3 - Zheng Research Group
... then, it has 36.4 g Mn, 21.2 g S, and 42.4 g O; Mn: 36.4 g / 54.9 g/mol = 0.663 mol Mn; S: 21.2 g / 32.1 g/mol = 0.660 mol S; O: 42.4 g / 16.0 g/mol = 2.65 mol O. therefore: divide the smallest number (0.660), the formula is: MnSO4. ...
... then, it has 36.4 g Mn, 21.2 g S, and 42.4 g O; Mn: 36.4 g / 54.9 g/mol = 0.663 mol Mn; S: 21.2 g / 32.1 g/mol = 0.660 mol S; O: 42.4 g / 16.0 g/mol = 2.65 mol O. therefore: divide the smallest number (0.660), the formula is: MnSO4. ...
Spring 2014 Chemistry Review
... 62) What is the relationship between volume and # of collisions: ____________ 63) What is the relationship between temperature and # of collisions: ____________ 64) What is the relationship between pressure and # of collisions: ____________ 65) What is the relationship between volume and pressure: _ ...
... 62) What is the relationship between volume and # of collisions: ____________ 63) What is the relationship between temperature and # of collisions: ____________ 64) What is the relationship between pressure and # of collisions: ____________ 65) What is the relationship between volume and pressure: _ ...
Concepts in Biochemistry 3/e
... Viruses: consist of a single DNA or RNA molecule wrapped in a protein package Not considered a life-form Deemed parasites – unable to carry out metabolism or reproduction without the assistance of host cell Are the caused of many plants and animals maladies and has resulted in much human suffering ...
... Viruses: consist of a single DNA or RNA molecule wrapped in a protein package Not considered a life-form Deemed parasites – unable to carry out metabolism or reproduction without the assistance of host cell Are the caused of many plants and animals maladies and has resulted in much human suffering ...
Chemistry of Proteins Model Making
... as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in regulatory capacity as enzymes and hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in many proteins. The amino acid is the basic structural unit of all proteins. There ...
... as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in regulatory capacity as enzymes and hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in many proteins. The amino acid is the basic structural unit of all proteins. There ...
Biomolecule Reading
... Proteins are organic molecules that form muscles, transport O2 (hemoglobin), and act as hormones and enzymes. Most importantly, proteins determine how our bodies look and function. Their building block is the amino acid. Proteins are made of amino acids linked by a peptide bond. When groups of amino ...
... Proteins are organic molecules that form muscles, transport O2 (hemoglobin), and act as hormones and enzymes. Most importantly, proteins determine how our bodies look and function. Their building block is the amino acid. Proteins are made of amino acids linked by a peptide bond. When groups of amino ...
2 HI
... All the polypeptides are denatured and behave as random coils All the polypeptides have the same charge per unit length All are subject to the same electromotive force in the electric field Separation based on the sieving effect of the polyacrylamide gel Separation is by molecular weight only SDS do ...
... All the polypeptides are denatured and behave as random coils All the polypeptides have the same charge per unit length All are subject to the same electromotive force in the electric field Separation based on the sieving effect of the polyacrylamide gel Separation is by molecular weight only SDS do ...
Molecular Clocks
... • Cannot distinguish a constant rate from an average variable rate within a lineage • None of the molecular clock tests examines whether the rate is constant over time Failure to reject molecular clock may be due to * lack of information in the data (small sample, little divergence) * lack of power ...
... • Cannot distinguish a constant rate from an average variable rate within a lineage • None of the molecular clock tests examines whether the rate is constant over time Failure to reject molecular clock may be due to * lack of information in the data (small sample, little divergence) * lack of power ...
Fats and Proteins
... Carbohydrates consist of many monosaccharides joined together while fats consist of glycerol and fatty acid molecules joined together. Proteins also consist of many small molecules joined together. In proteins, these smaller molecules are called amino acids. Examine the structural formulas and corre ...
... Carbohydrates consist of many monosaccharides joined together while fats consist of glycerol and fatty acid molecules joined together. Proteins also consist of many small molecules joined together. In proteins, these smaller molecules are called amino acids. Examine the structural formulas and corre ...
Quiz Chapter 5 Organic Molecules
... 19. A particular polypeptide contains 90 amino acids. When the polypeptide is completely hydrolyzed, how many water molecules are formed during this process? a. 2 d. 89 b. 30 e 90 c. 45 20. All of the following qualities contribute to capillary action EXCEPT: a. cohesion d. hydrogen bonding b. adhes ...
... 19. A particular polypeptide contains 90 amino acids. When the polypeptide is completely hydrolyzed, how many water molecules are formed during this process? a. 2 d. 89 b. 30 e 90 c. 45 20. All of the following qualities contribute to capillary action EXCEPT: a. cohesion d. hydrogen bonding b. adhes ...
TANNIC ACID
... Consists of gallotannins obtained by solvent extraction from certain natural sources; the substance is not an acid in the chemical sense. The common name "Tannic acid" has been adopted to distinguish the commercial substance from other tannins, such as condensed tannins. These specifications relate ...
... Consists of gallotannins obtained by solvent extraction from certain natural sources; the substance is not an acid in the chemical sense. The common name "Tannic acid" has been adopted to distinguish the commercial substance from other tannins, such as condensed tannins. These specifications relate ...
Chromatography
... The chromatographic media used in this technique are porous, polymeric organic compounds with molecular sieving properties. These are cross-linked polymers which swell in water forming a gel of 3-D networks. ...
... The chromatographic media used in this technique are porous, polymeric organic compounds with molecular sieving properties. These are cross-linked polymers which swell in water forming a gel of 3-D networks. ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... Plant cells store starch for energy potatoes and grains are major sources of starch in the human diet Glycogen Glycogen is an example of a polysaccharide in animals Animals store excess sugar in the form of glycogen Glycogen is similar in structure to starch Cellulose Cellulose is the most abundant ...
... Plant cells store starch for energy potatoes and grains are major sources of starch in the human diet Glycogen Glycogen is an example of a polysaccharide in animals Animals store excess sugar in the form of glycogen Glycogen is similar in structure to starch Cellulose Cellulose is the most abundant ...
File
... Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) - Can exist in a chain or a ring • Everything that happens in our body is due to changes in levels of molecules: 1) make new molecules 2) maintain existing molecules 3) dispose of dead molecules ...
... Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) - Can exist in a chain or a ring • Everything that happens in our body is due to changes in levels of molecules: 1) make new molecules 2) maintain existing molecules 3) dispose of dead molecules ...
GAS PRACTICE A sample of an ideal gas is cooled from 50.0 °C to
... is heated at a constant rate in an open vessel at 1.0 atm pressure. The substance changes from the solid to the liquid to the gas phase. 6. The substance is at its normal freezing point at time… 15. (A) t1 (B) t2 (C) t3 (D) t4 (E) t5 7. Which of the following best describes what happens to the subst ...
... is heated at a constant rate in an open vessel at 1.0 atm pressure. The substance changes from the solid to the liquid to the gas phase. 6. The substance is at its normal freezing point at time… 15. (A) t1 (B) t2 (C) t3 (D) t4 (E) t5 7. Which of the following best describes what happens to the subst ...
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW SHEET
... k. When something does not mix with water it is called “H_______________________” l. Draw the typical shape of a steroid: m. Name three steroids (hint: use online activity 5.3): n. Name an illegal steroid used for athletic enhancement_________________________ o. Cholesterol is needed in your cell m ...
... k. When something does not mix with water it is called “H_______________________” l. Draw the typical shape of a steroid: m. Name three steroids (hint: use online activity 5.3): n. Name an illegal steroid used for athletic enhancement_________________________ o. Cholesterol is needed in your cell m ...
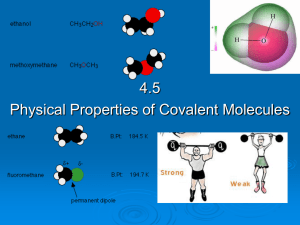
4.5 Physical properties of molecular covalent
... water but large protein polymers are generally insoluble. As the non-polar hydrocarbon chain of a polar molecule increases, the solubility of the molecule decreases because the non-polar carbon chain outweighs the polar part. E.g. ethanol (CH3CH2OH) is more soluble in water ...
... water but large protein polymers are generally insoluble. As the non-polar hydrocarbon chain of a polar molecule increases, the solubility of the molecule decreases because the non-polar carbon chain outweighs the polar part. E.g. ethanol (CH3CH2OH) is more soluble in water ...
Biochem Molecules Presentation
... making energy (ATP) for synthesis, growth & everyday functions ...
... making energy (ATP) for synthesis, growth & everyday functions ...
Spring Benchmark Exam
... 30. A technician prepared a solution by heating 100 milliliters of distilled water while adding KCl crystals until no more KCl would dissolve. She then capped the clear solution and set it aside on the lab bench. After several hours she noticed the solution had become cloudy and some solid had settl ...
... 30. A technician prepared a solution by heating 100 milliliters of distilled water while adding KCl crystals until no more KCl would dissolve. She then capped the clear solution and set it aside on the lab bench. After several hours she noticed the solution had become cloudy and some solid had settl ...
Apresentação do PowerPoint
... sample. (A) The sample is loaded and voltage is applied. The proteins will migrate to their isoelectric pH, the location at which they have no net charge. (B) The proteins form bands that can be excised and used for further experimentation. ...
... sample. (A) The sample is loaded and voltage is applied. The proteins will migrate to their isoelectric pH, the location at which they have no net charge. (B) The proteins form bands that can be excised and used for further experimentation. ...
Topic 2.1-2.4 Molecular Biology
... Denaturing Proteins • Intramolecular bonds that determine protein shape can be altered by temperature and pH. – Alteration of unique 3-D shape renders them useless in biochemical reactions – Can be reversible if most covalent bonds remain when temperature and pH return to normal ...
... Denaturing Proteins • Intramolecular bonds that determine protein shape can be altered by temperature and pH. – Alteration of unique 3-D shape renders them useless in biochemical reactions – Can be reversible if most covalent bonds remain when temperature and pH return to normal ...
chapter 3 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... 15. Some additional issues and questions to consider: Should individuals be responsible for the consequences of their own actions? What, if any, distinctions can you make between people choosing to smoke versus people who consume fast food? Should courts be involved in such decisions? What can fast- ...
... 15. Some additional issues and questions to consider: Should individuals be responsible for the consequences of their own actions? What, if any, distinctions can you make between people choosing to smoke versus people who consume fast food? Should courts be involved in such decisions? What can fast- ...
File
... 12. Why are there twenty types of R groups? 13. What is the difference between the amino acid cysteine and the amino acid alanine, be specific. Think “R-Group” (you will have to look this up). 14. Diagram the joining of 2 amino acids together through dehydration synthesis to form a dipeptide with a ...
... 12. Why are there twenty types of R groups? 13. What is the difference between the amino acid cysteine and the amino acid alanine, be specific. Think “R-Group” (you will have to look this up). 14. Diagram the joining of 2 amino acids together through dehydration synthesis to form a dipeptide with a ...
Summarised Notes
... separated by physical methods. separated by chemical methods or electricity. The chemical properties of a mixture are The physical and chemical properties of a the same as those of its components. compound are different from those of the elements in the compound. ...
... separated by physical methods. separated by chemical methods or electricity. The chemical properties of a mixture are The physical and chemical properties of a the same as those of its components. compound are different from those of the elements in the compound. ...
Slide 1
... IUPAC names for a carboxylic acid are derived from the name of the parent hydrocarbon. – The final -e is dropped from the name of the parent hydrocarbon – The suffix -oic is added followed by the word acid. Many organic acids are called by their common (trivial) names which are derived from Greek or ...
... IUPAC names for a carboxylic acid are derived from the name of the parent hydrocarbon. – The final -e is dropped from the name of the parent hydrocarbon – The suffix -oic is added followed by the word acid. Many organic acids are called by their common (trivial) names which are derived from Greek or ...
Size-exclusion chromatography

Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size, and in some cases molecular weight. It is usually applied to large molecules or macromolecular complexes such as proteins and industrial polymers. Typically, when an aqueous solution is used to transport the sample through the column, the technique is known as gel-filtration chromatography, versus the name gel permeation chromatography, which is used when an organic solvent is used as a mobile phase. SEC is a widely used polymer characterization method because of its ability to provide good molar mass distribution (Mw) results for polymers.