FEATURES APPLICATIONS D
... ESD Rating (Human Body Model) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2000V (Machine Model) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200V (Charge Device Model) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1500V ...
... ESD Rating (Human Body Model) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2000V (Machine Model) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200V (Charge Device Model) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1500V ...
bcd decade counters/ 4-bit binary counters 74ls160
... output when the CET input is HIGH while the counter is in state 9 (HLLH). From this state they increment to state 0 (LLLL). If loaded with a code in excess of 9 they return to their legitimate sequence within two counts, as explained in the state diagram. States 10 through 15 do not generate a TC ou ...
... output when the CET input is HIGH while the counter is in state 9 (HLLH). From this state they increment to state 0 (LLLL). If loaded with a code in excess of 9 they return to their legitimate sequence within two counts, as explained in the state diagram. States 10 through 15 do not generate a TC ou ...
$doc.title
... Figure 42. DC-Coupled, G = _1V/V, Bipolar Supply Specifications and Test Circuit These circuits show ±5V operation. The same circuits can be applied with bipolar supplies from ±2.5V to ±6V. Internal supply independent biasing gives nearly the same performance for the OPA4684 over this wide range of ...
... Figure 42. DC-Coupled, G = _1V/V, Bipolar Supply Specifications and Test Circuit These circuits show ±5V operation. The same circuits can be applied with bipolar supplies from ±2.5V to ±6V. Internal supply independent biasing gives nearly the same performance for the OPA4684 over this wide range of ...
Chapter 6: Parallel Circuits
... • To calculate the power dissipated by each resistor, use either VI, I2R, or V2/R • Total power consumed is the sum of the individual powers • Compare with IT2RT ...
... • To calculate the power dissipated by each resistor, use either VI, I2R, or V2/R • Total power consumed is the sum of the individual powers • Compare with IT2RT ...
FEATURES DESCRIPTION D
... voltage-feedback amplifier with a very low input noise voltage and high output current using a low 5.6mA supply current. At unity-gain, the OPA820 gives > 800MHz bandwidth with < 1dB peaking. The OPA820 complements this high-speed operation with excellent DC precision in a low-power device. A worst- ...
... voltage-feedback amplifier with a very low input noise voltage and high output current using a low 5.6mA supply current. At unity-gain, the OPA820 gives > 800MHz bandwidth with < 1dB peaking. The OPA820 complements this high-speed operation with excellent DC precision in a low-power device. A worst- ...
1. Introduction - About the journal
... and current gain was used for f0 and CO control. Electronic control of f0 in [18] is possible by adjustable current gain, but CO control is available only by adjusting of grounded resistor. Solution in [18] employs only one active element, but its disadvantage is the dependence of one of produced am ...
... and current gain was used for f0 and CO control. Electronic control of f0 in [18] is possible by adjustable current gain, but CO control is available only by adjusting of grounded resistor. Solution in [18] employs only one active element, but its disadvantage is the dependence of one of produced am ...
LT5518 - 1.5GHz - 2.4GHz High Linearity Direct
... LO (Pin 3): LO Input. The LO input is an AC-coupled singleended input with approximately 50Ω input impedance at RF frequencies. Externally applied DC voltage should be within the range –0.5V to VCC + 0.5V in order to avoid turning on ESD protection diodes. BBPQ, BBMQ (Pins 7, 5): Baseband Inputs for ...
... LO (Pin 3): LO Input. The LO input is an AC-coupled singleended input with approximately 50Ω input impedance at RF frequencies. Externally applied DC voltage should be within the range –0.5V to VCC + 0.5V in order to avoid turning on ESD protection diodes. BBPQ, BBMQ (Pins 7, 5): Baseband Inputs for ...
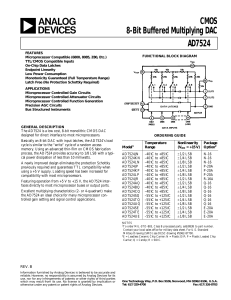
AD7524 CMOS 8-Bit Buffered Multiplying DAC
... highly stable thin film R-2R ladder and eight N-channel current switches on a monolithic chip. Most applications require the addition of only an output operational amplifier and a voltage or current reference. The simplified D/A circuit is shown in Figure 1. An inverted R-2R ladder structure is used ...
... highly stable thin film R-2R ladder and eight N-channel current switches on a monolithic chip. Most applications require the addition of only an output operational amplifier and a voltage or current reference. The simplified D/A circuit is shown in Figure 1. An inverted R-2R ladder structure is used ...
LF155/LF156/LF256 LF257 LF355 LF356
... and VOS, IB and IOS are measured at VCM = 0. The Temperature Coefficient of the adjusted input offset voltage changes only a small amount (0.5 μV/°C typically) for each mV of adjustment from its original unadjusted value. Common-mode rejection and open-loop voltage gain are also unaffected by offset ...
... and VOS, IB and IOS are measured at VCM = 0. The Temperature Coefficient of the adjusted input offset voltage changes only a small amount (0.5 μV/°C typically) for each mV of adjustment from its original unadjusted value. Common-mode rejection and open-loop voltage gain are also unaffected by offset ...
Dual-Channel Pulse-Width-Modulation (PWM
... voltage drops too low (to approximately 2.9 V) for proper operation. A hysteresis voltage of 200 mV eliminates false triggering on noise and chattering. short-circuit protection (SCP) The TL1454A SCP function prevents damage to the power switches when the converter output is shorted to ground. In no ...
... voltage drops too low (to approximately 2.9 V) for proper operation. A hysteresis voltage of 200 mV eliminates false triggering on noise and chattering. short-circuit protection (SCP) The TL1454A SCP function prevents damage to the power switches when the converter output is shorted to ground. In no ...
Digital Electronics
... would be very forgiving of imperfect input voltages ... VIN >VM = V+/ 2 --> VOUT = 0 V VIN < VM = V+/ 2 --> VOUT = V+ Note that the ideal inverter returns correct logical outputs (0 V or V+) even when the input voltage is corrupted by noise, voltage spikes, etc. that are nearly half the supply volta ...
... would be very forgiving of imperfect input voltages ... VIN >VM = V+/ 2 --> VOUT = 0 V VIN < VM = V+/ 2 --> VOUT = V+ Note that the ideal inverter returns correct logical outputs (0 V or V+) even when the input voltage is corrupted by noise, voltage spikes, etc. that are nearly half the supply volta ...
UCC28060 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... an offset of approximately 125 mV. During soft-start events (undervoltage, brownout, or disable), COMP is pulled low. Normal operation only resumes after the soft-start event clears and COMP has been discharged below 0.5 V, making sure that the circuit restarts with a low COMP voltage and a short on ...
... an offset of approximately 125 mV. During soft-start events (undervoltage, brownout, or disable), COMP is pulled low. Normal operation only resumes after the soft-start event clears and COMP has been discharged below 0.5 V, making sure that the circuit restarts with a low COMP voltage and a short on ...
EDM-M - Duplomatic Oleodinamica
... ok OUTPUT”, located on pin 9 (referred to zero power supply, pin 15) with load resistance of 220 KΩ and max current 100 mA . When the card works normally, on this pin there is the same voltage as the power supply; when there is an anomaly, the output voltage is zero. The anomalies could be: - low vo ...
... ok OUTPUT”, located on pin 9 (referred to zero power supply, pin 15) with load resistance of 220 KΩ and max current 100 mA . When the card works normally, on this pin there is the same voltage as the power supply; when there is an anomaly, the output voltage is zero. The anomalies could be: - low vo ...
Data Sheet Features
... Where L1, L2, etc. are the individual losses as a percentage of input power. Although all dissipative elements in the regulator produce losses, two major sources usually account for most of the power losses: VIN quiescent current and I2R losses. The VIN quiescent current loss dominates the efficienc ...
... Where L1, L2, etc. are the individual losses as a percentage of input power. Although all dissipative elements in the regulator produce losses, two major sources usually account for most of the power losses: VIN quiescent current and I2R losses. The VIN quiescent current loss dominates the efficienc ...
OPA684 Low-Power, Current Feedback OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER With Disable FEATURES
... output current to support this swing into a 100Ω load. This minimal output headroom requirement is complemented by a similar 1.2V input stage headroom giving exceptional capability for single +5V operation. The OPA684’s low 1.7mA supply current is precisely trimmed at 25°C. This trim, along with low ...
... output current to support this swing into a 100Ω load. This minimal output headroom requirement is complemented by a similar 1.2V input stage headroom giving exceptional capability for single +5V operation. The OPA684’s low 1.7mA supply current is precisely trimmed at 25°C. This trim, along with low ...
MAX1763 1.5A, Low-Noise, 1MHz, Step-Up DC-DC Converter General Description
... Note 1: Operating voltage. Because the regulator is bootstrapped to the output, once started, the MAX1763 will operate down to 0.7V input. For conditions where VIN might exceed the set VOUT, or where VOUT is set above 4V, an external Schottky diode must be connected from LX to POUT. Note 2: Startup ...
... Note 1: Operating voltage. Because the regulator is bootstrapped to the output, once started, the MAX1763 will operate down to 0.7V input. For conditions where VIN might exceed the set VOUT, or where VOUT is set above 4V, an external Schottky diode must be connected from LX to POUT. Note 2: Startup ...
Normalized calculation of impulse current circuits for given impulse
... with technical parameters, i.e. with the front time and time to halfvalue as well as with the amplitude (fig. 1) [ 1: 2 I ‘). A simple series oscillating circuit (fig. 2) with generally known analytical equations for the equalizing current is usually used to generate such current impulses. When desi ...
... with technical parameters, i.e. with the front time and time to halfvalue as well as with the amplitude (fig. 1) [ 1: 2 I ‘). A simple series oscillating circuit (fig. 2) with generally known analytical equations for the equalizing current is usually used to generate such current impulses. When desi ...
LTC3701 - 2-Phase, Low Input Voltage, Dual Step
... controlled by the voltage on the ITH/RUN pin, which is the output of each error amplifier, EAMP. The VFB pin receives the voltage feedback signal, which is compared to the internal reference voltage by the EAMP. When the load current increases, it causes a slight decrease in VFB relative to the 0.8V ...
... controlled by the voltage on the ITH/RUN pin, which is the output of each error amplifier, EAMP. The VFB pin receives the voltage feedback signal, which is compared to the internal reference voltage by the EAMP. When the load current increases, it causes a slight decrease in VFB relative to the 0.8V ...
Wilson current mirror

A Wilson current mirror is a three-terminal circuit (Fig. 1) that accepts an input current at the input terminal and provides a ""mirrored"" current source or sink output at the output terminal. The mirrored current is a precise copy of the input current. It may be used as a Wilson current source by applying a constant bias current to the input branch as in Fig. 2. The circuit is named after George R. Wilson, an integrated circuit design engineer who worked for Tektronix. Wilson devised this configuration in 1967 when he and Barrie Gilbert challenged each other to find an improved current mirror overnight that would use only three transistors. Wilson won the challenge.