Chapter 43 – The Immune System
... Once V-J rearrangement has occurred, the gene is transcribed and translated into a light chain with a variable and constant region. The light chains combine randomly with the heavy chains that are similarly produced. ...
... Once V-J rearrangement has occurred, the gene is transcribed and translated into a light chain with a variable and constant region. The light chains combine randomly with the heavy chains that are similarly produced. ...
Leaky gut, leaky brain: the role of zonulin
... • Increased passage of unwanted molecules causes damage to astrocytes. • Immune response is stimulated by microglia. • A vicious cycle of increased passage of stressors and inflammation develops, leading to neuroinflammation. • Neuroinflammation can also impact on brain communication with the gut an ...
... • Increased passage of unwanted molecules causes damage to astrocytes. • Immune response is stimulated by microglia. • A vicious cycle of increased passage of stressors and inflammation develops, leading to neuroinflammation. • Neuroinflammation can also impact on brain communication with the gut an ...
CARBOHYDRATES B: Polysaccharides Learning Goals/Objectives
... during protein folding, protection from proteolysis, and increases half-life of the proteins. In contrast to a protein sequence which is determined by a DNA template, sugars are attached to proteins by enzymes which recognize appropriate sites on proteins and attach the sugars. Since there are many ...
... during protein folding, protection from proteolysis, and increases half-life of the proteins. In contrast to a protein sequence which is determined by a DNA template, sugars are attached to proteins by enzymes which recognize appropriate sites on proteins and attach the sugars. Since there are many ...
press release - Innate Pharma
... Monalizumab is a first-in-class immune checkpoint inhibitor targeting NKG2A receptors expressed on tumor infiltrating cytotoxic CD8 T lymphocytes and NK cells. NKG2A is an inhibitory receptor binding HLA-E. Expression of HLA-E can protect cancer cells from killing by NKG2A+ immune cells. HLA-E is fr ...
... Monalizumab is a first-in-class immune checkpoint inhibitor targeting NKG2A receptors expressed on tumor infiltrating cytotoxic CD8 T lymphocytes and NK cells. NKG2A is an inhibitory receptor binding HLA-E. Expression of HLA-E can protect cancer cells from killing by NKG2A+ immune cells. HLA-E is fr ...
the cell cycle
... capacity to divide as they differentiate and mature. In the case of mammalian red blood cells only, once they have matured they _____________________ and thus have no instructions for cell division. From this moment they have __________________ days to function as oxygen (and carbon dioxide) trans ...
... capacity to divide as they differentiate and mature. In the case of mammalian red blood cells only, once they have matured they _____________________ and thus have no instructions for cell division. From this moment they have __________________ days to function as oxygen (and carbon dioxide) trans ...
B cells take their time: sequential IgG class switching over
... responses and the formation of diverse antigen-experienced B-cell subsets in humans. Furthermore, the diversity of antigens, anatomical locations of immune responses and the diversity of antigen-experienced human B-cell subsets can blur the effects of temporal CSR. To overcome these limitations, it ...
... responses and the formation of diverse antigen-experienced B-cell subsets in humans. Furthermore, the diversity of antigens, anatomical locations of immune responses and the diversity of antigen-experienced human B-cell subsets can blur the effects of temporal CSR. To overcome these limitations, it ...
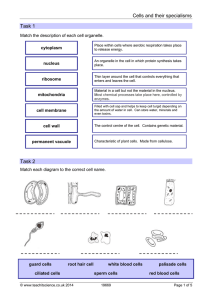
Cells and their specialisms Task 1 Task 2
... Cells and their specialisms Teaching notes and answers For the first three tasks students could be asked to cut and paste or simply draw a line to match up the correct statements. ...
... Cells and their specialisms Teaching notes and answers For the first three tasks students could be asked to cut and paste or simply draw a line to match up the correct statements. ...
Mechanisms of Disease: the hygiene hypothesis revisited
... Antigen-presenting cells take up a foreign antigen and degrade it to immunogenic peptides that are presented to the T-cell receptor. An immunological synapse is formed between the antigen-presenting cell and the T cell as indicated, resulting in cellular conditioning and various grades of activation ...
... Antigen-presenting cells take up a foreign antigen and degrade it to immunogenic peptides that are presented to the T-cell receptor. An immunological synapse is formed between the antigen-presenting cell and the T cell as indicated, resulting in cellular conditioning and various grades of activation ...
Document
... appearance on the surface of healing wounds may be seen as early as 3-5 days following implantation of a biomaterial New small blood vessels are formed by budding or sprouting of preexisting vessels in a process known as “neovascularization” or “angiogenesis” ...
... appearance on the surface of healing wounds may be seen as early as 3-5 days following implantation of a biomaterial New small blood vessels are formed by budding or sprouting of preexisting vessels in a process known as “neovascularization” or “angiogenesis” ...
Section 18 Immunity in the Fetus and Newborn
... migrate to the thymus and bursa at 5 to 7 days of incubation. • IgM+ lymphocytes are detected in the bursa by day 14. Antibodies are produced by 16 and 18d. • IgY+ lymphocytes develop on day 21 around the time of hatching. • IgA+ lymphocytes first appear in the intestine 3 to 7 days after hatching. ...
... migrate to the thymus and bursa at 5 to 7 days of incubation. • IgM+ lymphocytes are detected in the bursa by day 14. Antibodies are produced by 16 and 18d. • IgY+ lymphocytes develop on day 21 around the time of hatching. • IgA+ lymphocytes first appear in the intestine 3 to 7 days after hatching. ...
Lipids rule: resetting lipid metabolism restores T cell function in
... Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a devastating autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation and systemic destruction of host organs or tissue. A key feature of SLE is T cell dysfunction characterized by hyperresponsive antigen receptor signaling. In this issue of the JCI, McDonald a ...
... Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a devastating autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation and systemic destruction of host organs or tissue. A key feature of SLE is T cell dysfunction characterized by hyperresponsive antigen receptor signaling. In this issue of the JCI, McDonald a ...
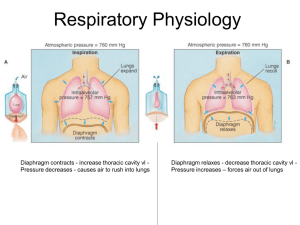
Respiratory Physiology
... Chronic exposure to irritants causes the number of layers to increase. The ciliated and mucus-secreting cells disappear and are replaced by a disorganized mass of cells with abnormal nuclei. If the process continues, the growing mass penetrates the underlying basement membrane. Malignant cells can b ...
... Chronic exposure to irritants causes the number of layers to increase. The ciliated and mucus-secreting cells disappear and are replaced by a disorganized mass of cells with abnormal nuclei. If the process continues, the growing mass penetrates the underlying basement membrane. Malignant cells can b ...
The Cell Membrane
... Their function, both in the recognition of antigenic variability and in effector activities, was initially revealed by protein, and more recently by DNA, studies of their structure. Ig structure – papain (a proteolytic enzyme), splits the Ig molecule into three fragments. Two fragments are similar, ...
... Their function, both in the recognition of antigenic variability and in effector activities, was initially revealed by protein, and more recently by DNA, studies of their structure. Ig structure – papain (a proteolytic enzyme), splits the Ig molecule into three fragments. Two fragments are similar, ...
Immune System Basics - Wayzata Public Schools
... More antibodies than the 2nd exposure Fewer antibodies than the 2nd exposure No antibodies The same number of antibodies than the ...
... More antibodies than the 2nd exposure Fewer antibodies than the 2nd exposure No antibodies The same number of antibodies than the ...
Tissues
... – Limited distribution in the body; surface cells are columnar, and cells underneath vary in size and shape; occurs at transition areas between 2 types of epithelium *Won’t need to identify picture ...
... – Limited distribution in the body; surface cells are columnar, and cells underneath vary in size and shape; occurs at transition areas between 2 types of epithelium *Won’t need to identify picture ...
Basic Laboratory Tests Complete Blood Counts (CBC)
... The total white blood cell count (WBC) is the number of white blood cells per unit volume blood. The white blood cells function as part of the immune system and their primary role is to protect the body from infection. The total white blood cell count is really a composite of six different subtypes ...
... The total white blood cell count (WBC) is the number of white blood cells per unit volume blood. The white blood cells function as part of the immune system and their primary role is to protect the body from infection. The total white blood cell count is really a composite of six different subtypes ...
Document
... Ricardo Chebel: Study various influences on innate immune functions and antibody responses before and after birth in cows – endometritis, metritis and mastitis (in vitro and in vivo studies in cattle). Troy Trumble: Discovery and translational research focusing on the onset and progression of osteoa ...
... Ricardo Chebel: Study various influences on innate immune functions and antibody responses before and after birth in cows – endometritis, metritis and mastitis (in vitro and in vivo studies in cattle). Troy Trumble: Discovery and translational research focusing on the onset and progression of osteoa ...
Cells Prokaryotes Classwork Describe the basic features present in
... antigen (Ag), either directly or after processing by a dendritic cell (DC). Activated T cells, dictated by their priming, are polarized to one of several T helper (TH) cell types, each associated with a distinct cytokine profile. Independently of the interaction with B cells, T cell activation leads ...
... antigen (Ag), either directly or after processing by a dendritic cell (DC). Activated T cells, dictated by their priming, are polarized to one of several T helper (TH) cell types, each associated with a distinct cytokine profile. Independently of the interaction with B cells, T cell activation leads ...
How Does Proliferative Homeostasis Change
... if any, do senescent cells contribute to aging phenotypes? Support for the idea that senescent cells can drive aging phenotypes comes from cell culture studies, which indicate that factors secreted by senescent cells can disrupt normal tissue architecture and create local inflammation, an important ...
... if any, do senescent cells contribute to aging phenotypes? Support for the idea that senescent cells can drive aging phenotypes comes from cell culture studies, which indicate that factors secreted by senescent cells can disrupt normal tissue architecture and create local inflammation, an important ...
Case Studies for Studying the Immune System
... At Wildcat High School, there was an unusual outbreak of mumps – 4 cases. The school nurse is checking the immunization records of all students at the high school. What is a possible explanation for the outbreak? Hint: there is more than one possible explanation! Case 10 Mike heard his cat yowl outs ...
... At Wildcat High School, there was an unusual outbreak of mumps – 4 cases. The school nurse is checking the immunization records of all students at the high school. What is a possible explanation for the outbreak? Hint: there is more than one possible explanation! Case 10 Mike heard his cat yowl outs ...