Asymmetrical Interrupting Current Rating of Medium-Voltage
... revision of the circuit breaker standards utilized the “S factor” as a multiplying factor that defined the total current a breaker was rated to interrupt at contact part. The newest revision of C37.04 replaced the S factor with the % dc as the method of evaluating the asymmetrical current offset. Th ...
... revision of the circuit breaker standards utilized the “S factor” as a multiplying factor that defined the total current a breaker was rated to interrupt at contact part. The newest revision of C37.04 replaced the S factor with the % dc as the method of evaluating the asymmetrical current offset. Th ...
74LS74 - eeshop home page
... Note 2: The “Absolute Maximum Ratings” are those values beyond which the safety of the device cannot be guaranteed. The device should not be operated at these limits. The parametric values defined in the Electrical Characteristics tables are not guaranteed at the absolute maximum ratings. The “Recom ...
... Note 2: The “Absolute Maximum Ratings” are those values beyond which the safety of the device cannot be guaranteed. The device should not be operated at these limits. The parametric values defined in the Electrical Characteristics tables are not guaranteed at the absolute maximum ratings. The “Recom ...
Discrete Input Source and Isolated Modules
... Both types of modules provide an LED to show when the input is active and use a scaling resistor for scaling the input range. The input for either module can be set up as momentary, latched, or time duration by means of the configuration software. ...
... Both types of modules provide an LED to show when the input is active and use a scaling resistor for scaling the input range. The input for either module can be set up as momentary, latched, or time duration by means of the configuration software. ...
Diodes
... Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown below. The purpose of the back-to-back power supplies is to make it easy to make measurements near zero supply voltage. Plot the V-I characteristic on graph paper to show the rapid rise in forwa ...
... Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown below. The purpose of the back-to-back power supplies is to make it easy to make measurements near zero supply voltage. Plot the V-I characteristic on graph paper to show the rapid rise in forwa ...
AD8565/AD8566/AD8567 (Rev. G)
... applied common-mode voltage: when the inputs of the AD8565/ AD8566/AD8567 are biased midway between the supplies, the differential signal path gain is controlled by resistive loads Q4 to Q5 (via R9, R10). As the input common-mode level is reduced toward the negative supply (VNEG or GND), the input t ...
... applied common-mode voltage: when the inputs of the AD8565/ AD8566/AD8567 are biased midway between the supplies, the differential signal path gain is controlled by resistive loads Q4 to Q5 (via R9, R10). As the input common-mode level is reduced toward the negative supply (VNEG or GND), the input t ...
Aug 2002 Power Op Amp Protects Load Circuitry with Precise Current Limiting
... when the current limit amplifiers become active and take control of the output voltage. The current limit amplifiers, labeled ISINK and ISRC, provide the unique output current limiting control in both the sinking and sourcing direction. These amplifiers connect to the high impedance output of the in ...
... when the current limit amplifiers become active and take control of the output voltage. The current limit amplifiers, labeled ISINK and ISRC, provide the unique output current limiting control in both the sinking and sourcing direction. These amplifiers connect to the high impedance output of the in ...
Application Note 56 1.2V Reference
... FIGURE 6. Low Voltage Regulator Circuit It is important to use an operational amplifier with low quiescent current such as an LM108. The quiescent current flows through R2 and tends to turn on Q2. However, the value shown is low enough to insure that Q2 can be turned off at worst case condition of n ...
... FIGURE 6. Low Voltage Regulator Circuit It is important to use an operational amplifier with low quiescent current such as an LM108. The quiescent current flows through R2 and tends to turn on Q2. However, the value shown is low enough to insure that Q2 can be turned off at worst case condition of n ...
Universal High Brightness LED Driver
... value can be calculated from the desired peakto-peak LED ripple current in the inductor. Typically, such ripple current is selected to be 30% of the nominal LED current. In the example given here, the nominal current ILED is 350mA. The next step is determining the total voltage drop across the LED s ...
... value can be calculated from the desired peakto-peak LED ripple current in the inductor. Typically, such ripple current is selected to be 30% of the nominal LED current. In the example given here, the nominal current ILED is 350mA. The next step is determining the total voltage drop across the LED s ...
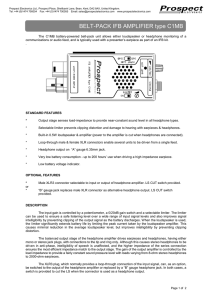
BELT-PACK IFB AMPLIFIER type C1MB
... mono or stereo jack plugs, with connections to the tip and ring only. Although this causes stereo headphones to be driven in anti-phase, intelligibility of speech is unaffected, and the higher impedance of the series connection ensures the most efficient impedance match to the output stage. The gain ...
... mono or stereo jack plugs, with connections to the tip and ring only. Although this causes stereo headphones to be driven in anti-phase, intelligibility of speech is unaffected, and the higher impedance of the series connection ensures the most efficient impedance match to the output stage. The gain ...
Low Cost Laser Diode Controller, High Frequency Modulator and
... amplitude and about 5 ns long with a rise and fall time less than 1 ns to the modulator input, at a frequency of 1 kHz. The voltages at the two ends of R7 were acquired, in two subsequent measurements, with a two GHz bandwidth digital oscilloscope using a high impedance probe in order to not disturb ...
... amplitude and about 5 ns long with a rise and fall time less than 1 ns to the modulator input, at a frequency of 1 kHz. The voltages at the two ends of R7 were acquired, in two subsequent measurements, with a two GHz bandwidth digital oscilloscope using a high impedance probe in order to not disturb ...
Buck Current/Voltage Fed Push-Pull PWM Controllers
... to Fig. 1, the synchronization threshold is 1.4V. The oscillator blanks any synchronization pulse that occurs when OSC is below 2.5V. This allows units, once they discharge below 2.5V, to continue through the current discharge and subsequent charge cycles whether or not other units on the CLKSYN bus ...
... to Fig. 1, the synchronization threshold is 1.4V. The oscillator blanks any synchronization pulse that occurs when OSC is below 2.5V. This allows units, once they discharge below 2.5V, to continue through the current discharge and subsequent charge cycles whether or not other units on the CLKSYN bus ...
Diodes
... Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown below. The purpose of the back-to-back power supplies is to make it easy to make measurements near zero supply voltage. Plot the V-I characteristic on graph paper to show the rapid rise in forwa ...
... Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown below. The purpose of the back-to-back power supplies is to make it easy to make measurements near zero supply voltage. Plot the V-I characteristic on graph paper to show the rapid rise in forwa ...
SN754410
... 2 enabled by 1,2EN and drivers 3 and 4 enabled by 3,4EN. When an enable input is high, the associated drivers are enabled and their outputs become active and in phase with their inputs. When the enable input is low, those drivers are disabled and their outputs are off and in a high-impedance state. ...
... 2 enabled by 1,2EN and drivers 3 and 4 enabled by 3,4EN. When an enable input is high, the associated drivers are enabled and their outputs become active and in phase with their inputs. When the enable input is low, those drivers are disabled and their outputs are off and in a high-impedance state. ...
LT1116 – 12ns, Single Supply Ground-Sensing Comparator
... for a wide range of operating conditions. The output stage provides active drive in both directions for maximum speed into TTL logic or passive loads, yet it has minimal crossconduction current. Unlike other fast comparators, the LT1116 remains stable even for slow transitions through the active reg ...
... for a wide range of operating conditions. The output stage provides active drive in both directions for maximum speed into TTL logic or passive loads, yet it has minimal crossconduction current. Unlike other fast comparators, the LT1116 remains stable even for slow transitions through the active reg ...
Wilson current mirror

A Wilson current mirror is a three-terminal circuit (Fig. 1) that accepts an input current at the input terminal and provides a ""mirrored"" current source or sink output at the output terminal. The mirrored current is a precise copy of the input current. It may be used as a Wilson current source by applying a constant bias current to the input branch as in Fig. 2. The circuit is named after George R. Wilson, an integrated circuit design engineer who worked for Tektronix. Wilson devised this configuration in 1967 when he and Barrie Gilbert challenged each other to find an improved current mirror overnight that would use only three transistors. Wilson won the challenge.