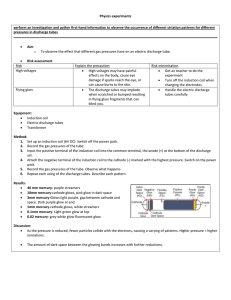
Magnetism Study Guide and Review WS
... Unlike a permanent magnet that keeps its magnetism when it is removed from a magnetic field, an electromagnet is a temporary magnet. It depends on electricity to work. In a simple electromagnet, a wire is wrapped around an iron object and a current is passed through the wire. The current creates a m ...
... Unlike a permanent magnet that keeps its magnetism when it is removed from a magnetic field, an electromagnet is a temporary magnet. It depends on electricity to work. In a simple electromagnet, a wire is wrapped around an iron object and a current is passed through the wire. The current creates a m ...
Chapter #9 electric-current-circuits-multiple
... 3. A wire of length L and cross-sectional area A has a resistivity ρ. Which of the following formulas can be used to calculate the resistance of the wire? ...
... 3. A wire of length L and cross-sectional area A has a resistivity ρ. Which of the following formulas can be used to calculate the resistance of the wire? ...
PSI Physics Electric Current and Circuits Multiple Choice Questions
... 3. A wire of length L and cross-sectional area A has a resistivity ρ. Which of the following formulas can be used to calculate the resistance of the wire? ...
... 3. A wire of length L and cross-sectional area A has a resistivity ρ. Which of the following formulas can be used to calculate the resistance of the wire? ...
DOC - People Server at UNCW
... four coils of copper wire and then determine the average resistivity of the set. We will a setup known as the Wheatstone bridge to determine the unknown resistance. Below are depicted the schematic and physical setup of such a bridge. One has a known, or standard, resistance RS, and two lengths of w ...
... four coils of copper wire and then determine the average resistivity of the set. We will a setup known as the Wheatstone bridge to determine the unknown resistance. Below are depicted the schematic and physical setup of such a bridge. One has a known, or standard, resistance RS, and two lengths of w ...
TEM Wave Electrodynamics Feb 18 2012
... The water in a river moves but the river level stays even. When the water-current is a steady flow, a depth gauge reads a steady depth. The energy current in an electrical device is measured with the voltmeter and the ammeter. When the energy current is steady the meters stand still. ...
... The water in a river moves but the river level stays even. When the water-current is a steady flow, a depth gauge reads a steady depth. The energy current in an electrical device is measured with the voltmeter and the ammeter. When the energy current is steady the meters stand still. ...
Section 22.2 - CPO Science
... 22.2 Electromagnets in Toasters By changing the amount of current, you can easily change the strength of an electromagnet or even turn its magnetism on and off. ...
... 22.2 Electromagnets in Toasters By changing the amount of current, you can easily change the strength of an electromagnet or even turn its magnetism on and off. ...
CTExIIIa
... D: some combination of these three forms of energy Answer: The correct answer is A: magnetic field energy only. The capacitor is initially uncharged. You need time to build up field energy in the capacitor, and dissipate thermal energy in the resistor. Although P(resistor)=I2R at t=0+, the total en ...
... D: some combination of these three forms of energy Answer: The correct answer is A: magnetic field energy only. The capacitor is initially uncharged. You need time to build up field energy in the capacitor, and dissipate thermal energy in the resistor. Although P(resistor)=I2R at t=0+, the total en ...
DC Voltmeters and Ammeters
... One solution to the problem of voltmeters and ammeters interfering with the circuits being measured is to use galvanometers with greater sensitivity. This allows construction of voltmeters with greater resistance and ammeters with smaller resistance than when less sensitive galvanometers are used. T ...
... One solution to the problem of voltmeters and ammeters interfering with the circuits being measured is to use galvanometers with greater sensitivity. This allows construction of voltmeters with greater resistance and ammeters with smaller resistance than when less sensitive galvanometers are used. T ...
Conceptual Physics - Southwest High School
... A magnetized bar has its power concentrated at two ends, its poles; they are known as its north (N) and south (S) poles, because if the bar is hung by its middle from a string, its N end tends to point northwards and its S end southwards. The N end will repel the N end of another magnet, S will repe ...
... A magnetized bar has its power concentrated at two ends, its poles; they are known as its north (N) and south (S) poles, because if the bar is hung by its middle from a string, its N end tends to point northwards and its S end southwards. The N end will repel the N end of another magnet, S will repe ...
Exercise 1:
... Exercise 1: Ohm’s Law Begin by reading the material on measuring voltage prepared by Prof E. J. Mastascusa at Bucknell University. Next create the following circuit on your breadboard: ...
... Exercise 1: Ohm’s Law Begin by reading the material on measuring voltage prepared by Prof E. J. Mastascusa at Bucknell University. Next create the following circuit on your breadboard: ...
Definitions of the SI base and derived units
... 0 or 1. Although computers usually provide instructions that can test and manipulate bits, they generally are designed to store data and execute instructions in bit multiples called bytes. In most computer systems, there are eight bits in a byte. The value of a bit is usually stored as either above ...
... 0 or 1. Although computers usually provide instructions that can test and manipulate bits, they generally are designed to store data and execute instructions in bit multiples called bytes. In most computer systems, there are eight bits in a byte. The value of a bit is usually stored as either above ...
LEM`s new class of Rogowski coil split
... bad loop will be bad for both. This is a result of Ampère’s theorem, which states that any error associated with any form of asymmetry is valid both inside and outside the loop. Let us take, for example, a conductor on which a 100 A current is circulating, situated inside the Rogowski coil and which ...
... bad loop will be bad for both. This is a result of Ampère’s theorem, which states that any error associated with any form of asymmetry is valid both inside and outside the loop. Let us take, for example, a conductor on which a 100 A current is circulating, situated inside the Rogowski coil and which ...
CHAPTER 17 17.1 Electric forces 17.2 Coulombs Law 17.3 Electric
... • There are two ways to calculate the magnetic field produced by a current – One way treats each small piece of wire as a separate source • Similar to using Coulomb’s Law for an electric field • Mathematically complicated ...
... • There are two ways to calculate the magnetic field produced by a current – One way treats each small piece of wire as a separate source • Similar to using Coulomb’s Law for an electric field • Mathematically complicated ...
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current through its coil in a magnetic field.Galvanometers were the first instruments used to detect and measure electric currents. Sensitive galvanometers were used to detect signals from long submarine cables, and to discover the electrical activity of the heart and brain. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals. Initially a laboratory instrument relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electrotechnology. A type of galvanometer that records measurements permanently is the chart recorder. The term has expanded to include use of the same mechanism in recording, positioning, and servomechanism equipment.