High Step-up Voltage Gain Converter with Ripple
... Actually, current harmonics in fuel cell stack or photovoltaics makes the control of maximum efficiency point difficult, and also generates excessive losses and overheating [20,21], i.e. input current ripple of power converter greatly impact its power conversion efficiency. Thus, high boost-ratio co ...
... Actually, current harmonics in fuel cell stack or photovoltaics makes the control of maximum efficiency point difficult, and also generates excessive losses and overheating [20,21], i.e. input current ripple of power converter greatly impact its power conversion efficiency. Thus, high boost-ratio co ...
30 W 18 to 60-V Input DC/DC Converter w/Auto Track Sequencing
... or 48–V telecom central office (CO) supply. Housed in a 1×2 package, each model has a wide-adjust output voltage that can be set to one of the common intermediate bus voltages of 3.3 V, 5 V, or 12 V. The PTB78560 series incorporates Auto-Track™, a feature that simplifies the power-up sequencing of m ...
... or 48–V telecom central office (CO) supply. Housed in a 1×2 package, each model has a wide-adjust output voltage that can be set to one of the common intermediate bus voltages of 3.3 V, 5 V, or 12 V. The PTB78560 series incorporates Auto-Track™, a feature that simplifies the power-up sequencing of m ...
LP5907-Q1 Automotive 250-mA, Ultra-Low
... Quiescent current is defined here as the difference in current between the input voltage source and the load at VOUT. Ground current is defined here as the total current flowing to ground as a result of all input voltages applied to the device. Dropout voltage is the voltage difference between the i ...
... Quiescent current is defined here as the difference in current between the input voltage source and the load at VOUT. Ground current is defined here as the total current flowing to ground as a result of all input voltages applied to the device. Dropout voltage is the voltage difference between the i ...
FEATURES DESCRIPTION D
... Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is not implied. ...
... Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is not implied. ...
+3 V/+5 V, Dual, Serial Input 12-Bit DAC AD7394
... THEORY OF OPERATION The AD7394 is a pin compatible, dual, 12-bit digital-to-analog converter. This single-supply operation device consumes less than 200 microamps of current while operating from power supplies in the 2.7 V to 5.5 V range, making it ideal for batteryoperated applications. The AD7394 ...
... THEORY OF OPERATION The AD7394 is a pin compatible, dual, 12-bit digital-to-analog converter. This single-supply operation device consumes less than 200 microamps of current while operating from power supplies in the 2.7 V to 5.5 V range, making it ideal for batteryoperated applications. The AD7394 ...
74ALVC162244 Low Voltage 16-Bit Buffer/Line Driver with 3.6V Tolerant Inputs and Outputs
... with 3-STATE outputs to be employed as a memory and address driver, clock driver, or bus oriented transmitter/ receiver. The device is nibble (4-bit) controlled. Each nibble has separate 3-STATE control inputs which can be shorted together for full 16-bit operation. The 74ALVC162244 is designed for ...
... with 3-STATE outputs to be employed as a memory and address driver, clock driver, or bus oriented transmitter/ receiver. The device is nibble (4-bit) controlled. Each nibble has separate 3-STATE control inputs which can be shorted together for full 16-bit operation. The 74ALVC162244 is designed for ...
LTC6403-1 - 200MHz, Low Noise, Low Power Fully Differential Input
... The voltage range for the output common mode range is tested using the test circuit of Figure 1 by applying a voltage on the VOCM pin and testing at both mid supply and at the Electrical Characteristics table limits to verify that the differential gain has not deviated from the mid supply VOCM case ...
... The voltage range for the output common mode range is tested using the test circuit of Figure 1 by applying a voltage on the VOCM pin and testing at both mid supply and at the Electrical Characteristics table limits to verify that the differential gain has not deviated from the mid supply VOCM case ...
DAC1280 - Texas Instruments
... Three gain control pins set the output range in 6dB steps from 0dB to –36db (±2.5V to ±0.039V differential). The attenuation ranges match the gains of the ADS1282 for testing at all gains. The DAC uses a reference voltage and bias resistor to set the full-scale output. The resistor can be adjusted t ...
... Three gain control pins set the output range in 6dB steps from 0dB to –36db (±2.5V to ±0.039V differential). The attenuation ranges match the gains of the ADS1282 for testing at all gains. The DAC uses a reference voltage and bias resistor to set the full-scale output. The resistor can be adjusted t ...
LTM8052/LTM8052A - 36VIN, 5A, 2-Quadrant CVCC Step-Down uModule Regulator
... the positive and negative current limits. This output current limit can be set by a control voltage, a single resistor or a thermistor. LTM8052 features a 125% output overvoltage protection, while LTM8052A does not, allowing operation when the output is above the target regulation point. ...
... the positive and negative current limits. This output current limit can be set by a control voltage, a single resistor or a thermistor. LTM8052 features a 125% output overvoltage protection, while LTM8052A does not, allowing operation when the output is above the target regulation point. ...
3-A Step-Down Converter with Hiccup Short
... output voltage and reaches the nominal output voltage during a soft-start time of typically 0.8 ms. This avoids excessive inrush current and creates a smooth output voltage slope. It also prevents excessive voltage drops of primary cells and rechargeable batteries with high internal impedance. The d ...
... output voltage and reaches the nominal output voltage during a soft-start time of typically 0.8 ms. This avoids excessive inrush current and creates a smooth output voltage slope. It also prevents excessive voltage drops of primary cells and rechargeable batteries with high internal impedance. The d ...
INA301-Q1 36-V, Automotive, High-Speed, Zero
... INA301-Q1 36-V, Automotive, High-Speed, Zero-Drift, Voltage-Output Current-Shunt Monitor With High-Speed, Overcurrent Protection Comparator 1 Features ...
... INA301-Q1 36-V, Automotive, High-Speed, Zero-Drift, Voltage-Output Current-Shunt Monitor With High-Speed, Overcurrent Protection Comparator 1 Features ...
LM56 - Texas Instruments
... point error specification does not include any error introduced by the tolerance of the actual resistors used, nor any error introduced by power supply variation. If the resistors have a ±0.5% tolerance, an additional error of ±0.4°C will be introduced. This error will increase to ±0.8°C when both e ...
... point error specification does not include any error introduced by the tolerance of the actual resistors used, nor any error introduced by power supply variation. If the resistors have a ±0.5% tolerance, an additional error of ±0.4°C will be introduced. This error will increase to ±0.8°C when both e ...
ISL6308 - Intersil
... This pin can be connected to the DAC pin using a resistor (1kΩ to 5kΩ) when the internal DAC voltage is used as the reference voltage. When an external voltage reference is used, it must be connected directly to the REF pin, while the DAC pin is left unconnected. The output voltage will be regulated ...
... This pin can be connected to the DAC pin using a resistor (1kΩ to 5kΩ) when the internal DAC voltage is used as the reference voltage. When an external voltage reference is used, it must be connected directly to the REF pin, while the DAC pin is left unconnected. The output voltage will be regulated ...
DC Biasing using a S..
... cutoff. 3) Minimize Sensitivity to changes in β Manufacturing and temperature variances will result in significant changes in the value β . We seek to design the bias network such that the amplifier parameters will be insensitive to these changes. Q: You’re kidding me right? We’re supposed to achiev ...
... cutoff. 3) Minimize Sensitivity to changes in β Manufacturing and temperature variances will result in significant changes in the value β . We seek to design the bias network such that the amplifier parameters will be insensitive to these changes. Q: You’re kidding me right? We’re supposed to achiev ...
LT5537 - Wide Dynamic Range RF/IF Log Detector.
... terminate the input signal with a 50Ω resistor and AC couple it to one of the input pins while AC grounding the other input pin (Figure 13). The sensitivity (defined as the minimum input power required for the output to be within 3dB of the ideal log-linear response) is –76.4dBm at 200MHz in this ca ...
... terminate the input signal with a 50Ω resistor and AC couple it to one of the input pins while AC grounding the other input pin (Figure 13). The sensitivity (defined as the minimum input power required for the output to be within 3dB of the ideal log-linear response) is –76.4dBm at 200MHz in this ca ...
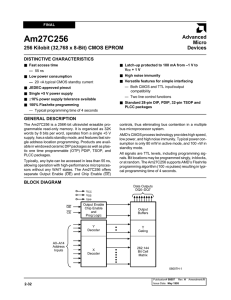
Am27C256
... should be used for device selection. Output Enable (OE) is the output control and should be used to gate data to the output pins, independent of device selection. Assuming that addresses are stable, address access time (tACC) is equal to the delay from CE to output (tCE). Data is available at the ou ...
... should be used for device selection. Output Enable (OE) is the output control and should be used to gate data to the output pins, independent of device selection. Assuming that addresses are stable, address access time (tACC) is equal to the delay from CE to output (tCE). Data is available at the ou ...
MAX9157 Quad Bus LVDS Transceiver General Description Features
... voltage transition time = 1ns (20% to 80%). Input common-mode voltage VCM = 1.2V to 1.8V, DE_ = high, RE_ = low, TA = -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at VCC = 3.3V, |VID| = 0.2V, VCM = 1.2V, and TA = +25°C.) (Notes 3 and 5) ...
... voltage transition time = 1ns (20% to 80%). Input common-mode voltage VCM = 1.2V to 1.8V, DE_ = high, RE_ = low, TA = -40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise noted. Typical values are at VCC = 3.3V, |VID| = 0.2V, VCM = 1.2V, and TA = +25°C.) (Notes 3 and 5) ...
STLC3080
... most of the circuitry is idle and only a low power Off-Hook detection circuit is kept alive. Direct Polarity only is assumed , independently of the selected one. To minimise the power consumption the Off-Hook detection circuit has low common mode current rejection. - Stand by Notice that in Stand-By ...
... most of the circuitry is idle and only a low power Off-Hook detection circuit is kept alive. Direct Polarity only is assumed , independently of the selected one. To minimise the power consumption the Off-Hook detection circuit has low common mode current rejection. - Stand by Notice that in Stand-By ...
Wilson current mirror

A Wilson current mirror is a three-terminal circuit (Fig. 1) that accepts an input current at the input terminal and provides a ""mirrored"" current source or sink output at the output terminal. The mirrored current is a precise copy of the input current. It may be used as a Wilson current source by applying a constant bias current to the input branch as in Fig. 2. The circuit is named after George R. Wilson, an integrated circuit design engineer who worked for Tektronix. Wilson devised this configuration in 1967 when he and Barrie Gilbert challenged each other to find an improved current mirror overnight that would use only three transistors. Wilson won the challenge.