An introduction to the immune system: how vaccines work
... Contra-indications: Hypersensitivity to any component of the vaccine or to diphtheria toxoid. Warnings and Precautions: Do not administer intravenously. Appropriate treatment must be available in case of anaphylaxis. The potential risk of apnoea and the need for respiratory monitoring for 48-72 hour ...
... Contra-indications: Hypersensitivity to any component of the vaccine or to diphtheria toxoid. Warnings and Precautions: Do not administer intravenously. Appropriate treatment must be available in case of anaphylaxis. The potential risk of apnoea and the need for respiratory monitoring for 48-72 hour ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... CD15 Granulocytes; also expressed by Reed-Sternberg cells and variants in classical Hodgkin lymphoma CD33 Myeloid progenitors and monocytes CD64 Mature myeloid cells Primarily NK-Cell Associated CD16 NK cells and granulocytes CD56 NK cells and a subset of T cells Primarily Stem Cell and Progenitor C ...
... CD15 Granulocytes; also expressed by Reed-Sternberg cells and variants in classical Hodgkin lymphoma CD33 Myeloid progenitors and monocytes CD64 Mature myeloid cells Primarily NK-Cell Associated CD16 NK cells and granulocytes CD56 NK cells and a subset of T cells Primarily Stem Cell and Progenitor C ...
PVF2, a PDGF/VEGFlike growth factor, induces
... their capacity to produce antibodies that recognize cell surface antigens on live mbn-2 cells. This recognition was monitored by flow cytometric analysis (Figure 1A and B), and selected antibodies were tested for their abilities to affect the mitotic rate of mbn-2 cells. In these series, one antibod ...
... their capacity to produce antibodies that recognize cell surface antigens on live mbn-2 cells. This recognition was monitored by flow cytometric analysis (Figure 1A and B), and selected antibodies were tested for their abilities to affect the mitotic rate of mbn-2 cells. In these series, one antibod ...
the PDF - British Society for Immunology
... molecules produced by white blood cells are ‘poisonous’ for bacteria. However the immune system also has cells (cytotoxic T cells) that can kill other cells of the body that have become infected. They use a variety of toxic molecules to kill the infected cells, and it is only because the molecules a ...
... molecules produced by white blood cells are ‘poisonous’ for bacteria. However the immune system also has cells (cytotoxic T cells) that can kill other cells of the body that have become infected. They use a variety of toxic molecules to kill the infected cells, and it is only because the molecules a ...
Towards understanding the immune system
... thinks that this theory has some problems: One can't consider MHC I, II as a kind of self markers?. Also if only the danger signals initiate IS then why some organs are rejected after a long time of being transplanted i.e. after the danger signals should have disappeared? Moreover, danger signals in ...
... thinks that this theory has some problems: One can't consider MHC I, II as a kind of self markers?. Also if only the danger signals initiate IS then why some organs are rejected after a long time of being transplanted i.e. after the danger signals should have disappeared? Moreover, danger signals in ...
Slide 1
... • Results in infiltration of lymphocytes and macrophages, and subsequent proliferation of T lymphocytes (T-cells), at site of injection • Measures cell-mediated immune function: activation of macrophages, natural killer cells, cytotoxic T-cells and cytokines (NOT antibodies) ...
... • Results in infiltration of lymphocytes and macrophages, and subsequent proliferation of T lymphocytes (T-cells), at site of injection • Measures cell-mediated immune function: activation of macrophages, natural killer cells, cytotoxic T-cells and cytokines (NOT antibodies) ...
Protect
... Wellmune®is a natural ingredient. It is a specialized and standardized form of 1,3/1,6 Beta-glucans from a proprietary strain from the cell wall of baker’s yeast. This is an important nutrient that can only be obtained in a very few foodstuffs, or in supplements. PROTECTED Protect is the result of ...
... Wellmune®is a natural ingredient. It is a specialized and standardized form of 1,3/1,6 Beta-glucans from a proprietary strain from the cell wall of baker’s yeast. This is an important nutrient that can only be obtained in a very few foodstuffs, or in supplements. PROTECTED Protect is the result of ...
Document
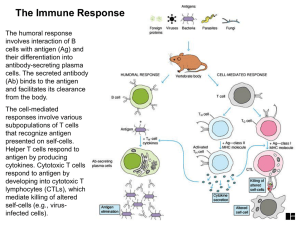
... antigen by producing cytokines. Cytotoxic T cells respond to antigen by developing into cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), which mediate killing of altered self-cells (e.g., virusinfected cells). ...
... antigen by producing cytokines. Cytotoxic T cells respond to antigen by developing into cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), which mediate killing of altered self-cells (e.g., virusinfected cells). ...
Blood = formed elements + plasma
... The extracellular surface of the red blood cell plasmalemma has specific inherited carbohydrate chains that act as antigens and determine the blood group of an individual for the purposes of blood transfusion. The most notable of these are the A and B antigens, which determine the four primary blood ...
... The extracellular surface of the red blood cell plasmalemma has specific inherited carbohydrate chains that act as antigens and determine the blood group of an individual for the purposes of blood transfusion. The most notable of these are the A and B antigens, which determine the four primary blood ...
Immune Responses to Infectious Diseases
... However the phagocytic activity is strictly dependent on the size of the pathogens [15]. This is well demonstrated with respect to the host defense against helminths, in which phagocytosis by macrophages or neutrophils are prevented by the parasite size. This restriction demands a different strategy ...
... However the phagocytic activity is strictly dependent on the size of the pathogens [15]. This is well demonstrated with respect to the host defense against helminths, in which phagocytosis by macrophages or neutrophils are prevented by the parasite size. This restriction demands a different strategy ...
Respiratory infections
... • Her exam reveals mild fine inspiratory ralesnothing impressive • The Dr sends her for an xray that reveals bilateral infiltrates ...
... • Her exam reveals mild fine inspiratory ralesnothing impressive • The Dr sends her for an xray that reveals bilateral infiltrates ...
What are Viruses? - Northwest ISD Moodle
... is called antibody-mediated immunity, meaning it is controlled by antibodies This represents the third line of defense in the immune system ...
... is called antibody-mediated immunity, meaning it is controlled by antibodies This represents the third line of defense in the immune system ...
lesson-1-active
... • State how active immunity can be achieved • describe what a vaccine is • describe the effect of a vaccine on the immune system immediately after vaccination • describe the effect of a vaccine on the immune system when the body comes into contact with the same pathogen in later ...
... • State how active immunity can be achieved • describe what a vaccine is • describe the effect of a vaccine on the immune system immediately after vaccination • describe the effect of a vaccine on the immune system when the body comes into contact with the same pathogen in later ...
Type 2 Diabetes and Islet Immune Response
... to B-cell dysfunction. There are also several reports indicating that islets from patients with type 2 diabetes are infiltrated with macrophages, and human islets exposed to metabolic stress release increased levels of cytokines. Thus, chronic innate inflammation due to local cytokine generation is ...
... to B-cell dysfunction. There are also several reports indicating that islets from patients with type 2 diabetes are infiltrated with macrophages, and human islets exposed to metabolic stress release increased levels of cytokines. Thus, chronic innate inflammation due to local cytokine generation is ...
Transcriptomic response of goat mammary epithelial cells to
... tissue and challenged with Ma. High-throughput mRNA sequencing was performed to reveal differentially expressed genes (DEG) at different time-points (3 h, 12 h, and 24 h) post infection (PI). The pathway enrichment analysis of the DEG showed that infection significantly affected pathways associated ...
... tissue and challenged with Ma. High-throughput mRNA sequencing was performed to reveal differentially expressed genes (DEG) at different time-points (3 h, 12 h, and 24 h) post infection (PI). The pathway enrichment analysis of the DEG showed that infection significantly affected pathways associated ...
Cancer immunotherapy

Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncology) is the use of the immune system to treat cancer. Immunotherapies fall into three main groups: cellular, antibody and cytokine. They exploit the fact that cancer cells often have subtly different molecules on their surface that can be detected by the immune system. These molecules, known as cancer antigens, are most commonly proteins, but also include molecules such as carbohydrates. Immunotherapy is used to provoke the immune system into attacking the tumor cells by using these antigens as targets.Antibody therapies are the most successful immunotherapy, treating a wide range of cancers. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that bind to a target antigen on the cell surface. In normal physiology the immune system uses them to fight pathogens. Each antibody is specific to one or a few proteins. Those that bind to cancer antigens are used to treat cancer. Cell surface receptors are common targets for antibody therapies and include the CD20, CD274, and CD279. Once bound to a cancer antigen, antibodies can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, activate the complement system, or prevent a receptor from interacting with its ligand, all of which can lead to cell death. Multiple antibodies are approved to treat cancer, including Alemtuzumab, Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, Ofatumumab, and Rituximab.Cellular therapies, also known as cancer vaccines, usually involve the removal of immune cells from the blood or from a tumor. Immune cells specific for the tumor are activated, cultured and returned to the patient where the immune cells attack the cancer. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells, cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells. The only cell-based therapy approved in the US is Dendreon's Provenge, for the treatment of prostate cancer.Interleukin-2 and interferon-α are examples of cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behaviour of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.