eecs.tufts.edu - Tufts University
... PCB will not require any input signals, for everything will be housed on-board. The only human interaction required will be to physically put the sample on the sensor structures (coil or capacitive). The user will also have to indicate which test to run (dielectric or magnetic) and start the actual ...
... PCB will not require any input signals, for everything will be housed on-board. The only human interaction required will be to physically put the sample on the sensor structures (coil or capacitive). The user will also have to indicate which test to run (dielectric or magnetic) and start the actual ...
Fundamental nuclear symmetries meet classical electrodynamic
... Permanent magnets (magnetization), not electric currents No magnetic (point) charge (monopole) –> dipole effect (N,S poles) 1-d currents instead of 0-d charges –> can’t split a wire! Static electricity produced in the lab long before steady currents ...
... Permanent magnets (magnetization), not electric currents No magnetic (point) charge (monopole) –> dipole effect (N,S poles) 1-d currents instead of 0-d charges –> can’t split a wire! Static electricity produced in the lab long before steady currents ...
Code Spec`s DL 2160 BASIC ELECTRICITY KIT – didactic
... The kit is composed of a set of components and devices that allow a practical demonstration of the most important laws of electricity and electromagnetism. All the components are mounted on metal or plastic bases complete with 4 mm. terminals for an easy connection of the test circuits through multi ...
... The kit is composed of a set of components and devices that allow a practical demonstration of the most important laws of electricity and electromagnetism. All the components are mounted on metal or plastic bases complete with 4 mm. terminals for an easy connection of the test circuits through multi ...
FRS 104 Electrical System
... (1)The engine crankshaft spins the alternator’s rotor (magnets) (2)As the rotor (magnets) spins and passes by the stator’s spokes of coiled copper wire, voltage is produced (via magnetic induction) (3)Meanwhile in the distributor, an engine gear drives the distributor shaft, which in turn spins the ...
... (1)The engine crankshaft spins the alternator’s rotor (magnets) (2)As the rotor (magnets) spins and passes by the stator’s spokes of coiled copper wire, voltage is produced (via magnetic induction) (3)Meanwhile in the distributor, an engine gear drives the distributor shaft, which in turn spins the ...
Experiment 4
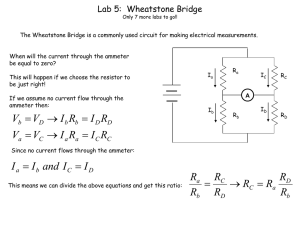
... Bridge circuits are designed to allow the determination of the value of an unknown circuit element such as a resistor, capacitor, or an inductor. The circuit diagram for a typical bridge is shown in Figure 1. The bridge elements are connected between junctions AC, BC, AD, and BD. V represents either ...
... Bridge circuits are designed to allow the determination of the value of an unknown circuit element such as a resistor, capacitor, or an inductor. The circuit diagram for a typical bridge is shown in Figure 1. The bridge elements are connected between junctions AC, BC, AD, and BD. V represents either ...
Answer the following questions :-
... 1- The effective shunt resistance for each range ( RSHE ). 2- The effective meter resistance. ( RME ). 3- The input resistance ( RIN ). 4- Accuracy of the meter on the scales, if the RTH for the circuit under measurements is 40 K Ω. ( RTH = 40 K Ω ) 5- Error for each range. ...
... 1- The effective shunt resistance for each range ( RSHE ). 2- The effective meter resistance. ( RME ). 3- The input resistance ( RIN ). 4- Accuracy of the meter on the scales, if the RTH for the circuit under measurements is 40 K Ω. ( RTH = 40 K Ω ) 5- Error for each range. ...
Chapter 16
... When you ___ a magnet in half, you end up with __ magnets. Name four kinds of magnets: Some magnets, called __________________________, are made of iron, nickel, cobalt, or mixtures of those metals. Another kind of magnet is the ________________________. This is a magnet made by an electric cu ...
... When you ___ a magnet in half, you end up with __ magnets. Name four kinds of magnets: Some magnets, called __________________________, are made of iron, nickel, cobalt, or mixtures of those metals. Another kind of magnet is the ________________________. This is a magnet made by an electric cu ...
29-008-exam3
... A complete circuit is one where current can flow all the way around. Note that the schematic drawing doesn’t look much like the physical circuit! ...
... A complete circuit is one where current can flow all the way around. Note that the schematic drawing doesn’t look much like the physical circuit! ...
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current through its coil in a magnetic field.Galvanometers were the first instruments used to detect and measure electric currents. Sensitive galvanometers were used to detect signals from long submarine cables, and to discover the electrical activity of the heart and brain. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals. Initially a laboratory instrument relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electrotechnology. A type of galvanometer that records measurements permanently is the chart recorder. The term has expanded to include use of the same mechanism in recording, positioning, and servomechanism equipment.