 32
... The plasma in a tokamak is heated in part by the current driven by the induced electric field. The magnetic field B in the center of a tokamak is provided by coils (not shown in picture). This field is confined to a circular area of radius 50 cm. (a) If the magnetic field changes at the rate of 5100 ...
... The plasma in a tokamak is heated in part by the current driven by the induced electric field. The magnetic field B in the center of a tokamak is provided by coils (not shown in picture). This field is confined to a circular area of radius 50 cm. (a) If the magnetic field changes at the rate of 5100 ...
Name_________________________________
... 12. If the gases of a space ship press down and the space ship flies up, which of Newton’s Laws best describes this scenario? _________________________________________________________________ 13. When electrons flow through a wire it is known as a(n) a. electric current b. magnetic field c. electric ...
... 12. If the gases of a space ship press down and the space ship flies up, which of Newton’s Laws best describes this scenario? _________________________________________________________________ 13. When electrons flow through a wire it is known as a(n) a. electric current b. magnetic field c. electric ...
Section Summary - Login for National High School Learn Center
... Whenever there is electricity, there is magnetism. An electric current produces a magnetic field. This relationship between electricity and magnetism is called electromagnetism. You cannot see electromagnetism, but you can observe its effects. When a wire has a current, the needle of a compass align ...
... Whenever there is electricity, there is magnetism. An electric current produces a magnetic field. This relationship between electricity and magnetism is called electromagnetism. You cannot see electromagnetism, but you can observe its effects. When a wire has a current, the needle of a compass align ...
Two ways of looking at a transformer
... magnet (small motors) or by a current-carrying coil as above. The rotating assembly (known as the Armature) is supplied with current via the Commutator and the Brushes which make a sliding contact with the commutator. The purpose of the commutator is to reverse the armature current every half-revolu ...
... magnet (small motors) or by a current-carrying coil as above. The rotating assembly (known as the Armature) is supplied with current via the Commutator and the Brushes which make a sliding contact with the commutator. The purpose of the commutator is to reverse the armature current every half-revolu ...
Magnetic exam, sample
... The cross sectional dimensions of the iron circuit is 40mm x 50mm, of which 10 percent is taken up by insulation between the laminations. The magnetic circuit has a mean length of 0.6m and an air gap of 2mm with an effective area the same as the iron core. μr= 2000. If a coil is wound with 800 turns ...
... The cross sectional dimensions of the iron circuit is 40mm x 50mm, of which 10 percent is taken up by insulation between the laminations. The magnetic circuit has a mean length of 0.6m and an air gap of 2mm with an effective area the same as the iron core. μr= 2000. If a coil is wound with 800 turns ...
Section-A - CBSE PORTAL
... 5. Derive an expression for the magnetic field on the axis of the current carrying coil. 6. State and prove prism formula. 7. Draw the well labeled diagram of the astronomical telescope at the least distance of distinct vision. 8. Draw the well labeled diagram of the davisson and germer experiment w ...
... 5. Derive an expression for the magnetic field on the axis of the current carrying coil. 6. State and prove prism formula. 7. Draw the well labeled diagram of the astronomical telescope at the least distance of distinct vision. 8. Draw the well labeled diagram of the davisson and germer experiment w ...
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current through its coil in a magnetic field.Galvanometers were the first instruments used to detect and measure electric currents. Sensitive galvanometers were used to detect signals from long submarine cables, and to discover the electrical activity of the heart and brain. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals. Initially a laboratory instrument relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electrotechnology. A type of galvanometer that records measurements permanently is the chart recorder. The term has expanded to include use of the same mechanism in recording, positioning, and servomechanism equipment.