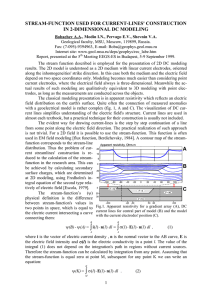
current fuction usage for current lines construction in 2d models
... along the inhomogeneities' strike direction. In this case both the medium and the electric field depend on two space coordinates only. Modeling becomes much easier than considering point current electrodes, where the electrical field always is three-dimensional. Meanwhile the actual results of such ...
... along the inhomogeneities' strike direction. In this case both the medium and the electric field depend on two space coordinates only. Modeling becomes much easier than considering point current electrodes, where the electrical field always is three-dimensional. Meanwhile the actual results of such ...
Chapter 20
... As the coil begins to rotate, the induced back emf opposes the applied voltage The current in the coil is reduced The power requirements for starting a motor and for running it under heavy loads are greater than those for running the motor under average loads ...
... As the coil begins to rotate, the induced back emf opposes the applied voltage The current in the coil is reduced The power requirements for starting a motor and for running it under heavy loads are greater than those for running the motor under average loads ...
Electromagnetic Information
... With the exception of special applications such as a medical MRI scanner in which a very heavy and liquid helium-cooled superconducting magnet of an extremely strong static magnetic field excites atomic nuclei in the human body, the technical fields usually require a specific motion, attraction, or ...
... With the exception of special applications such as a medical MRI scanner in which a very heavy and liquid helium-cooled superconducting magnet of an extremely strong static magnetic field excites atomic nuclei in the human body, the technical fields usually require a specific motion, attraction, or ...
EET-027, Experiment # 3
... the comparison method. The bridge is named after Charles Wheatstone who invented it in ...
... the comparison method. The bridge is named after Charles Wheatstone who invented it in ...
KEY - Rose
... EXECUTE: B is larger at segment 1 since it is closer to the long wire, so FB is larger in segment 1 and the induced current in the loop is clockwise. This agrees with the direction deduced in (i) using Lenz’s law. (c) EVALUATE: When v = 0 the induced emf should be zero; the expression in part (a) g ...
... EXECUTE: B is larger at segment 1 since it is closer to the long wire, so FB is larger in segment 1 and the induced current in the loop is clockwise. This agrees with the direction deduced in (i) using Lenz’s law. (c) EVALUATE: When v = 0 the induced emf should be zero; the expression in part (a) g ...
Basic Physical Principles of MRI
... How do protons interact with a magnetic field? • Moving (spinning) charged particle generates its own little magnetic field – Such particles will tend to line up with external magnetic field lines (think of iron filings around a magnet) ...
... How do protons interact with a magnetic field? • Moving (spinning) charged particle generates its own little magnetic field – Such particles will tend to line up with external magnetic field lines (think of iron filings around a magnet) ...
QUESTIONS ON OHM`S LAW AND KIRCHHOFF`S LAW A
... the fraction form. This helps to check the correctness of the current values. In a given problem, if the cells are of different e.m.f.s and also in parallel, that problem can be solved using only Kirchhoff’s Law. ...
... the fraction form. This helps to check the correctness of the current values. In a given problem, if the cells are of different e.m.f.s and also in parallel, that problem can be solved using only Kirchhoff’s Law. ...
volt current ampere - Crompton Instruments
... Current is a flow of electrical charge carriers, usually electrons or electron-deficient atoms. The common symbol for current is the uppercase letter I. The standard unit is the ampere, symbolized by A. One ampere of current represents one coulomb of electrical charge (6.24 x 1018 charge carriers) m ...
... Current is a flow of electrical charge carriers, usually electrons or electron-deficient atoms. The common symbol for current is the uppercase letter I. The standard unit is the ampere, symbolized by A. One ampere of current represents one coulomb of electrical charge (6.24 x 1018 charge carriers) m ...
ii `I I
... Two horizontal conducting rails form an angle 8 where their ends are joined. A conducting rod slides on the rails without friction with constant velocity v as shown in the figure. At tO it starts from x=d from rest. There is a resistor R in one of the rails. There is a uniform magnetic field in the ...
... Two horizontal conducting rails form an angle 8 where their ends are joined. A conducting rod slides on the rails without friction with constant velocity v as shown in the figure. At tO it starts from x=d from rest. There is a resistor R in one of the rails. There is a uniform magnetic field in the ...
SERIES CENTIGRID® ESTABLISHED RELIABILITY RELAYS
... armature relay. Its low profile height (.275") and .100" grid spaced terminals, which precludes the need for spreader pads, make it ideal for applications where extreme packaging density and/or close PC board spacing are required. The basic design and internal construction are similar to the standar ...
... armature relay. Its low profile height (.275") and .100" grid spaced terminals, which precludes the need for spreader pads, make it ideal for applications where extreme packaging density and/or close PC board spacing are required. The basic design and internal construction are similar to the standar ...
Digital multimeters
... want to make. If the meter is switched to 20 V DC, for example, then 20 V is the maximum voltage which can be measured, this is sometimes called 20 V fsd, where fsd is short for full scale deflection. For circuits with power supplies of up to 20 V, which includes all the circuits you are likely to b ...
... want to make. If the meter is switched to 20 V DC, for example, then 20 V is the maximum voltage which can be measured, this is sometimes called 20 V fsd, where fsd is short for full scale deflection. For circuits with power supplies of up to 20 V, which includes all the circuits you are likely to b ...
PROBLEM SET Current, Voltage, and Resistance
... Solve the following problems on another sheet of paper. All answers should be expressed in four significant digits with correct units. ...
... Solve the following problems on another sheet of paper. All answers should be expressed in four significant digits with correct units. ...
Practice Unit Test - hhs-snc1d
... the day. The energy wasted is: a) 8 Watt hours b) 480 Watt hours c) 60 Watt hours d) 3840 Watt hours 11. The purpose of a fuse is: a) to break a circuit if too much current is passing through b) to add resistance to a circuit c) to make a battery less powerful d) to make a short circuit ...
... the day. The energy wasted is: a) 8 Watt hours b) 480 Watt hours c) 60 Watt hours d) 3840 Watt hours 11. The purpose of a fuse is: a) to break a circuit if too much current is passing through b) to add resistance to a circuit c) to make a battery less powerful d) to make a short circuit ...
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current through its coil in a magnetic field.Galvanometers were the first instruments used to detect and measure electric currents. Sensitive galvanometers were used to detect signals from long submarine cables, and to discover the electrical activity of the heart and brain. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals. Initially a laboratory instrument relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electrotechnology. A type of galvanometer that records measurements permanently is the chart recorder. The term has expanded to include use of the same mechanism in recording, positioning, and servomechanism equipment.























