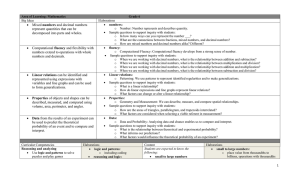
Algebra II - Curriculum Map 2014-2015
... rational exponents. For example, we define 51/3 to be the cube root of 5 because we want (51/3)3 = 5(1/3)3 to hold, so (51/3)3 must equal 5. N.RN.A.2 - Rewrite expressions involving radicals and rational exponents using the properties of exponents. S.IC.A.1 - Understand statistics as a process for m ...
... rational exponents. For example, we define 51/3 to be the cube root of 5 because we want (51/3)3 = 5(1/3)3 to hold, so (51/3)3 must equal 5. N.RN.A.2 - Rewrite expressions involving radicals and rational exponents using the properties of exponents. S.IC.A.1 - Understand statistics as a process for m ...
Machine Learning Methods for Decision Support
... Create branches under the variable corresponding to its values Under each branch repeat the process with the remaining ...
... Create branches under the variable corresponding to its values Under each branch repeat the process with the remaining ...
Presentation file I - Discovery Systems Laboratory
... Create branches under the variable corresponding to its values Under each branch repeat the process with the remaining ...
... Create branches under the variable corresponding to its values Under each branch repeat the process with the remaining ...
Reasoning with Uncertainty
... into the calculations. For the rigours of the scientific method, this is an appropriate response to prevent the introduction of extraneous data that might skew the experimental ...
... into the calculations. For the rigours of the scientific method, this is an appropriate response to prevent the introduction of extraneous data that might skew the experimental ...
Improper Fraction
... Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, create a story context for (2/3) ÷ (3/4) and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient ...
... Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, create a story context for (2/3) ÷ (3/4) and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient ...
Science- Kindergarten
... (e.g., spin a spinner, roll a die, toss a coin) o listing all possible outcomes to ...
... (e.g., spin a spinner, roll a die, toss a coin) o listing all possible outcomes to ...
Poster - The University of Manchester
... I The second term measures the quality of our selected feature set Xθ , and is small when we ...
... I The second term measures the quality of our selected feature set Xθ , and is small when we ...
Solving Everyday Physical Reasoning Problems
... about technical domains, little progress has been made on applying QR ideas to common sense reasoning per se. A key difference between common sense problems and reasoning in technical domains is breadth. In domains such as electronics or thermodynamics, a small library of components and relationship ...
... about technical domains, little progress has been made on applying QR ideas to common sense reasoning per se. A key difference between common sense problems and reasoning in technical domains is breadth. In domains such as electronics or thermodynamics, a small library of components and relationship ...