DCAC_Circuits-Voltmeter_Design_Testing-Student_Guide
... the most common type of analog measuring instrument. Historical Note: The Deprez-d'Arsonvol galvanometer was introduced by JaquesArsène d'Arsonvol and Marcel Deprez. Referred to as the mobile circuit galvanometer, this invention was a new galvanometer developed in 1880. Instead of a magnetized needl ...
... the most common type of analog measuring instrument. Historical Note: The Deprez-d'Arsonvol galvanometer was introduced by JaquesArsène d'Arsonvol and Marcel Deprez. Referred to as the mobile circuit galvanometer, this invention was a new galvanometer developed in 1880. Instead of a magnetized needl ...
Slide 1
... opposing fields to cancel their effects, these electrons have an orbital magnetic moment. Iron and other ferromagnetic materials are crystalline. As they cool from a molten state, groups of atoms with parallel orbital spin line up within the crystal structure, forming a permanent ...
... opposing fields to cancel their effects, these electrons have an orbital magnetic moment. Iron and other ferromagnetic materials are crystalline. As they cool from a molten state, groups of atoms with parallel orbital spin line up within the crystal structure, forming a permanent ...
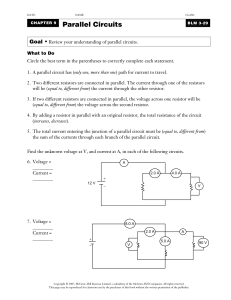
Parallel Circuits Worksheet File
... 1. A parallel circuit has (only one, more than one) path for current to travel. 2. Two different resistors are connected in parallel. The current through one of the resistors will be (equal to, different from) the current through the other resistor. 3. If two different resistors are connected in par ...
... 1. A parallel circuit has (only one, more than one) path for current to travel. 2. Two different resistors are connected in parallel. The current through one of the resistors will be (equal to, different from) the current through the other resistor. 3. If two different resistors are connected in par ...
Circular Motion HW-1
... A conducting rod slides on two wires in a region with a magnetic field. The two wires are not connected. Is a force required to keep the rod moving with constant speed? Explain. Many equal-arm balances have a small metal plate attached to one of the two arms. The plate passes between the poles of a ...
... A conducting rod slides on two wires in a region with a magnetic field. The two wires are not connected. Is a force required to keep the rod moving with constant speed? Explain. Many equal-arm balances have a small metal plate attached to one of the two arms. The plate passes between the poles of a ...
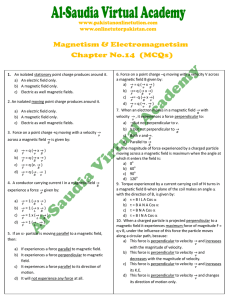
1. An isolated stationary point charge produces around it. a) An
... d) They will not be deflected at all. 47. Transformer works on: (4-a, 2002, P.E) a) Ohm’s law. b) Self induction. c) Mutual induction. d) Gauss’s law. 48. The deflecting torque on a current carrying coil placed in a magnetic field is maximum when the angle between the magnetic field and the plane of ...
... d) They will not be deflected at all. 47. Transformer works on: (4-a, 2002, P.E) a) Ohm’s law. b) Self induction. c) Mutual induction. d) Gauss’s law. 48. The deflecting torque on a current carrying coil placed in a magnetic field is maximum when the angle between the magnetic field and the plane of ...
PS 6.11 - S2TEM Centers SC
... The armature spins because other magnets in the motor push and pull the armature and cause it to spin. Motors use the magnetic force from magnets to spin an armature (magnetized by an electric current) and thus change electric energy to mechanical energy. Generators: ○ A generator changes mech ...
... The armature spins because other magnets in the motor push and pull the armature and cause it to spin. Motors use the magnetic force from magnets to spin an armature (magnetized by an electric current) and thus change electric energy to mechanical energy. Generators: ○ A generator changes mech ...
The Nature of Electric and Magnetic Fields
... in understanding this. Where a TV is switched off but plugged into a live socket, an electric field will be associated with the power lead. It is only when the TV is turned on and current flows in the power lead that a magnetic field will also arise. The amount of electric power transmitted along a ...
... in understanding this. Where a TV is switched off but plugged into a live socket, an electric field will be associated with the power lead. It is only when the TV is turned on and current flows in the power lead that a magnetic field will also arise. The amount of electric power transmitted along a ...
AC Circuits
... configurations (includes the Law of Biot and Savart for magnetic fields). Maxwell's equations - Maxwell's contribution and significance. DC circuits - Ohm's Law, Kirchhoff's Rules, power, series-parallel combinations. Series RLC circuits - phasor diagrams, phase angle, current, power factor Vectors ...
... configurations (includes the Law of Biot and Savart for magnetic fields). Maxwell's equations - Maxwell's contribution and significance. DC circuits - Ohm's Law, Kirchhoff's Rules, power, series-parallel combinations. Series RLC circuits - phasor diagrams, phase angle, current, power factor Vectors ...
Generating Electricity
... by: - Using a stronger magnet - Increasing the number of turns on the coil - Rotating the magnet faster The output from a dynamo can be displayed on an oscilloscope which shows how the current produced by the dynamo varies with time. The time for one complete cycle is called the period of alternatin ...
... by: - Using a stronger magnet - Increasing the number of turns on the coil - Rotating the magnet faster The output from a dynamo can be displayed on an oscilloscope which shows how the current produced by the dynamo varies with time. The time for one complete cycle is called the period of alternatin ...
Induct202draft
... yellow coil with one of the big copper coils on the table (hook the big coil up in series with the DMM as an ammeter and with the other DMM in parallel as a voltmeter just as you had for the yellow coil). Just as you did in part II, move the bar magnet into and out of the big coil. Look at the curre ...
... yellow coil with one of the big copper coils on the table (hook the big coil up in series with the DMM as an ammeter and with the other DMM in parallel as a voltmeter just as you had for the yellow coil). Just as you did in part II, move the bar magnet into and out of the big coil. Look at the curre ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... • Magnetic forces are similar to electrical forces. They cause attractions and repulsions of objects without actually touching. • Magnetic poles produce magnetic forces. ...
... • Magnetic forces are similar to electrical forces. They cause attractions and repulsions of objects without actually touching. • Magnetic poles produce magnetic forces. ...
Chapter 27 Current and Resistance The Development of Voltage
... charge through a surface. The SI unit of current is the Ampere (A). 1 A =1 C/s The direction of I is taken by convention to be that the flow of positive charge. ...
... charge through a surface. The SI unit of current is the Ampere (A). 1 A =1 C/s The direction of I is taken by convention to be that the flow of positive charge. ...
NMR_basics - Louisiana Tech University
... T1 relaxation: the magnetization returns to equilibrium magnetization. T2 relaxation: the magnetization remains transverse, but the spins from different molecules precess with slightly different frequencies, causing dephasing and, hence, decay of the macroscopic magnetization. (Relaxation is mostly ...
... T1 relaxation: the magnetization returns to equilibrium magnetization. T2 relaxation: the magnetization remains transverse, but the spins from different molecules precess with slightly different frequencies, causing dephasing and, hence, decay of the macroscopic magnetization. (Relaxation is mostly ...
Electromagnetic Waves
... ! We will see that light is an electromagnetic wave ! Electromagnetic waves have electric and magnetic fields ! We will see Maxwell’s Equations that describe electromagnetic phenomena ! We will see that the speed of light is constant and can be related to ε0 and μ0 ! We will see that electromag ...
... ! We will see that light is an electromagnetic wave ! Electromagnetic waves have electric and magnetic fields ! We will see Maxwell’s Equations that describe electromagnetic phenomena ! We will see that the speed of light is constant and can be related to ε0 and μ0 ! We will see that electromag ...
Currents and Magnetism
... Torque tries to line up the normal with B! (when normal lines up with B, f=0, so t=0! ) ...
... Torque tries to line up the normal with B! (when normal lines up with B, f=0, so t=0! ) ...
Ozone Cell
... If separation is d, then V = dE = dQ/ 0A or Q= (0A/d) If the capacitance C = 0A/d then Q = C V Energy W = ½ QV = ½ 0E2 (dA) Or, W = ½ C V2 ...
... If separation is d, then V = dE = dQ/ 0A or Q= (0A/d) If the capacitance C = 0A/d then Q = C V Energy W = ½ QV = ½ 0E2 (dA) Or, W = ½ C V2 ...
1. (a) - PLK Vicwood KT Chong Sixth Form College
... (ii) (I) The CRO trace represents the induced e.m.f. in the search coil and it is proportional to the peak value of the sinusoidal B-field produced by the wires. - The search coil detects alternating B-field. Therefore the earth’s field is not detected. - Measurable induced e.m.f. can be produced by ...
... (ii) (I) The CRO trace represents the induced e.m.f. in the search coil and it is proportional to the peak value of the sinusoidal B-field produced by the wires. - The search coil detects alternating B-field. Therefore the earth’s field is not detected. - Measurable induced e.m.f. can be produced by ...
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current through its coil in a magnetic field.Galvanometers were the first instruments used to detect and measure electric currents. Sensitive galvanometers were used to detect signals from long submarine cables, and to discover the electrical activity of the heart and brain. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals. Initially a laboratory instrument relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electrotechnology. A type of galvanometer that records measurements permanently is the chart recorder. The term has expanded to include use of the same mechanism in recording, positioning, and servomechanism equipment.