Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
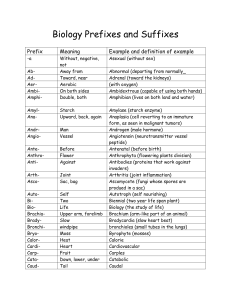
... heterozygous (having two different alleles for a given trait) histoma (tumor derived from mature tissue) holotrophs (organisms that eat other organisms whole or in pieces) homozygous (having two alleles for a given trait that are the same) hydrophilic (having an affinity for water; water loving) hyp ...
... heterozygous (having two different alleles for a given trait) histoma (tumor derived from mature tissue) holotrophs (organisms that eat other organisms whole or in pieces) homozygous (having two alleles for a given trait that are the same) hydrophilic (having an affinity for water; water loving) hyp ...
Mammalian Differentiated Cell Types, Part 2
... Blood contains about one leucocyte for every 100 red blood cells. Although leucocytes travel in the circulation, they can pass through the walls of blood vessels to do their work in the surrounding tissues. There are several different kinds, including lymphocytes—responsible for immune responses suc ...
... Blood contains about one leucocyte for every 100 red blood cells. Although leucocytes travel in the circulation, they can pass through the walls of blood vessels to do their work in the surrounding tissues. There are several different kinds, including lymphocytes—responsible for immune responses suc ...
Diabetes basics: Helping you understand the science Science can
... body as foreign ‐‐ and attacks them. In other words, the body actually attacks its own cells. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. The immune system destroys the insulin‐producing “beta” cells in the pancreas. ...
... body as foreign ‐‐ and attacks them. In other words, the body actually attacks its own cells. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. The immune system destroys the insulin‐producing “beta” cells in the pancreas. ...
glucocerebrosidease
... • Trace the path for synthesizing the protein glucocerebrosidease. (Start with DNA) • Trace the path for synthesizing the lipid glucocerebroside. (Synthesis of the lipid part starts in the smooth ER) • Explain the digestion of glucocerebroside by glucocerebrosidease. • Note: You will not be expecte ...
... • Trace the path for synthesizing the protein glucocerebrosidease. (Start with DNA) • Trace the path for synthesizing the lipid glucocerebroside. (Synthesis of the lipid part starts in the smooth ER) • Explain the digestion of glucocerebroside by glucocerebrosidease. • Note: You will not be expecte ...
Reading Chapter 27 NERVOUS SYSTEM Neurons
... antibodies which protect neurons from infection of the wild type. RABIES rhabdovirus; transmitted by animal bites. Virus multiplies at site of inoculation remains localized for days to months, before infecting the peripheral nerves. Once virus reaches spinal cord rapid infection of brain follows. Vi ...
... antibodies which protect neurons from infection of the wild type. RABIES rhabdovirus; transmitted by animal bites. Virus multiplies at site of inoculation remains localized for days to months, before infecting the peripheral nerves. Once virus reaches spinal cord rapid infection of brain follows. Vi ...
Lecture 1 Food Allergy Immunology and Symptoms
... • Specific antibodies are then produced in a process of class switching, driven by exposure to specific antigens • In the presence of antigen, B cells expressing specific antibodies are selected • Class switching occurs at this stage • The direction of switching is regulated by cytokines secreted by ...
... • Specific antibodies are then produced in a process of class switching, driven by exposure to specific antigens • In the presence of antigen, B cells expressing specific antibodies are selected • Class switching occurs at this stage • The direction of switching is regulated by cytokines secreted by ...
The Immune System and Infertility
... The body’s immune system includes among its functions the ability to distinguish self from non-self. This ability (probably not as absolute as once believed) is crucial in the recognition of ‘foreign’ or threatening invasion by infection or cancer cells. In some instances (called autoimmune diseases ...
... The body’s immune system includes among its functions the ability to distinguish self from non-self. This ability (probably not as absolute as once believed) is crucial in the recognition of ‘foreign’ or threatening invasion by infection or cancer cells. In some instances (called autoimmune diseases ...
File
... 2. The digestive system- is made up of organs that break down food to small, soluble molecules (monomers): proteins amino acids, vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates sugars, and fats (lipids). Nutrients which the body needs for energy, growth, and repair. Digestion absorption into the circulatory ...
... 2. The digestive system- is made up of organs that break down food to small, soluble molecules (monomers): proteins amino acids, vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates sugars, and fats (lipids). Nutrients which the body needs for energy, growth, and repair. Digestion absorption into the circulatory ...
Belikov
... MPhs acquire repertoires of active enhancers that are instructed by the microenvironmental signals specific to given tissue… … which affects the regulatory landscape of a cell via the induction of specific trx factors, leading to the expression of genes involved in the unique functional pathways of ...
... MPhs acquire repertoires of active enhancers that are instructed by the microenvironmental signals specific to given tissue… … which affects the regulatory landscape of a cell via the induction of specific trx factors, leading to the expression of genes involved in the unique functional pathways of ...
Slide 1
... excess osmosis into the cell, which could potentially cause the cell to burst. • b. The pump maintains the concentration gradients of Na+ and K+ across the cell membrane, which many cells use to help in the transport of other substances, such as glucose across the cell membrane ...
... excess osmosis into the cell, which could potentially cause the cell to burst. • b. The pump maintains the concentration gradients of Na+ and K+ across the cell membrane, which many cells use to help in the transport of other substances, such as glucose across the cell membrane ...
Disease Test - bms8thgradescience
... MRSA stands for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA is a “staph” germ that does not get better with the first-line antibiotics that usually cure staph infections. When this occurs, the germ is “resistant” to the antibiotic. MRSA is the result of decades of often unnecessary antibiotic ...
... MRSA stands for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA is a “staph” germ that does not get better with the first-line antibiotics that usually cure staph infections. When this occurs, the germ is “resistant” to the antibiotic. MRSA is the result of decades of often unnecessary antibiotic ...
CD4 and HIV
... – signaling other cells in immune system – healthy: 800~1200 CD4+ T cells/mm3 – AIDS: < 200 CD4+ T cells/mm3 • less densely on macrophages, dendritic cell* and microglial cells ...
... – signaling other cells in immune system – healthy: 800~1200 CD4+ T cells/mm3 – AIDS: < 200 CD4+ T cells/mm3 • less densely on macrophages, dendritic cell* and microglial cells ...
Slide 1
... The Immune System ‘’ It’s me your friendly neighbourhood white blood cell again. This is how we kill microbes’’ 1. We find them, surround them and digest them, BURP! (phagocytosis) AND 2. Some of us make chemicals called antibodies that stick to microbes. Each microbe has antigens ( molecules on th ...
... The Immune System ‘’ It’s me your friendly neighbourhood white blood cell again. This is how we kill microbes’’ 1. We find them, surround them and digest them, BURP! (phagocytosis) AND 2. Some of us make chemicals called antibodies that stick to microbes. Each microbe has antigens ( molecules on th ...
16-Immune
... The body uses nonspecific cellular and chemical devices to protect itself Phagocytes and natural killer (NK) cells Antimicrobial proteins in blood and tissue fluid Inflammatory response enlists macrophages, mast cells, WBCs, and chemicals ...
... The body uses nonspecific cellular and chemical devices to protect itself Phagocytes and natural killer (NK) cells Antimicrobial proteins in blood and tissue fluid Inflammatory response enlists macrophages, mast cells, WBCs, and chemicals ...
Lymphatic System/Immunity
... T-cells have receptors on their membranes that bind antigen. Each T-cell has a specific receptor that binds a specific antigen, so a dendritic cell may have to display its antigen to many T-cells before it finds a Tcell that can recognize it. b. Costimulation- in order for a T-cell to be activated f ...
... T-cells have receptors on their membranes that bind antigen. Each T-cell has a specific receptor that binds a specific antigen, so a dendritic cell may have to display its antigen to many T-cells before it finds a Tcell that can recognize it. b. Costimulation- in order for a T-cell to be activated f ...
Apoptosis
... Pathways for the breakdown of GM1, globoside, and sphingomyelin to ceramide. A defect in the enzyme hydrolyzing a particular step is indicated by the partial breakdown product is noted. ...
... Pathways for the breakdown of GM1, globoside, and sphingomyelin to ceramide. A defect in the enzyme hydrolyzing a particular step is indicated by the partial breakdown product is noted. ...
Targeting FMDV minigenes to SLA II positive cells enhances the induction of cellular responses (...)
... Results expressed as: black cell: both swab samples (nasal and pharyngeal) positive; grey cell, only one sample positive; white cell: both samples negative. Results expressed as OD at day 10 - OD at day 0 in a 3ABC-ELISA. ...
... Results expressed as: black cell: both swab samples (nasal and pharyngeal) positive; grey cell, only one sample positive; white cell: both samples negative. Results expressed as OD at day 10 - OD at day 0 in a 3ABC-ELISA. ...
cells - Glow Blogs
... Which line the table records the results most likely obtained by this treatment. ...
... Which line the table records the results most likely obtained by this treatment. ...
prevent - Model High School
... for proteins crucial for the immune system are defective. Children born with SCID have no immune system. • Gene therapy has been used to inject a good copy of the defective gene into blood cells or bone marrow cells. In several cases this has been effective, though it is still experimental. ...
... for proteins crucial for the immune system are defective. Children born with SCID have no immune system. • Gene therapy has been used to inject a good copy of the defective gene into blood cells or bone marrow cells. In several cases this has been effective, though it is still experimental. ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.