
Unit 1 STUDY GUIDE
... Microeconomics studies individual markets. So, we are studying the behavior of people producing and exchanging to get the stuff they want in a particular case. This might be a market for a specific product, like Coca-Cola, or an entire (but specific) industry, like soda or beverages. There concepts ...
... Microeconomics studies individual markets. So, we are studying the behavior of people producing and exchanging to get the stuff they want in a particular case. This might be a market for a specific product, like Coca-Cola, or an entire (but specific) industry, like soda or beverages. There concepts ...
Experimental Macroeconomics - UCI School of Social Sciences
... second design is to introduce a constant small probability, 1 − δ, that each period will be the last one played in a sequence, and allow enough time for several indefinite sequences to be played in an experimental session [Duffy and Ochs (1999, 2002), Noussair and Lei (2002), Capra et al. (2005)]. Th ...
... second design is to introduce a constant small probability, 1 − δ, that each period will be the last one played in a sequence, and allow enough time for several indefinite sequences to be played in an experimental session [Duffy and Ochs (1999, 2002), Noussair and Lei (2002), Capra et al. (2005)]. Th ...
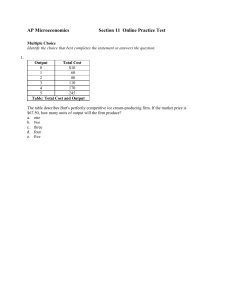
S 11 Practice MC Test
... e. entry; shutdown 9. Suppose that the market for haircuts in a community is a perfectly competitive constant-cost industry and that the market is initially in long-run equilibrium. Subsequently, an increase in population increases the demand for haircuts. In the long run, we expect that: a. more fi ...
... e. entry; shutdown 9. Suppose that the market for haircuts in a community is a perfectly competitive constant-cost industry and that the market is initially in long-run equilibrium. Subsequently, an increase in population increases the demand for haircuts. In the long run, we expect that: a. more fi ...
GRANITE HILLS HIGH SCHOOL Department of Social Sciences
... average revenues, marginal and average costs, and profits. Students should understand the adjustment process to long-run equilibrium. In considering the market behavior of a monopolist, students identify and examine the sources of monopoly power and understand the relationship between a monopolist’ ...
... average revenues, marginal and average costs, and profits. Students should understand the adjustment process to long-run equilibrium. In considering the market behavior of a monopolist, students identify and examine the sources of monopoly power and understand the relationship between a monopolist’ ...
Measuring the efficiency of Capital Market regulations
... policies that are primary input variables. The given result - the regulation set should accomplish as much as possible of given goals. It doesn't look a very difficult task if these goals, objectives and policies are not contradictory. However in reality there are plenty if policies that are in conf ...
... policies that are primary input variables. The given result - the regulation set should accomplish as much as possible of given goals. It doesn't look a very difficult task if these goals, objectives and policies are not contradictory. However in reality there are plenty if policies that are in conf ...
Shortages and Surpluses
... 2.d.3. According to the graph above, the market equilibrium is when the price is $10 and the quantity demanded is 3. However, at a price of $14, the quantity of pizza supplied is 4 and the quantity of pizza demanded is only 2. This means that the suppliers are willing to supply more pizza and the bu ...
... 2.d.3. According to the graph above, the market equilibrium is when the price is $10 and the quantity demanded is 3. However, at a price of $14, the quantity of pizza supplied is 4 and the quantity of pizza demanded is only 2. This means that the suppliers are willing to supply more pizza and the bu ...
UP School of Economics Discussion Papers
... Note that now (N, N) is the Nash (also the Dominant Strategy) equilibrium of the S = (5, 2, 1)modified game. The after-tax payoff delivered by (N, N) is now (8, 8) > (3, 3), the payoff from (D, D) for the players in the original Fishing Game market failure. Thus, the statute S is now, as it were, a ...
... Note that now (N, N) is the Nash (also the Dominant Strategy) equilibrium of the S = (5, 2, 1)modified game. The after-tax payoff delivered by (N, N) is now (8, 8) > (3, 3), the payoff from (D, D) for the players in the original Fishing Game market failure. Thus, the statute S is now, as it were, a ...
EconomicsToday-Chapter24
... firms are adjusting all of the time) – At break-even, resources will not enter or exit the market. – In competitive long-run equilibrium, firms will make zero economic profits. ...
... firms are adjusting all of the time) – At break-even, resources will not enter or exit the market. – In competitive long-run equilibrium, firms will make zero economic profits. ...
Chap002
... showed why when B > C the action is taken. (In this case, the item is bought.) Also when C > B the action is rejected. (In this case, the item is not purchased.) Thus where supply equals demand, the purchasing stops and equilibrium is reached. The sum of the net benefits of each participant in the m ...
... showed why when B > C the action is taken. (In this case, the item is bought.) Also when C > B the action is rejected. (In this case, the item is not purchased.) Thus where supply equals demand, the purchasing stops and equilibrium is reached. The sum of the net benefits of each participant in the m ...
Producer Surplus - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... produces the smallest deadweight loss. But how can we predict the size of the deadweight loss associated with a given policy? For a tax imposed when demand or supply, or both, is inelastic will cause a relatively small decrease in quantity transacted and a small deadweight loss. ...
... produces the smallest deadweight loss. But how can we predict the size of the deadweight loss associated with a given policy? For a tax imposed when demand or supply, or both, is inelastic will cause a relatively small decrease in quantity transacted and a small deadweight loss. ...
Consumer and Producer Surplus
... produces the smallest deadweight loss. But how can we predict the size of the deadweight loss associated with a given policy? For a tax imposed when demand or supply, or both, is inelastic will cause a relatively small decrease in quantity transacted and a small deadweight loss. ...
... produces the smallest deadweight loss. But how can we predict the size of the deadweight loss associated with a given policy? For a tax imposed when demand or supply, or both, is inelastic will cause a relatively small decrease in quantity transacted and a small deadweight loss. ...
Core course: EC02 B02 Micro economics II
... a) Firm is the price giver and the industry is a price taker b) Firm is the price taker and the industry is a price giver c) Both are price makers d) Both are price takers 42.One of the essential conditions of perfect competition is a) Product Differentiation b) Multiplicity of prices for identical ...
... a) Firm is the price giver and the industry is a price taker b) Firm is the price taker and the industry is a price giver c) Both are price makers d) Both are price takers 42.One of the essential conditions of perfect competition is a) Product Differentiation b) Multiplicity of prices for identical ...
Lecture 4: Markets In Action
... demanded and quantity supplied are influenced by changing opportunity costs. The law of supply and the law of demand describe producers’ and consumers’ predictable reactions to changes in price. Economics for Leaders ...
... demanded and quantity supplied are influenced by changing opportunity costs. The law of supply and the law of demand describe producers’ and consumers’ predictable reactions to changes in price. Economics for Leaders ...
FREE Sample Here
... 2. The U.S. national market graph and the international market graph. Question to the class: “Let’s say that the United States is willing to open up to free trade and integrate into the world market. If it does this, the world price will also be the price within the United States. How much will the ...
... 2. The U.S. national market graph and the international market graph. Question to the class: “Let’s say that the United States is willing to open up to free trade and integrate into the world market. If it does this, the world price will also be the price within the United States. How much will the ...
CREF Money Market
... Active Management: The investment is actively managed and subject to the risk that the advisor’s usage of investment techniques and risk analyses to make investment decisions fails to perform as expected, which may cause the portfolio to lose value or underperform investments with similar objectives ...
... Active Management: The investment is actively managed and subject to the risk that the advisor’s usage of investment techniques and risk analyses to make investment decisions fails to perform as expected, which may cause the portfolio to lose value or underperform investments with similar objectives ...
ECON 3070-001 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory
... price discrimination. Market theory continued: monopolistic competition, industrial organization, oligopoly and duopoly. game theory. Ch. 26 & 27 ...
... price discrimination. Market theory continued: monopolistic competition, industrial organization, oligopoly and duopoly. game theory. Ch. 26 & 27 ...
Name: Per. ____ Date: Ch. 5 Study Guide / Review Multiple Choice
... 13. When the selling price of a good goes up, what is the relationship to the quantity supplied? A. The cost of production goes down. B. The profit made on each item goes down. C. It becomes practical to produce more goods. D. There is no relationship between the two. ...
... 13. When the selling price of a good goes up, what is the relationship to the quantity supplied? A. The cost of production goes down. B. The profit made on each item goes down. C. It becomes practical to produce more goods. D. There is no relationship between the two. ...









![ECONOMICS – I – [1.2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008346471_1-f2a3a71e5a31e7d1d392b3a8eac2c132-300x300.png)

![Producer Surplus - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/012360938_1-b51a69a69f55945a4ed39010195f11e1-300x300.png)










