today b cell development
... PRESENTATION OF ANTIGENS TO T HELPER CELLS BY B CELLS 1. The naïve B cell receptor binds its cognate antigen. ...
... PRESENTATION OF ANTIGENS TO T HELPER CELLS BY B CELLS 1. The naïve B cell receptor binds its cognate antigen. ...
341-541 - McDermott.doc
... Completion of the Objective Sheet questions soon after completion of the topic will allow you to solidify the knowledge you have obtained from that topic. In addition, it will allow you to organize your thought and put them into writing in preparation for exams, forming stronger neural connections i ...
... Completion of the Objective Sheet questions soon after completion of the topic will allow you to solidify the knowledge you have obtained from that topic. In addition, it will allow you to organize your thought and put them into writing in preparation for exams, forming stronger neural connections i ...
AUTOIMMUNE ENDOCRINE DISEASES
... has an antigen that shares an epitope with insulin or beta cells. Beta cells “look” like viral infected cells (mimicry) and are attacked by CD8 and CD4 and ?Th17 cell mechanisms. Yet another possibility is that CD4,25, FoxP3 pancreatic beta cell specific T cells are preferentially destroyed by virus ...
... has an antigen that shares an epitope with insulin or beta cells. Beta cells “look” like viral infected cells (mimicry) and are attacked by CD8 and CD4 and ?Th17 cell mechanisms. Yet another possibility is that CD4,25, FoxP3 pancreatic beta cell specific T cells are preferentially destroyed by virus ...
Measurement of Rainbow Trout and Hybrid Striped Bass Antibody
... arm of the immune system, they can elicit both cellular and humoral (e.g., antibody) responses against that particular antigen. The primary cell types involved in a specific antibody response are small cells having little cytoplasm termed lymphocytes. While morphologically similar, lymphocytes are c ...
... arm of the immune system, they can elicit both cellular and humoral (e.g., antibody) responses against that particular antigen. The primary cell types involved in a specific antibody response are small cells having little cytoplasm termed lymphocytes. While morphologically similar, lymphocytes are c ...
Medical Technology 2003 Dr
... Antibody binds to bacterial antigen, lableling the bacteria as targets for destruction ...
... Antibody binds to bacterial antigen, lableling the bacteria as targets for destruction ...
SpecificDefensessimple version
... HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) budding. HIV infects a number of cells in the body, though the main target is a lymphocyte cell, which is a type of T-cell. Once the HIV virus has infected the host cell it then replicates itself with thousands of copies. TEM X120,000. ...
... HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) budding. HIV infects a number of cells in the body, though the main target is a lymphocyte cell, which is a type of T-cell. Once the HIV virus has infected the host cell it then replicates itself with thousands of copies. TEM X120,000. ...
Practice Questions for Test 3
... b. Hypothalamus c. Ovary d. Thymus e. Thyroid 3. Draw an antibody and label these parts: heavy chain, light chain, V, C, Fc. 4. Describe the six antibody functions. 5. Draw a graph of an immune response. Include a primary and secondary exposure. Include a primary and secondary response. 6. What type ...
... b. Hypothalamus c. Ovary d. Thymus e. Thyroid 3. Draw an antibody and label these parts: heavy chain, light chain, V, C, Fc. 4. Describe the six antibody functions. 5. Draw a graph of an immune response. Include a primary and secondary exposure. Include a primary and secondary response. 6. What type ...
ANTIGEN – ANTIBODY REACTIONS
... Immunoflourescence (IF) is a technique based on the antigen-antibody reaction for detection of particular molecule that uses antibodies labeled with fluorescent dye (fluorochrome). Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation (It is ...
... Immunoflourescence (IF) is a technique based on the antigen-antibody reaction for detection of particular molecule that uses antibodies labeled with fluorescent dye (fluorochrome). Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation (It is ...
61. DNA vaccines based on FMDV minigenes in a mouse model
... tandem with TVP4 (BT) or with TVP4 and T3A (BTT) (Table 1). Before testing the plasmids in vivo we checked their expression after transfection in BHK-21 cells by immunostaining with a specific monoclonal antibody against the B epitope. Only cells transfected with pCMV-BTT, expressing the three epito ...
... tandem with TVP4 (BT) or with TVP4 and T3A (BTT) (Table 1). Before testing the plasmids in vivo we checked their expression after transfection in BHK-21 cells by immunostaining with a specific monoclonal antibody against the B epitope. Only cells transfected with pCMV-BTT, expressing the three epito ...
Annexure `CD-01` L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 3 0 2 0 4
... Types of immunity - humoral and cellular immunity, Innate and adaptive immunity, Physiology of immune response, Specificity and memory, Hematopoiesis and differentiation, Primary and secondary lymphoid organs. Cells of the immune system: T-cells, B-cells, NK cells, antigen-presenting cells, phagocyt ...
... Types of immunity - humoral and cellular immunity, Innate and adaptive immunity, Physiology of immune response, Specificity and memory, Hematopoiesis and differentiation, Primary and secondary lymphoid organs. Cells of the immune system: T-cells, B-cells, NK cells, antigen-presenting cells, phagocyt ...
Cell Biology
... Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions (2 points each) 1. You attempt to study a particular cell-signaling pathway of C. elegans. However, though the signal continues to be transducted, a response fails to take place. Which of the following amino acids is the most likely to have been affected? A. Ty ...
... Cell Biology Multiple Choice Questions (2 points each) 1. You attempt to study a particular cell-signaling pathway of C. elegans. However, though the signal continues to be transducted, a response fails to take place. Which of the following amino acids is the most likely to have been affected? A. Ty ...
2008 CELL BIOLOGY – TRAINING HANDOUT
... Enzymes are catalysts. They lower activation energy and remain unchanged by the reaction because they do take part in the reaction. Enzyme vs. other catalysts: enzymes are very specific and only work on one or a few molecules substrate: molecule(s) upon which enzyme works active site: part of enzyme ...
... Enzymes are catalysts. They lower activation energy and remain unchanged by the reaction because they do take part in the reaction. Enzyme vs. other catalysts: enzymes are very specific and only work on one or a few molecules substrate: molecule(s) upon which enzyme works active site: part of enzyme ...
Skin and Mucus: Pathogens-Away!
... the primary immune response Artificially acquired active immunity can be induced by a vaccine, a substance that contains the antigen (vaccine stimulates a primary response against the antigen w/o causing symptoms of the disease) Passive immunity Artificially acquired passive immunity is a short- ...
... the primary immune response Artificially acquired active immunity can be induced by a vaccine, a substance that contains the antigen (vaccine stimulates a primary response against the antigen w/o causing symptoms of the disease) Passive immunity Artificially acquired passive immunity is a short- ...
Vaksin dan sera
... DNA Vaccines DNA vaccines are at present experimental, but hold promise for future therapy since they will evoke both humoral and cellmediated immunity, without the dangers associated with live virus vaccines. The gene for an antigenic determinant of a pathogenic organism is inserted into a plasmid ...
... DNA Vaccines DNA vaccines are at present experimental, but hold promise for future therapy since they will evoke both humoral and cellmediated immunity, without the dangers associated with live virus vaccines. The gene for an antigenic determinant of a pathogenic organism is inserted into a plasmid ...
Semester 1 - TJ
... 3. Make a Venn Diagram for Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes. Use the following points: - example: bacteria - has nucleus (and other organelles) - example: plants & animals - has cell membrane - does not have nucleus - smaller, simple - has DNA - bigger, more complex ...
... 3. Make a Venn Diagram for Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes. Use the following points: - example: bacteria - has nucleus (and other organelles) - example: plants & animals - has cell membrane - does not have nucleus - smaller, simple - has DNA - bigger, more complex ...
Immune System - Madeira High School
... of invading • form a membrane attack complex microbe • perforate target cell • apoptosis – cell lysis ...
... of invading • form a membrane attack complex microbe • perforate target cell • apoptosis – cell lysis ...
DOC
... Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A) is the founding member of a family of angiogenic proteins with various binding abilities to three cognate VEGF receptors. Previously, a gene encoding from the genome of parapox orf virus (OV) with about 25% amino acid identity to mammalian VEGF-A was named ...
... Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A) is the founding member of a family of angiogenic proteins with various binding abilities to three cognate VEGF receptors. Previously, a gene encoding from the genome of parapox orf virus (OV) with about 25% amino acid identity to mammalian VEGF-A was named ...
Treg - immunology.unideb.hu
... Development and function of regulatory T cells. CD4+ T cells that recognize self antigens may differentiate into regulatory cells in the thymus or peripheral tissues, in a process that is dependent on the transcription factor FoxP3. (The larger arrow from the thymus, compared to the one from periphe ...
... Development and function of regulatory T cells. CD4+ T cells that recognize self antigens may differentiate into regulatory cells in the thymus or peripheral tissues, in a process that is dependent on the transcription factor FoxP3. (The larger arrow from the thymus, compared to the one from periphe ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... Bases of tumor immunity • The reaction of immunity is based on reaction to foreign antigen • Tumor must be recognised as foreign – endogennous antigen on the surface of self cells MHC I – Ts, Tc, NK • Alteration of cell antigens during tumorgenesis (lack of MHC I – desactivation of KIR, new antgien ...
... Bases of tumor immunity • The reaction of immunity is based on reaction to foreign antigen • Tumor must be recognised as foreign – endogennous antigen on the surface of self cells MHC I – Ts, Tc, NK • Alteration of cell antigens during tumorgenesis (lack of MHC I – desactivation of KIR, new antgien ...
S1 File - PLoS ONE
... numbers to that of injected WT cells. Data are means ± SD of groups of five mice. In langerin+ DC-ablated mice, we consistently observe severely impaired proliferation of adoptively transferred OT-1 T cells but enhanced OVA-specific responses of endogenous CD8+ T cells. While this opposing behavior ...
... numbers to that of injected WT cells. Data are means ± SD of groups of five mice. In langerin+ DC-ablated mice, we consistently observe severely impaired proliferation of adoptively transferred OT-1 T cells but enhanced OVA-specific responses of endogenous CD8+ T cells. While this opposing behavior ...
Malaria in the Immune System
... - Malaria is a disease that is transferred usually by mosquito - The mosquito passes on parasites that it contains in it’s own system. The parasites are passed into the blood stream. ...
... - Malaria is a disease that is transferred usually by mosquito - The mosquito passes on parasites that it contains in it’s own system. The parasites are passed into the blood stream. ...
Interferon Type II & III - Bite
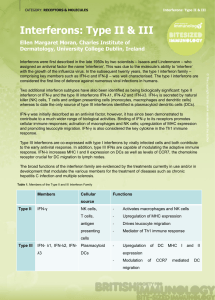
... Two additional interferon subtypes have also been identified as being biologically significant: type II interferon or IFN-γ and the type III interferons IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2 and IFN-λ3. IFN-γ is secreted by natural killer (NK) cells, T cells and antigen presenting cells (monocytes, macrophages and dendrit ...
... Two additional interferon subtypes have also been identified as being biologically significant: type II interferon or IFN-γ and the type III interferons IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2 and IFN-λ3. IFN-γ is secreted by natural killer (NK) cells, T cells and antigen presenting cells (monocytes, macrophages and dendrit ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.