Kirchhoff_Laws
... positive sign of the voltage drop will be assigned to the end of R3 where current enters the resistor. As I1 is in series with R3, the direction of current through R3 is determined by the direction of current flowing out of the current source. Because I1 and R3 are in series, the magnitude of th ...
... positive sign of the voltage drop will be assigned to the end of R3 where current enters the resistor. As I1 is in series with R3, the direction of current through R3 is determined by the direction of current flowing out of the current source. Because I1 and R3 are in series, the magnitude of th ...
MIC39150-1.8WUTR - Datasheet.Directory
... A trade-off for the low dropout voltage is a varying base drive requirement. Micrel’s Super βeta PNP® process reduces this drive requirement to only 2% to 5% of the load current. The MIC39150/1/2 regulators are fully protected from damage due to fault conditions. Current limiting is provided. This l ...
... A trade-off for the low dropout voltage is a varying base drive requirement. Micrel’s Super βeta PNP® process reduces this drive requirement to only 2% to 5% of the load current. The MIC39150/1/2 regulators are fully protected from damage due to fault conditions. Current limiting is provided. This l ...
Analysis, Design and Control of Zero Current Switching DC To DC
... through the resonant inductor start increasing and it reaches maximum current (I max) during resonance and again come back to zero .And that instant gate pulse has to be turned off. Then also current flow in small amount in negative direction due to the inherent diode connected inside the MOSFET. So ...
... through the resonant inductor start increasing and it reaches maximum current (I max) during resonance and again come back to zero .And that instant gate pulse has to be turned off. Then also current flow in small amount in negative direction due to the inherent diode connected inside the MOSFET. So ...
high-frequency response modelling of continuous-time
... amplifier design. In this last application, where current mirrors are used as active loads or as supply-current sensing circuits, there is a need for accurate frequency modelling of the mirrors. The reason is that current mirror excellent high frequency behaviour becomes second-order dynamics in amp ...
... amplifier design. In this last application, where current mirrors are used as active loads or as supply-current sensing circuits, there is a need for accurate frequency modelling of the mirrors. The reason is that current mirror excellent high frequency behaviour becomes second-order dynamics in amp ...
LM321 Low Power Single Op Amp (Rev. C)
... are not needed, no large input currents result from large differential input voltages. The differential input voltage may be larger than V+ without damaging the device. Protection should be provided to prevent the input voltages from going negative more than −0.3 VDC (at 25°C).An input clamp diode w ...
... are not needed, no large input currents result from large differential input voltages. The differential input voltage may be larger than V+ without damaging the device. Protection should be provided to prevent the input voltages from going negative more than −0.3 VDC (at 25°C).An input clamp diode w ...
Voltage, Current and Ohm`s Law
... 1. Using your voltmeter and your ammeter, determine the resistance of each light bulb twice: once when the filament is relatively cool (measure I when V = 1 volt and note brightness of bulb) and again when the filament is very hot (measure I when V = 5 volts and note brightness of bulb). In the case ...
... 1. Using your voltmeter and your ammeter, determine the resistance of each light bulb twice: once when the filament is relatively cool (measure I when V = 1 volt and note brightness of bulb) and again when the filament is very hot (measure I when V = 5 volts and note brightness of bulb). In the case ...
High Voltage Current Shunt Monitor AD8212
... Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. N ...
... Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. N ...
AD8200 High Common-Mode Voltage, Single
... The AD8200 consists of a preamp and buffer arranged as shown in Figure 3. Like-named resistors have equal values. The preamp incorporates a dynamic bridge (subtractor) circuit. Identical networks (within the shaded areas), consisting of RA, RB, RC, and RG, attenuate input signals applied to Pins 1 a ...
... The AD8200 consists of a preamp and buffer arranged as shown in Figure 3. Like-named resistors have equal values. The preamp incorporates a dynamic bridge (subtractor) circuit. Identical networks (within the shaded areas), consisting of RA, RB, RC, and RG, attenuate input signals applied to Pins 1 a ...
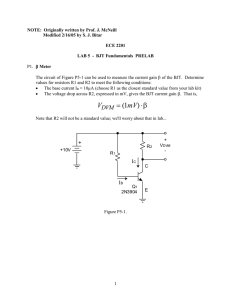
ece2201_lab5_modified
... BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT): iC-vBE CHARACTERISTIC L1. Build the BJT circuit shown in Fig. 5-1, using the 2N3904 NPN BJT. By using different values for resistors RB and RC, you will measure the base current iB, collector current iC, and base-emitter voltage vBE over a range of DC collector cu ...
... BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT): iC-vBE CHARACTERISTIC L1. Build the BJT circuit shown in Fig. 5-1, using the 2N3904 NPN BJT. By using different values for resistors RB and RC, you will measure the base current iB, collector current iC, and base-emitter voltage vBE over a range of DC collector cu ...
To All Customers Notification of selling digital input and output units
... External power supply for transistor drive Output circuit Type characteristics Max. load current Output delay timer Output Overload protection protection Surge suppression Other protection Insulation method No. of occupied words Station no. setting function ...
... External power supply for transistor drive Output circuit Type characteristics Max. load current Output delay timer Output Overload protection protection Surge suppression Other protection Insulation method No. of occupied words Station no. setting function ...
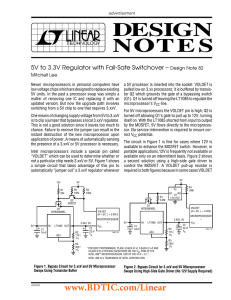
DN82 - 5V to 3.3V Regulator with Fail-Safe Switchover
... For certain families of microprocessors, 3.3V is required. The circuits shown in Figures 1 and 2 are fully compatible with 3.3V applications by simply substituting a fixed 3.3V version of the regulator (use an LT10853.3). Higher current operation is also possible. The LT1085 is suitable for 3A appli ...
... For certain families of microprocessors, 3.3V is required. The circuits shown in Figures 1 and 2 are fully compatible with 3.3V applications by simply substituting a fixed 3.3V version of the regulator (use an LT10853.3). Higher current operation is also possible. The LT1085 is suitable for 3A appli ...
Unit 21
... power supply units are more economical and reliable and can provide larger powers. They can also supply very steady voltages when this is essential. (b) Test instruments These are required for circuit design, maintenance and fault-finding. The main features of multimeters, oscilloscopes and signal g ...
... power supply units are more economical and reliable and can provide larger powers. They can also supply very steady voltages when this is essential. (b) Test instruments These are required for circuit design, maintenance and fault-finding. The main features of multimeters, oscilloscopes and signal g ...
TSM9634F - Silicon Labs
... Silicon Laboratories assumes no responsibility for errors and omissions, and disclaims responsibility for any consequences resulting from the use of information included herein. Additionally, Silicon Laboratories assumes no responsibility for the functioning of undescribed features or parameters. Si ...
... Silicon Laboratories assumes no responsibility for errors and omissions, and disclaims responsibility for any consequences resulting from the use of information included herein. Additionally, Silicon Laboratories assumes no responsibility for the functioning of undescribed features or parameters. Si ...
Lecture 7
... (Sum of currents entering node) (Sum of currents leaving node) = 0 Charge stored in node is zero (e.g. capacitor is part of a branch) Assume zero capacitance from node to ground unless explicit capacitor ...
... (Sum of currents entering node) (Sum of currents leaving node) = 0 Charge stored in node is zero (e.g. capacitor is part of a branch) Assume zero capacitance from node to ground unless explicit capacitor ...
Symbols and Terminology - Alphabetically
... specified value on the leading edge of the pulse and the specified value on the trailing edge of the output pulse. Note: In most cases the specified value is 50 % of the signal Rise time; the time interval between the lower specified value and the upper specified value on the trailing edge of the pu ...
... specified value on the leading edge of the pulse and the specified value on the trailing edge of the output pulse. Note: In most cases the specified value is 50 % of the signal Rise time; the time interval between the lower specified value and the upper specified value on the trailing edge of the pu ...
INA111 High Speed FET-Input INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER
... Input circuitry must provide a path for this input bias current if the INA111 is to operate properly. Figure 3 shows various provisions for an input bias current path. Without a bias current return path, the inputs will float to a potential which exceeds the common-mode range of the INA111 and the i ...
... Input circuitry must provide a path for this input bias current if the INA111 is to operate properly. Figure 3 shows various provisions for an input bias current path. Without a bias current return path, the inputs will float to a potential which exceeds the common-mode range of the INA111 and the i ...
NCP1207AADAPGEVB Implementing NCP1207 in QR 24 W AC-DC Converter with Synchronous Rectifier
... are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC). SCILLC owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www.onsemi.com/site/pdf/Patent−Marki ...
... are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC). SCILLC owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent coverage may be accessed at www.onsemi.com/site/pdf/Patent−Marki ...
OP-AMPS - ECE, Rutgers
... 2.2.4 Building Amplifier Circuits Using Op Amps There are two standard closed-loop connections for an Op Amp. Both have in common the connection (Rf) from the output terminal to the inverting input terminal. This connection provides the negative feedback and ensures the virtual short. The analysis i ...
... 2.2.4 Building Amplifier Circuits Using Op Amps There are two standard closed-loop connections for an Op Amp. Both have in common the connection (Rf) from the output terminal to the inverting input terminal. This connection provides the negative feedback and ensures the virtual short. The analysis i ...
Exp5 Full Wave Rectifier
... Rectifier circuits are used to convert an ac voltage into a dc voltage. The current always flows in the same direction through the load resistor of a rectifier circuit. However, its magnitude changes: ...
... Rectifier circuits are used to convert an ac voltage into a dc voltage. The current always flows in the same direction through the load resistor of a rectifier circuit. However, its magnitude changes: ...
AD8517
... Most amplifiers have difficulty driving capacitance due to degradation of phase caused by additional phase lag from the capacitive load. Higher capacitance at the output can increase the amount of overshoot and ringing in the amplifier’s step response and could even affect the stability of the devic ...
... Most amplifiers have difficulty driving capacitance due to degradation of phase caused by additional phase lag from the capacitive load. Higher capacitance at the output can increase the amount of overshoot and ringing in the amplifier’s step response and could even affect the stability of the devic ...
Wilson current mirror

A Wilson current mirror is a three-terminal circuit (Fig. 1) that accepts an input current at the input terminal and provides a ""mirrored"" current source or sink output at the output terminal. The mirrored current is a precise copy of the input current. It may be used as a Wilson current source by applying a constant bias current to the input branch as in Fig. 2. The circuit is named after George R. Wilson, an integrated circuit design engineer who worked for Tektronix. Wilson devised this configuration in 1967 when he and Barrie Gilbert challenged each other to find an improved current mirror overnight that would use only three transistors. Wilson won the challenge.