OKO guide to adaptive optics
... DMs have many inherent advantages, such as they do not introduce chromatic aberrations, they can be coated with extremely highly reflective coatings so that they cause no power loss in the optical system, and - from the control perspective - they can be represented as linear systems, so that the ada ...
... DMs have many inherent advantages, such as they do not introduce chromatic aberrations, they can be coated with extremely highly reflective coatings so that they cause no power loss in the optical system, and - from the control perspective - they can be represented as linear systems, so that the ada ...
MEMS Corner Cube Retroreflectors for Free-Space
... A. Calculating the DSCS for ideal and non-ideal CCRs Diffractive spreading of the reflected beam puts a fundamental limit on the performance of a long-range optical link using this device. In order to model nonflatness, misalignment and diffraction on an equal footing, a finite-element analysis of t ...
... A. Calculating the DSCS for ideal and non-ideal CCRs Diffractive spreading of the reflected beam puts a fundamental limit on the performance of a long-range optical link using this device. In order to model nonflatness, misalignment and diffraction on an equal footing, a finite-element analysis of t ...
AOK2-UP01 - February 2, 2015
... 15 Hz CCD Shack-Hartmann Wavefront Sensor* Thorlabs' adaptive optics kits are a complete adaptive optics imaging solution, including a deformable mirror, wavefront sensor, control software, and optomechanics for assembly. These miniature, precision wavefront control devices are useful for beam formi ...
... 15 Hz CCD Shack-Hartmann Wavefront Sensor* Thorlabs' adaptive optics kits are a complete adaptive optics imaging solution, including a deformable mirror, wavefront sensor, control software, and optomechanics for assembly. These miniature, precision wavefront control devices are useful for beam formi ...
Characterization of high-finesse mirrors: Loss, phase shifts, and
... total cavity losses L⫽T 1 ⫹T 2 ⫹l 1 ⫹l 2 can be determined from the cavity finesse F, given by (FSR)/2 , with FSR as the cavity free spectral range and as the half-width at half maximum for the TEM00 mode of the cavity; equivalently, F⫽2 /L. The cavity linewidth  ⫽2 can be determined from a ...
... total cavity losses L⫽T 1 ⫹T 2 ⫹l 1 ⫹l 2 can be determined from the cavity finesse F, given by (FSR)/2 , with FSR as the cavity free spectral range and as the half-width at half maximum for the TEM00 mode of the cavity; equivalently, F⫽2 /L. The cavity linewidth  ⫽2 can be determined from a ...
Design, near-field characterization, and modeling of 45° surface
... intended for far-field observation is that, in the former ones, the single gold lines surrounding the mirror are not included. In this way, we avoid the scattered radiative contribution provided by these single lines, some part of which could be captured by the probe tip thereby resulting in an over ...
... intended for far-field observation is that, in the former ones, the single gold lines surrounding the mirror are not included. In this way, we avoid the scattered radiative contribution provided by these single lines, some part of which could be captured by the probe tip thereby resulting in an over ...
Chapter 30 The Law of Reflection
... image of the woman. The minimum length of the mirror for the woman to see her entire height is just the length BD, which we must now determine. The tangent of the angle of incidence i is ...
... image of the woman. The minimum length of the mirror for the woman to see her entire height is just the length BD, which we must now determine. The tangent of the angle of incidence i is ...
Mirror contamination in space I: mirror modelling
... 1999). The change to the model, as presented in Sect. 2.2, is only in the equations for the reflection coefficients rs and rp , combined here as an implied s- and p-specific reflection coefficient Rt . We employ a capital R for combined multilayer intensity reflections at a certain interface, which ...
... 1999). The change to the model, as presented in Sect. 2.2, is only in the equations for the reflection coefficients rs and rp , combined here as an implied s- and p-specific reflection coefficient Rt . We employ a capital R for combined multilayer intensity reflections at a certain interface, which ...
Miscellaeous features - JLab Tech Notes Home Page
... The gain is optimized if the optical mode is wrapped tightly around the electron beam. The optical power output is optimized when the maximum number of electrons is enclosed in the optical mode. Typically, a compromise is made between these two effects. The beam size and divergence around an optical ...
... The gain is optimized if the optical mode is wrapped tightly around the electron beam. The optical power output is optimized when the maximum number of electrons is enclosed in the optical mode. Typically, a compromise is made between these two effects. The beam size and divergence around an optical ...
Fabry-Perot Interferometer
... whose components are linearly polarized in perpendicular directions. • Three pairs of mirrors are provided, two spherical sets with radii of curvature r of 75 mm and 100 mm, respectively; and one set of plane mirrors. The reflectivity of the mirrors is 96% for each set. Please, do not touch the mirr ...
... whose components are linearly polarized in perpendicular directions. • Three pairs of mirrors are provided, two spherical sets with radii of curvature r of 75 mm and 100 mm, respectively; and one set of plane mirrors. The reflectivity of the mirrors is 96% for each set. Please, do not touch the mirr ...
Practical Aspects of Mirror Usage in Optical Systems for
... for a specific purpose, wavelength range, etc. The newcomer first wonders, “Why are there so many varieties of mirrors?” and shortly afterwards, “How do I know which mirror to use for my specific purpose?” This paper seeks to answer that question, by providing practical, useful information on the sp ...
... for a specific purpose, wavelength range, etc. The newcomer first wonders, “Why are there so many varieties of mirrors?” and shortly afterwards, “How do I know which mirror to use for my specific purpose?” This paper seeks to answer that question, by providing practical, useful information on the sp ...
Practical Aspects of Mirror Usage in Optical Systems for
... for a specific purpose, wavelength range, etc. The newcomer first wonders, “Why are there so many varieties of mirrors?” and shortly afterwards, “How do I know which mirror to use for my specific purpose?” This paper seeks to answer that question, by providing practical, useful information on the sp ...
... for a specific purpose, wavelength range, etc. The newcomer first wonders, “Why are there so many varieties of mirrors?” and shortly afterwards, “How do I know which mirror to use for my specific purpose?” This paper seeks to answer that question, by providing practical, useful information on the sp ...
unit 29: reflection and mirrors
... are coming from the pin to your eye. If you place something between the pin and your eye, you will block the light from the first pin. You can trace a ray of light by putting pins along its path as shown in Figure 29.1. Call the pin that is the source of the ray the object pin O. If you look at the ...
... are coming from the pin to your eye. If you place something between the pin and your eye, you will block the light from the first pin. You can trace a ray of light by putting pins along its path as shown in Figure 29.1. Call the pin that is the source of the ray the object pin O. If you look at the ...
At-wavelength figure metrology of hard x
... hard x-ray microscopy, microdiffraction, and spectromicroscopy using a hard x-ray microprobe have the ability to analyze materials nondestructively with precise spatial information. In these techniques, not only the focusing size of the hard x rays, but also the focusing intensity distribution prope ...
... hard x-ray microscopy, microdiffraction, and spectromicroscopy using a hard x-ray microprobe have the ability to analyze materials nondestructively with precise spatial information. In these techniques, not only the focusing size of the hard x rays, but also the focusing intensity distribution prope ...
Two-Mirror Apodization for High-Contrast Imaging
... In a recent paper, Goncharov et al. (2002) propose using two mirrors to convert a uniform-intensity beam to one of nonuniform intensity—that is, an apodized exit beam. The motivation for their work was to “mask” the secondary mirror in designs of large twomirror telescopes with fast spherical primar ...
... In a recent paper, Goncharov et al. (2002) propose using two mirrors to convert a uniform-intensity beam to one of nonuniform intensity—that is, an apodized exit beam. The motivation for their work was to “mask” the secondary mirror in designs of large twomirror telescopes with fast spherical primar ...
Standing-wave transform spectrometer based on integrated MEMS
... cessing [7] that has enabled the real-time discrimination of different spectra. This simple processing also means that the operation of the spectrometer need not correspond exactly to the standard Fourier transform response, as long as the response of the spectrometer is linear in the signal; other ...
... cessing [7] that has enabled the real-time discrimination of different spectra. This simple processing also means that the operation of the spectrometer need not correspond exactly to the standard Fourier transform response, as long as the response of the spectrometer is linear in the signal; other ...
Chapter O2
... incidence. As you can see, the reflected rays all pass through one point as they travel away from the mirror. If a piece of paper or screen were placed at O2.1 A real object and a concave mirror forming a this point, an image of the real image. arrow head would appear. In fact, this is called a real ...
... incidence. As you can see, the reflected rays all pass through one point as they travel away from the mirror. If a piece of paper or screen were placed at O2.1 A real object and a concave mirror forming a this point, an image of the real image. arrow head would appear. In fact, this is called a real ...
Fast-Fourier-domain delay line for in vivo optical coherence
... Often these parameters are conflicting, forcing a compromise of one for another. It is also important to note that, although the maximum scan rate is typically desired, an increase in speed requires a proportional increase in optical power to maintain the same SNR.6 In recent years there has been mu ...
... Often these parameters are conflicting, forcing a compromise of one for another. It is also important to note that, although the maximum scan rate is typically desired, an increase in speed requires a proportional increase in optical power to maintain the same SNR.6 In recent years there has been mu ...
Fabrication of elliptically figured mirror for focusing hard x rays to
... to obtain the optimum performances of focusing mirrors. Equation 共1兲 shows that the longer the object distance u, the smaller the focal size obtained. In this study, a focusing test was carried out at the 1-km-long beamline 共BL29XUL兲 of SPring-8. The geometrical relationships between the x-ray sourc ...
... to obtain the optimum performances of focusing mirrors. Equation 共1兲 shows that the longer the object distance u, the smaller the focal size obtained. In this study, a focusing test was carried out at the 1-km-long beamline 共BL29XUL兲 of SPring-8. The geometrical relationships between the x-ray sourc ...
Pupil Mapping in 2-D for High-Contrast Imaging
... permits us to separate starlight from planet-light. For perspective, sidelobes less than 10−10 are roughly 8 orders of magnitude lower than the Airy-ring pattern that would be expected from an idealized conventional telescope image. Several other coronagraphic methods have been suggested. One of the ...
... permits us to separate starlight from planet-light. For perspective, sidelobes less than 10−10 are roughly 8 orders of magnitude lower than the Airy-ring pattern that would be expected from an idealized conventional telescope image. Several other coronagraphic methods have been suggested. One of the ...
Constant Resolution Omnidirectional Cameras
... some cases, one can design the shape of the mirror in such a way that certain world-to-image geometric properties are preserved - which we will refer to as linear projection properties. The choice of the properties that should be preserved by the catadioptric imaging system is naturally related to t ...
... some cases, one can design the shape of the mirror in such a way that certain world-to-image geometric properties are preserved - which we will refer to as linear projection properties. The choice of the properties that should be preserved by the catadioptric imaging system is naturally related to t ...
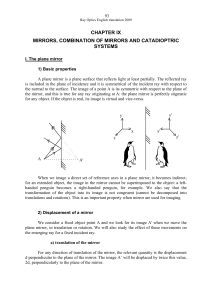
mirrors, combination of mirrors and catadioptric systems
... comes out parallel to the incident ray. Such a system is often used instead of a single plane mirror when you cannot adjust its direction. For example, such retro reflectors have been set on the Moon to measure the Moon-to-Earth distance, through a measurement of the time it takes for light to trave ...
... comes out parallel to the incident ray. Such a system is often used instead of a single plane mirror when you cannot adjust its direction. For example, such retro reflectors have been set on the Moon to measure the Moon-to-Earth distance, through a measurement of the time it takes for light to trave ...
Mirrors - Purdue Physics
... § The image has a height hi located a distance di from the surface of the mirror on the same side of the mirror as the object with height ho and distance do from the mirror § The image is inverted and reduced in size relative to the object that produced the image § The image is called real when you ...
... § The image has a height hi located a distance di from the surface of the mirror on the same side of the mirror as the object with height ho and distance do from the mirror § The image is inverted and reduced in size relative to the object that produced the image § The image is called real when you ...
Mirrors and Reflection NOTES
... 3. Be able to determine the focal length when given the radius of curvature. 4. Know that parallel light rays (those from a very distant object) converge at the focus. 5. Be able to locate the position of an object formed by a plane mirror. Be able to predict the image's orientation. AP Free Respons ...
... 3. Be able to determine the focal length when given the radius of curvature. 4. Know that parallel light rays (those from a very distant object) converge at the focus. 5. Be able to locate the position of an object formed by a plane mirror. Be able to predict the image's orientation. AP Free Respons ...
Mirrors
... In this and the next chapter we will study the behavior of visible light using ray optics. In ray optics one replaces the original electromagnetic wave with light rays. The direction of propagation of the wave is then determined by simple rules involving the interaction of the light rays with solid ...
... In this and the next chapter we will study the behavior of visible light using ray optics. In ray optics one replaces the original electromagnetic wave with light rays. The direction of propagation of the wave is then determined by simple rules involving the interaction of the light rays with solid ...
Spherical Mirrors
... Image Formation by a Convex Mirror Place an object (represented by an upright arrow) on the principle axis of a convex mirror. Once again we can locate the image with the help of three light rays emerging from the top of the arrow. ...
... Image Formation by a Convex Mirror Place an object (represented by an upright arrow) on the principle axis of a convex mirror. Once again we can locate the image with the help of three light rays emerging from the top of the arrow. ...
Magic Mirror (Snow White)

The Magic Mirror is a mystical object that is featured in the story of Snow White.