Ions and isotopes
... Quick Review • Atoms are made up of three particles: • Protons • Neutrons • Electrons • Question: Which of the three particles identifies what element an atom is? • The PROTON! (very important) ...
... Quick Review • Atoms are made up of three particles: • Protons • Neutrons • Electrons • Question: Which of the three particles identifies what element an atom is? • The PROTON! (very important) ...
Valence electrons and Lewis Dot Structures
... Means that one or more electrons are ____________ from the metal to the nonmetal (no longer neutral) these are now ions ...
... Means that one or more electrons are ____________ from the metal to the nonmetal (no longer neutral) these are now ions ...
History of the Atom
... Foil Experiment and suggested the following characteristics of the atom: ...
... Foil Experiment and suggested the following characteristics of the atom: ...
4.1 Studying Atoms
... a. All elements are composed of atoms. b. In a particular compound, atoms of different elements always combine the same way. c. All atoms have the same mass. d. Compounds contain atoms of more than one element. ...
... a. All elements are composed of atoms. b. In a particular compound, atoms of different elements always combine the same way. c. All atoms have the same mass. d. Compounds contain atoms of more than one element. ...
Section 4.1 Studying Atoms Reading Strategy
... a. All elements are composed of atoms. b. In a particular compound, atoms of different elements always combine the same way. c. All atoms have the same mass. d. Compounds contain atoms of more than one element. ...
... a. All elements are composed of atoms. b. In a particular compound, atoms of different elements always combine the same way. c. All atoms have the same mass. d. Compounds contain atoms of more than one element. ...
Timeline of Atomic Theory--pdf
... Niels Bohr modified Rutherford's model of the atom to incorporate the ideas of quantum physics. This required a new mechanism for the way electrons emitted energy. Transformation of Atoms ...
... Niels Bohr modified Rutherford's model of the atom to incorporate the ideas of quantum physics. This required a new mechanism for the way electrons emitted energy. Transformation of Atoms ...
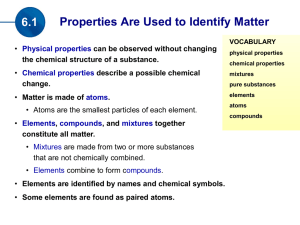
Atoms have a structure that determines their properties.
... • Physical properties can be observed without changing the chemical structure of a substance. • Chemical properties describe a possible chemical change. • Matter is made of atoms. • Atoms are the smallest particles of each element. • Elements, compounds, and mixtures together constitute all matter. ...
... • Physical properties can be observed without changing the chemical structure of a substance. • Chemical properties describe a possible chemical change. • Matter is made of atoms. • Atoms are the smallest particles of each element. • Elements, compounds, and mixtures together constitute all matter. ...
20161010170338
... • Main Points of Theory 1. All elements are composed of atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element have the same mass, and atoms of different elements have different masses. 3. Compounds contain atoms of more than one element. 4. In a particular compound, atoms of different elements always combine in t ...
... • Main Points of Theory 1. All elements are composed of atoms. 2. All atoms of the same element have the same mass, and atoms of different elements have different masses. 3. Compounds contain atoms of more than one element. 4. In a particular compound, atoms of different elements always combine in t ...
Covalent Bonds - WordPress.com
... • Molecules or atoms that are very close together can be attracted by temporary charge differences • These weak attractions are called van der ...
... • Molecules or atoms that are very close together can be attracted by temporary charge differences • These weak attractions are called van der ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure Notes
... Structure of the Atom In 1911, Ernest Rutherford performs the gold foil experiment which determined: A. Atoms consist of a small positively charged dense nuclei B. Almost all of the mass is in the nucleus C. The negatively charged electrons are in the area that creates most of the volume of the atom ...
... Structure of the Atom In 1911, Ernest Rutherford performs the gold foil experiment which determined: A. Atoms consist of a small positively charged dense nuclei B. Almost all of the mass is in the nucleus C. The negatively charged electrons are in the area that creates most of the volume of the atom ...
Atomic Theory
... 4. Dalton’s Theory: All matter is composed of atoms; atoms of different elements differ; and chemical change involves a rearrangement of atoms. 5. Democritus’s ideas were not based on experimental results and did not explain chemical behavior. Dalton’s were based on experimental results and explaine ...
... 4. Dalton’s Theory: All matter is composed of atoms; atoms of different elements differ; and chemical change involves a rearrangement of atoms. 5. Democritus’s ideas were not based on experimental results and did not explain chemical behavior. Dalton’s were based on experimental results and explaine ...
Unit 3: Quantum Mechanics Section A: History of Atomic Theory
... elements according to their atomic weight; however, when isotopes of elements were discovered in the late 1800s this concept changed. Chemical reactions involve the combination of atoms, not the destruction of atoms. This is largely based on Antonie Lavoisier’s law of conservation of matter. Whe ...
... elements according to their atomic weight; however, when isotopes of elements were discovered in the late 1800s this concept changed. Chemical reactions involve the combination of atoms, not the destruction of atoms. This is largely based on Antonie Lavoisier’s law of conservation of matter. Whe ...
History of Atomic Model - Physics
... extremely thin gold foil • - This result was thought to be like cannon balls bouncing off • - Most went right through with little deflection, but some bounced back tissue paper ...
... extremely thin gold foil • - This result was thought to be like cannon balls bouncing off • - Most went right through with little deflection, but some bounced back tissue paper ...
Introduction_to_Geochemistry_Pre-Lecture_Quiz
... detach the loosest electron from atoms of that element. (e) All alkali metals have similar chemical properties. (f) Alkali earths have one electron in the outer shell. (g) Electronegativity is the amount of negative charge on an atom. (h) Ca has a valency of 2. (i) True ionic bonds are unknown and a ...
... detach the loosest electron from atoms of that element. (e) All alkali metals have similar chemical properties. (f) Alkali earths have one electron in the outer shell. (g) Electronegativity is the amount of negative charge on an atom. (h) Ca has a valency of 2. (i) True ionic bonds are unknown and a ...
Development of Atomic Theory
... they kept seeing that the atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus, equivalent to the positive charge of the atom) was less than the atomic mass (average mass of the atom). For example, a helium atom has an atomic mass of 4, but an atomic number (or positive charge) of 2. Since electrons have ...
... they kept seeing that the atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus, equivalent to the positive charge of the atom) was less than the atomic mass (average mass of the atom). For example, a helium atom has an atomic mass of 4, but an atomic number (or positive charge) of 2. Since electrons have ...
Development of Atomic Theory
... they kept seeing that the atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus, equivalent to the positive charge of the atom) was less than the atomic mass (average mass of the atom). For example, a helium atom has an atomic mass of 4, but an atomic number (or positive charge) of 2. Since electrons have ...
... they kept seeing that the atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus, equivalent to the positive charge of the atom) was less than the atomic mass (average mass of the atom). For example, a helium atom has an atomic mass of 4, but an atomic number (or positive charge) of 2. Since electrons have ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... of each element in a given compound is always the same. 3. Chemical reactions only involve the rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
... of each element in a given compound is always the same. 3. Chemical reactions only involve the rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
1 - kjpederson
... 1. Describe Democritus’s atomic theory. Everything in the universe is made up of atoms. 2. Summarize the main ideas of Dalton’s theory. a. Elements are made up of tiny unique particles called atoms. b. Atoms cannot be divided. c. Atoms of the same element are identical. d. Atoms of different element ...
... 1. Describe Democritus’s atomic theory. Everything in the universe is made up of atoms. 2. Summarize the main ideas of Dalton’s theory. a. Elements are made up of tiny unique particles called atoms. b. Atoms cannot be divided. c. Atoms of the same element are identical. d. Atoms of different element ...
Development of Atomic Theory: Democritus to Thomson
... of matter in half over and over? 4. What does the Greek word atomos” mean? 5. What is our modern definition of the atom? 6. In the late 1700’s a British chemist and schoolteacher, John Dalton, brought back Democritus’s idea of the atom. What 3 ideas did his new theory of the atom propose? 7. In 1897 ...
... of matter in half over and over? 4. What does the Greek word atomos” mean? 5. What is our modern definition of the atom? 6. In the late 1700’s a British chemist and schoolteacher, John Dalton, brought back Democritus’s idea of the atom. What 3 ideas did his new theory of the atom propose? 7. In 1897 ...
Chapter 3 pages 65
... same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers Daltons Atomic Theory 1) All matter made up of atoms 2) Atoms of same element have same size, mass, and other properties 3) Atoms cannot be ...
... same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers Daltons Atomic Theory 1) All matter made up of atoms 2) Atoms of same element have same size, mass, and other properties 3) Atoms cannot be ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.