Unit 3 - High School Chemistry
... same electron configurations as the noble gas of the previous row. - for non-metals, which like to gain electrons to form anions, they have the same electron configurations as the noble gas at the end of the same row. Alkali Cations: - cations that were the result as alkali metals (Group 1 or IA) lo ...
... same electron configurations as the noble gas of the previous row. - for non-metals, which like to gain electrons to form anions, they have the same electron configurations as the noble gas at the end of the same row. Alkali Cations: - cations that were the result as alkali metals (Group 1 or IA) lo ...
No Slide Title
... A sphere of radius a has a total charge Q and uniform charge density throughout. What is the direction and magnitude of the electric field everywhere? • When computing the flux for a Gaussian surface, only include the electric charges inside the surface ...
... A sphere of radius a has a total charge Q and uniform charge density throughout. What is the direction and magnitude of the electric field everywhere? • When computing the flux for a Gaussian surface, only include the electric charges inside the surface ...
Chapter 2 Elements and Compounds 2.1 The Structure of the Atom
... similar masses, both have a mass of approximately 1 u. The mass of an electron is about 2000 times less that of protons and neutrons, and it has a mass of approximately zero on the atomic mass unit scale. Atoms are neutral because protons and electrons have equal, opposite charges and atoms have e ...
... similar masses, both have a mass of approximately 1 u. The mass of an electron is about 2000 times less that of protons and neutrons, and it has a mass of approximately zero on the atomic mass unit scale. Atoms are neutral because protons and electrons have equal, opposite charges and atoms have e ...
Symbols and Terms - IXYS Corporation
... liability is only assumed for components per se, not for applications, processes and circuits implemented with components or assemblies. The information describes the type of component and shall not be considered as assured characteristics. Stress above one or more of the limiting values may cause p ...
... liability is only assumed for components per se, not for applications, processes and circuits implemented with components or assemblies. The information describes the type of component and shall not be considered as assured characteristics. Stress above one or more of the limiting values may cause p ...
Dynamic electrostatic force microscopy in liquid media
... First, for a given high frequency and given liquid properties, the probe geometry (R and h) and the native oxide capacitance (Cnative) were calibrated by fitting the numerical calculations to the approach curve measured on the Siþþ substrate in electrolyte solution. Then, these parameters were used t ...
... First, for a given high frequency and given liquid properties, the probe geometry (R and h) and the native oxide capacitance (Cnative) were calibrated by fitting the numerical calculations to the approach curve measured on the Siþþ substrate in electrolyte solution. Then, these parameters were used t ...
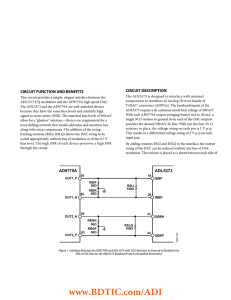
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... Figure 2. Relationship Between the AC Swing-Limiting Resistor and the Peak-to-Peak Voltage Swing with 50 Ω Bias-Setting Resistors ...
... Figure 2. Relationship Between the AC Swing-Limiting Resistor and the Peak-to-Peak Voltage Swing with 50 Ω Bias-Setting Resistors ...
An electric current is a flow of charge
... If your body is earthed, that is touching the ground or another conductive object that is touching the ground, and then you come in contact with an electrical source you will form a circuit for a current to flow. The electrical current will follow a path of least resistance which may be across your ...
... If your body is earthed, that is touching the ground or another conductive object that is touching the ground, and then you come in contact with an electrical source you will form a circuit for a current to flow. The electrical current will follow a path of least resistance which may be across your ...
A-level Paper 3 Practice Paper 3 - A
... Give one large-scale application of the use of chlorine in water. Explain why it is used in this application even though chlorine is very toxic. Do not include cost. Example of application…..................................................................... Explanation of use ...................... ...
... Give one large-scale application of the use of chlorine in water. Explain why it is used in this application even though chlorine is very toxic. Do not include cost. Example of application…..................................................................... Explanation of use ...................... ...
Document
... it is bonded to metals in binary compounds. In these cases, its oxidation number is –1. 5. Group IA metals are +1, IIA metals are +2 and fluorine is always –1. 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to the charge on the molecule or ion. ...
... it is bonded to metals in binary compounds. In these cases, its oxidation number is –1. 5. Group IA metals are +1, IIA metals are +2 and fluorine is always –1. 6. The sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a molecule or ion is equal to the charge on the molecule or ion. ...
Section 20.1 Electric Charge and Static Electricity
... (pages 600–603) This section explains how electric charge is created and how positive and negative charges affect each other. It also discusses the different ways that electric charge can be transferred. ...
... (pages 600–603) This section explains how electric charge is created and how positive and negative charges affect each other. It also discusses the different ways that electric charge can be transferred. ...
View File - UET Taxila
... • Voltage is the difference in electric potential between two points. To express this difference, we b a label a voltage with a “+” and “-” : 1.5V Here, V1 is the potential at “a” minus + V1 the potential at “b”, which is -1.5 V. • Current is the flow of positive charge. Current has a value and a di ...
... • Voltage is the difference in electric potential between two points. To express this difference, we b a label a voltage with a “+” and “-” : 1.5V Here, V1 is the potential at “a” minus + V1 the potential at “b”, which is -1.5 V. • Current is the flow of positive charge. Current has a value and a di ...
Nanofluidic circuitry
Nanofluidic circuitry is a nanotechnology aiming for control of fluids in nanometer scale. Due to the effect of an electrical double layer within the fluid channel, the behavior of nanofluid is observed to be significantly different compared with its microfluidic counterparts. Its typical characteristic dimensions fall within the range of 1–100 nm. At least one dimension of the structure is in nanoscopic scale. Phenomena of fluids in nano-scale structure are discovered to be of different properties in electrochemistry and fluid dynamics.