Markets
... If the market increases greatly in size (number of buyers) or all the buyers have greater incomes over time, we have a change in demand. The entire schedule and P,$ • P Q curves must be redrawn. ...
... If the market increases greatly in size (number of buyers) or all the buyers have greater incomes over time, we have a change in demand. The entire schedule and P,$ • P Q curves must be redrawn. ...
Chapter 8 - Perfect Competition
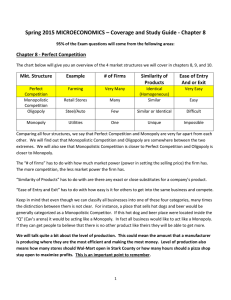
... The “# of firms” has to do with how much market power (power in setting the selling price) the firm has. The more competition, the less market power the firm has. “Similarity of Products” has to do with are there any exact or close substitutes for a company’s product. “Ease of Entry and Exit” has to ...
... The “# of firms” has to do with how much market power (power in setting the selling price) the firm has. The more competition, the less market power the firm has. “Similarity of Products” has to do with are there any exact or close substitutes for a company’s product. “Ease of Entry and Exit” has to ...
Worksheet 2 2.1 Economic systems - Liceo Ginnasio Statale «Virgilio
... Firms will allocate resources to the production of the most profitable goods and services There will always be full employment of resources Firms have an incentive to keep their costs of production as low as possible Consumers will only get what they want depending on their willingness and ability t ...
... Firms will allocate resources to the production of the most profitable goods and services There will always be full employment of resources Firms have an incentive to keep their costs of production as low as possible Consumers will only get what they want depending on their willingness and ability t ...
Review Class Eight
... First we discuss the behavior of firm supply in the perfectly competitive market. Technical assumptions of Pure competition: There are many small firms and millions of consumers such that individuals in the market are price takers. The goods produced by every firm are identical, so the main segment ...
... First we discuss the behavior of firm supply in the perfectly competitive market. Technical assumptions of Pure competition: There are many small firms and millions of consumers such that individuals in the market are price takers. The goods produced by every firm are identical, so the main segment ...
Chapter 6: The Role of Profit
... The effects of profit-maximizing behavior on consumers in each market structure The short-run and long-run outcomes of profit-maximizing behavior natural monopolies and how governments regulate them ...
... The effects of profit-maximizing behavior on consumers in each market structure The short-run and long-run outcomes of profit-maximizing behavior natural monopolies and how governments regulate them ...
ECON 2010-200 Principles of Microeconomics
... exams. A small percentage of the final grade will be determined by performance in a game, and by some data collection exercises to be given out in class. ...
... exams. A small percentage of the final grade will be determined by performance in a game, and by some data collection exercises to be given out in class. ...
Short Run Market Equilibrium
... of pro¯t opportunities, and existing ¯rms can exit the market if they are receiving negative pro¯ts. To make things simple, we will assume that there is free entry and exit, and that all ¯rms have the same technology and therefore the same cost functions. We will also assume that good x is a constan ...
... of pro¯t opportunities, and existing ¯rms can exit the market if they are receiving negative pro¯ts. To make things simple, we will assume that there is free entry and exit, and that all ¯rms have the same technology and therefore the same cost functions. We will also assume that good x is a constan ...
Student Study Guide for Chapter 11
... 20. 1. There are numerous small sellers and buyers, so small that no individual seller or buyer can affect the market price. 2. Within any particular market, only one kind of good or service is traded, and all units are identical. 3. Producers can freely enter or exit the industry. 4. Buyers and sel ...
... 20. 1. There are numerous small sellers and buyers, so small that no individual seller or buyer can affect the market price. 2. Within any particular market, only one kind of good or service is traded, and all units are identical. 3. Producers can freely enter or exit the industry. 4. Buyers and sel ...
Chapter 11: Markets Without Market Power
... 20. 1. There are numerous small sellers and buyers, so small that no individual seller or buyer can affect the market price. 2. Within any particular market, only one kind of good or service is traded, and all units are identical. 3. Producers can freely enter or exit the industry. 4. Buyers and sel ...
... 20. 1. There are numerous small sellers and buyers, so small that no individual seller or buyer can affect the market price. 2. Within any particular market, only one kind of good or service is traded, and all units are identical. 3. Producers can freely enter or exit the industry. 4. Buyers and sel ...
2017 nc-ccim commercial market forecast
... • Please register by March 13, 2017. NC-CCIM Members: $45, Non-Members: $55 • Reserved Table of 10 may be purchased for $400.00 (Attendee names can be emailed to [email protected]) • Walk-in Registration: Everyone: $75 (if space is available) Market Forecast Tickets are Non Refundable - Plea ...
... • Please register by March 13, 2017. NC-CCIM Members: $45, Non-Members: $55 • Reserved Table of 10 may be purchased for $400.00 (Attendee names can be emailed to [email protected]) • Walk-in Registration: Everyone: $75 (if space is available) Market Forecast Tickets are Non Refundable - Plea ...
Seven Out of Seven Times, Emerging Market
... Past performance is no guarantee of future results, and there is no assurance that the fund will achieve its investment objectives. Current performance may be lower or higher than the performance quoted. The principal value and return of an investment will fluctuate so that your shares, when redeeme ...
... Past performance is no guarantee of future results, and there is no assurance that the fund will achieve its investment objectives. Current performance may be lower or higher than the performance quoted. The principal value and return of an investment will fluctuate so that your shares, when redeeme ...
VII. The firm`s short
... As S0 shifts to S1, the market price rises hence pushing the firms demand curve back to its original level. The higher price encourages firms to increase production back to q0. So now we have fewer firms, but all producing at the old equilibrium output level. Point c is a long run equilibrium. The l ...
... As S0 shifts to S1, the market price rises hence pushing the firms demand curve back to its original level. The higher price encourages firms to increase production back to q0. So now we have fewer firms, but all producing at the old equilibrium output level. Point c is a long run equilibrium. The l ...
Class 3
... Comparison between long run industry equilibrium under perfect competition and long run profit maximization under monopoly: – Under monopoly, market price is higher and output is ...
... Comparison between long run industry equilibrium under perfect competition and long run profit maximization under monopoly: – Under monopoly, market price is higher and output is ...
MC ATC
... price, marginal revenue, marginal cost, average total cost, and profits in a monopolistic market. • Measure the degree of market power with the Lerner index. • Describe 4 barriers to entry that may enable monopoly power. ...
... price, marginal revenue, marginal cost, average total cost, and profits in a monopolistic market. • Measure the degree of market power with the Lerner index. • Describe 4 barriers to entry that may enable monopoly power. ...
Aalborg Universitet Globalization and the Next Economy Li, Xing; Clark, Woodrow W.
... international community or seeking economic aid from international financial institutions. This position can be seen repeatedly in a number of international multi-lateral organizations such as the UN, World Bank, WTO and others throughout the early and mid-1990s. Besides dramatic transformations in ...
... international community or seeking economic aid from international financial institutions. This position can be seen repeatedly in a number of international multi-lateral organizations such as the UN, World Bank, WTO and others throughout the early and mid-1990s. Besides dramatic transformations in ...
S&D powerpoint
... Pre-game instructions: 1. The teacher is the umpire and will be the judge on any close calls. 2. Divide the class up into two or three teams of nine players on each team. (if this doesn’t work for the number of students in your class, some students may have to go to the board twice). ...
... Pre-game instructions: 1. The teacher is the umpire and will be the judge on any close calls. 2. Divide the class up into two or three teams of nine players on each team. (if this doesn’t work for the number of students in your class, some students may have to go to the board twice). ...
ECON 2010-400 Principles of Microeconomics
... decide how much to produce and with what technology. The course explores how "the magic of the market" coordinates these decisons.In addition, the course considers such questions as: Why is competition socially desirable? Is competition likely? How do firms behave in the absence of ...
... decide how much to produce and with what technology. The course explores how "the magic of the market" coordinates these decisons.In addition, the course considers such questions as: Why is competition socially desirable? Is competition likely? How do firms behave in the absence of ...
Slide 1
... For example, if you have a job, most likely someone tells you what to do. Your labor time is allocated to specific tasks by command. A command system works well in organizations with clear lines of authority but badly in an entire economy. ...
... For example, if you have a job, most likely someone tells you what to do. Your labor time is allocated to specific tasks by command. A command system works well in organizations with clear lines of authority but badly in an entire economy. ...
ch5
... For example, if you have a job, most likely someone tells you what to do. Your labor time is allocated to specific tasks by command. A command system works well in organizations with clear lines of authority but badly in an entire economy. ...
... For example, if you have a job, most likely someone tells you what to do. Your labor time is allocated to specific tasks by command. A command system works well in organizations with clear lines of authority but badly in an entire economy. ...
Chapter 6 PowerPoint
... resources go to the uses that consumers value most highly. • Market Problems – Imperfect competition between firms in a market can affect prices and consumer decisions. ...
... resources go to the uses that consumers value most highly. • Market Problems – Imperfect competition between firms in a market can affect prices and consumer decisions. ...