week11-faraday
... burst of electromagnetic radiation. The abrupt pulse of electromagnetic radiation usually results from certain types of high energy explosions, (such as a nuclear explosion), or from a suddenly fluctuating magnetic field. The resulting rapidly changing A electric fields and magnetic fields couple wi ...
... burst of electromagnetic radiation. The abrupt pulse of electromagnetic radiation usually results from certain types of high energy explosions, (such as a nuclear explosion), or from a suddenly fluctuating magnetic field. The resulting rapidly changing A electric fields and magnetic fields couple wi ...
Electrical Current Creates a Magnetic Field - e
... What conclusions can you make regarding the relationship between an electrical power source and current flowing through a wire? What conclusions can you make regarding the relationship between the electrical power source and the magnetic field produced by the electrical current? ...
... What conclusions can you make regarding the relationship between an electrical power source and current flowing through a wire? What conclusions can you make regarding the relationship between the electrical power source and the magnetic field produced by the electrical current? ...
Electromagnetism - Delta Education
... In this Delta Science Module, students are introduced to electromagnetism and the conversion of energy from one form into another by means of electric currents and magnetic fields. ACTIVITY 1 Students review the properties of magnetism by observing the interaction of magnets with ferrous and nonferr ...
... In this Delta Science Module, students are introduced to electromagnetism and the conversion of energy from one form into another by means of electric currents and magnetic fields. ACTIVITY 1 Students review the properties of magnetism by observing the interaction of magnets with ferrous and nonferr ...
Installation Guide Azatrax Dual Block Occupancy Detector (DCC
... What it is: The DBD has two current sensing block occupancy detection circuits that operate independently. Each detector circuit senses whether electrical current is flowing into a section of track. If current is flowing, the circuit closes a relay contact. The relay contact is used to activate a si ...
... What it is: The DBD has two current sensing block occupancy detection circuits that operate independently. Each detector circuit senses whether electrical current is flowing into a section of track. If current is flowing, the circuit closes a relay contact. The relay contact is used to activate a si ...
Lecture 24 - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... The current does not go from zero to ε/R in the circuit immediately after the switch is closed: 1. as the current flows through, magnetic flux through the loop is set up 2. this is opposed by induced emf in the loop which opposes the change in net magnetic flux 3. by Lentz’s law, the induced E-field ...
... The current does not go from zero to ε/R in the circuit immediately after the switch is closed: 1. as the current flows through, magnetic flux through the loop is set up 2. this is opposed by induced emf in the loop which opposes the change in net magnetic flux 3. by Lentz’s law, the induced E-field ...
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
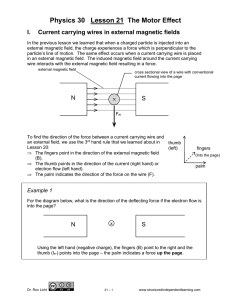
... B Using the left hand (negative charge), the fingers (B) point to the left and the thumb (e- flow) points down the page – the palm indicates a force which is out of the ...
... B Using the left hand (negative charge), the fingers (B) point to the left and the thumb (e- flow) points down the page – the palm indicates a force which is out of the ...
Lecture 15 - UConn Physics
... moving in the wire. What will be the total force dF on a length dl of the wire? • Suppose current is made up of n charges/volume each carrying charge q and moving with velocity v through a wire of crosssection A. • Force on each charge = ...
... moving in the wire. What will be the total force dF on a length dl of the wire? • Suppose current is made up of n charges/volume each carrying charge q and moving with velocity v through a wire of crosssection A. • Force on each charge = ...
PHYSICS - tutorialspoint.com
... Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment Magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron Magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) along its axis and perpendicular to its axis Torque on a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) in a uniform magnetic field: ...
... Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic dipole moment Magnetic dipole moment of a revolving electron Magnetic field intensity due to a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) along its axis and perpendicular to its axis Torque on a magnetic dipole (bar magnet) in a uniform magnetic field: ...
Chapter 11 - Inductors
... • The inherent resistance is called the dc resistance or the winding resistance (RW) • When two conductors are placed side-by-side, there is always some capacitance between them • When many turns of wire are placed close together in a coil, there is a winding capacitance (CW) • CW becomes significan ...
... • The inherent resistance is called the dc resistance or the winding resistance (RW) • When two conductors are placed side-by-side, there is always some capacitance between them • When many turns of wire are placed close together in a coil, there is a winding capacitance (CW) • CW becomes significan ...
Introduction - Union College
... 5. Compare the circular electron beam with the mirrored ruler behind the glass bulb. Adjust the current in the coils until the circle is the size such that the ruler crosses through the middle of the circle. Practice reading the radius of the electron beam. To avoid parallax errors, move your head t ...
... 5. Compare the circular electron beam with the mirrored ruler behind the glass bulb. Adjust the current in the coils until the circle is the size such that the ruler crosses through the middle of the circle. Practice reading the radius of the electron beam. To avoid parallax errors, move your head t ...
lab9 - Suffolk University
... Hint: You can prove this relationship by comparing the expressions (1) of the mutual inductances with those of the equivalent circuit: find the expressions of V1 and V2 as a function of I1 and I2 for the circuit of Figure 3. These expressions should be the same as those if Figure 2. ...
... Hint: You can prove this relationship by comparing the expressions (1) of the mutual inductances with those of the equivalent circuit: find the expressions of V1 and V2 as a function of I1 and I2 for the circuit of Figure 3. These expressions should be the same as those if Figure 2. ...
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current through its coil in a magnetic field.Galvanometers were the first instruments used to detect and measure electric currents. Sensitive galvanometers were used to detect signals from long submarine cables, and to discover the electrical activity of the heart and brain. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals. Initially a laboratory instrument relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electrotechnology. A type of galvanometer that records measurements permanently is the chart recorder. The term has expanded to include use of the same mechanism in recording, positioning, and servomechanism equipment.