IC31 and IC30, novel types of vaccine adjuvant based on peptide
... The potent function of polycationic peptides as cellular delivery systems has been recognized for several years. For example, a complex with a transfering polycation was able to transport bacterial DNA into cells [3]. Polycationic compounds have also been used previously to transport proteins, such ...
... The potent function of polycationic peptides as cellular delivery systems has been recognized for several years. For example, a complex with a transfering polycation was able to transport bacterial DNA into cells [3]. Polycationic compounds have also been used previously to transport proteins, such ...
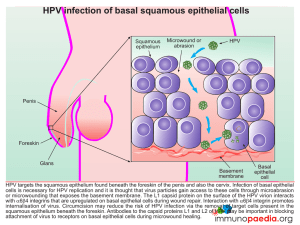
HPV infection of basal squamous epithelial cells
... oncoproteins interfere with type 1 interferon responses that initiate intracellular antiviral cascades. A lack of release of proinflammatory cytokines limits the activation of resident skin Langerhan’s cells required for induction of adaptive immunity. HPV escapes CD8+ cytotoxic T cell detection by ...
... oncoproteins interfere with type 1 interferon responses that initiate intracellular antiviral cascades. A lack of release of proinflammatory cytokines limits the activation of resident skin Langerhan’s cells required for induction of adaptive immunity. HPV escapes CD8+ cytotoxic T cell detection by ...
J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference 2017
... or is based on studies, publications, surveys and other data obtained from third-party sources and Atara's own internal estimates and research. While Atara believes these third-party studies, publications, surveys and other data to be reliable as of the date of this presentation, it has not independ ...
... or is based on studies, publications, surveys and other data obtained from third-party sources and Atara's own internal estimates and research. While Atara believes these third-party studies, publications, surveys and other data to be reliable as of the date of this presentation, it has not independ ...
Effect of TGF-beta on interferon-gamma-induced HLA-DR
... There are indications that, in other cell types, IFNy may induce MHC class II antigens through activation of the PKC pathway,23 whereas TGF-/3 may be acting, in part, by PKC inhibition. 26 It has also been proposed that transcriptional regulation of HLA-DR antigen is modulated by PKC.27 Attempts to ...
... There are indications that, in other cell types, IFNy may induce MHC class II antigens through activation of the PKC pathway,23 whereas TGF-/3 may be acting, in part, by PKC inhibition. 26 It has also been proposed that transcriptional regulation of HLA-DR antigen is modulated by PKC.27 Attempts to ...
Immunomodulatory effects of Lactobacillus casei Shirota
... reactions and factors critical for the subsequent initiation of adaptive immunity (Medzhitov and Janeway, 2000). PRRs, such as Toll-like receptors, C-type lectin receptors, RIG-I-like receptors and nucleotide-binding domain (NODs) sense pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and transmit act ...
... reactions and factors critical for the subsequent initiation of adaptive immunity (Medzhitov and Janeway, 2000). PRRs, such as Toll-like receptors, C-type lectin receptors, RIG-I-like receptors and nucleotide-binding domain (NODs) sense pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and transmit act ...
Regulation of the Germinal Center Dynamics Modelling Two
... Research on the germinal center has tried to unravel the mechanisms that control its dynamics. In this study we focus on the termination of the germinal center reaction, which is still an open problem. We propose two hypothetical biological mechanisms that may be responsible for the control of germi ...
... Research on the germinal center has tried to unravel the mechanisms that control its dynamics. In this study we focus on the termination of the germinal center reaction, which is still an open problem. We propose two hypothetical biological mechanisms that may be responsible for the control of germi ...
The Immunology of Allograft Rejection
... To minimize the risk of allograft rejection, transplant recipients require lifelong immunosuppression. Several immunosuppressive drugs introduced in the past two decades have helped to avert tissue damage and disruption of organ function, decreased the rate of acute graft rejection, and improved one ...
... To minimize the risk of allograft rejection, transplant recipients require lifelong immunosuppression. Several immunosuppressive drugs introduced in the past two decades have helped to avert tissue damage and disruption of organ function, decreased the rate of acute graft rejection, and improved one ...
cell growth, division, and reproduction
... growth and division b. Some sources of gene defects are smoking tobacco, radiation exposure, defective genes, and viral infection. c. A damaged or defective p53 gene is common in cancer cells. It causes cells to lose the information needed to respond to ...
... growth and division b. Some sources of gene defects are smoking tobacco, radiation exposure, defective genes, and viral infection. c. A damaged or defective p53 gene is common in cancer cells. It causes cells to lose the information needed to respond to ...
Vaccines Learning Module | Vaccine Education Center
... antibodies •Antibodies are specific to antigens and have the ability to remember them, so that if the same (or a very similar) antigen tries to infect the person again, the immune response will be stronger and faster thereby protecting the person from infection—and illness. ...
... antibodies •Antibodies are specific to antigens and have the ability to remember them, so that if the same (or a very similar) antigen tries to infect the person again, the immune response will be stronger and faster thereby protecting the person from infection—and illness. ...
Thesis - KI Open Archive
... which is a protein that regulates activation of the complement system (9, 10). Infections with CVBs are very common and are usually associated with mild flu-like symptoms. However, they can in some cases give rise to more severe diseases such as myocarditis, hepatitis, pancreatitis and meningitis, w ...
... which is a protein that regulates activation of the complement system (9, 10). Infections with CVBs are very common and are usually associated with mild flu-like symptoms. However, they can in some cases give rise to more severe diseases such as myocarditis, hepatitis, pancreatitis and meningitis, w ...
REVIEWS
... and parasitic microbial groups (TABLE 2). In contrast to the use of mAb therapy to treat malignancies, which depends on discriminating between self-antigens that are expressed by normal and tumour cells, passive antibody therapy for infectious diseases is aided by the large antigenic differences bet ...
... and parasitic microbial groups (TABLE 2). In contrast to the use of mAb therapy to treat malignancies, which depends on discriminating between self-antigens that are expressed by normal and tumour cells, passive antibody therapy for infectious diseases is aided by the large antigenic differences bet ...
A New Strategy of Cancer Immunotherapy Combining Hyperthermia
... instead of an immune responses. DCs are not only activators but also modulators of immune responses. Depending on the context in which DCs interact with antigens they will affect T helper precursor cells in different ways, for instance to differentiate into Th1, Th2, Th17 or Treg. To avoid a wrong p ...
... instead of an immune responses. DCs are not only activators but also modulators of immune responses. Depending on the context in which DCs interact with antigens they will affect T helper precursor cells in different ways, for instance to differentiate into Th1, Th2, Th17 or Treg. To avoid a wrong p ...
Immune system
... The spleen is situated in the left superior part of abdomen. It has exterior capsula from conjunctive tissue which sends in parenchyma prolongations forming trabeculae. These together with the reticular cells network form a support for a great lot of cells. Two types of tissue enter in the spleen st ...
... The spleen is situated in the left superior part of abdomen. It has exterior capsula from conjunctive tissue which sends in parenchyma prolongations forming trabeculae. These together with the reticular cells network form a support for a great lot of cells. Two types of tissue enter in the spleen st ...
Lesson Overview - Southgate Schools
... and responds appropriately to dangerous invaders in the body. Sometimes, however, the immune system attacks the wrong targets. Other times, the immune system itself is disabled by disease. What happens in these cases? ...
... and responds appropriately to dangerous invaders in the body. Sometimes, however, the immune system attacks the wrong targets. Other times, the immune system itself is disabled by disease. What happens in these cases? ...
a,
... Complete antigens include foreign protein, nucleic acid, some lipids, and large polysaccharides ...
... Complete antigens include foreign protein, nucleic acid, some lipids, and large polysaccharides ...
The homeostatic properties of the mannose receptor in health and
... CR domain (CR–L) in secondary lymphoid organs(13-15) and in kidneys(16), a role can be envisaged for sMR in the delivery of soluble CTLD ligands to these relevant sites. Under homeostatic conditions CR-L are present in selected macrophage populations deficient in MR expression adjacent to B cell fol ...
... CR domain (CR–L) in secondary lymphoid organs(13-15) and in kidneys(16), a role can be envisaged for sMR in the delivery of soluble CTLD ligands to these relevant sites. Under homeostatic conditions CR-L are present in selected macrophage populations deficient in MR expression adjacent to B cell fol ...
Blood is a complex, living tissue that contains many cell types and
... cells and plasma, which is the liquid the red blood cells are suspended in. The plasma is packed with proteins called antibodies. The body produces a wide variety of antibodies that will recognize and attack foreign molecules that may enter from the outside world. A person’s plasma does not contain ...
... cells and plasma, which is the liquid the red blood cells are suspended in. The plasma is packed with proteins called antibodies. The body produces a wide variety of antibodies that will recognize and attack foreign molecules that may enter from the outside world. A person’s plasma does not contain ...
Lymphatic System: Overview
... and help activate T cells Dendritic cells – spiny-looking cells with functions similar to macrophages Reticular cells – fibroblast–like cells that produce a stroma, or network, that supports other cell types in lymphoid organs ...
... and help activate T cells Dendritic cells – spiny-looking cells with functions similar to macrophages Reticular cells – fibroblast–like cells that produce a stroma, or network, that supports other cell types in lymphoid organs ...
Candida albicans Pathogenicity and Epithelial Immunity
... The most common Candida species that causes human mucosal infections is Candida albicans, an endogenous commensal in approximately 50% of individuals. C. albicans is able to undergo morphological switching between a yeast and hyphal form, and the ability to switch to the hyphal form is a critical fe ...
... The most common Candida species that causes human mucosal infections is Candida albicans, an endogenous commensal in approximately 50% of individuals. C. albicans is able to undergo morphological switching between a yeast and hyphal form, and the ability to switch to the hyphal form is a critical fe ...
Inflammation: Mechanisms, Costs, and Natural Variation
... Inflammation consists of a tightly regulated cascade of immunological, physiological, and behavioral processes that are orchestrated by soluble immune signaling molecules called cytokines. The first step of the inflammatory cascade involves recognition of infection or damage (Figure 1b). This is typica ...
... Inflammation consists of a tightly regulated cascade of immunological, physiological, and behavioral processes that are orchestrated by soluble immune signaling molecules called cytokines. The first step of the inflammatory cascade involves recognition of infection or damage (Figure 1b). This is typica ...
Pivotal Role of the B7:CD28 Pathway in
... ' (eg, endothelium) can also present antigen under certain condition^.**^*^ Three distinct stages of cell-cell interaction between APCs and antigen-specificT cells are required to induce an antigenspecific immune response. Figure 1 depicts the known cell interaction molecules that are responsible fo ...
... ' (eg, endothelium) can also present antigen under certain condition^.**^*^ Three distinct stages of cell-cell interaction between APCs and antigen-specificT cells are required to induce an antigenspecific immune response. Figure 1 depicts the known cell interaction molecules that are responsible fo ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.