HCC4 Chapter 4 Objectives and Notes
... 4.1 Defining the Atom a. Early Models of the Atom 1. atom: The atom is so small. How small? It is so small that it is the smallest part of an element that maintains the properties of that element. It is an electrically neutral particle, therefore, it has no charge. 2. element: A substance that is c ...
... 4.1 Defining the Atom a. Early Models of the Atom 1. atom: The atom is so small. How small? It is so small that it is the smallest part of an element that maintains the properties of that element. It is an electrically neutral particle, therefore, it has no charge. 2. element: A substance that is c ...
Chemistry Calendar Omega 10 10/24 – 10/28 Monday Oct 24
... presence of certain atoms within a compound ...
... presence of certain atoms within a compound ...
Preview Sample 1
... 1. Which of the following pH values indicates the greater concentration of acid: pH 1 or pH 4? pH 1 pH 5 or pH 3? pH 3 2. Which of the following pH values indicates the greater concentration of base: pH 8 or pH 10? pH 10 pH 7 or pH 11? pH 11 3. What does a pH of 7 indicate? ...
... 1. Which of the following pH values indicates the greater concentration of acid: pH 1 or pH 4? pH 1 pH 5 or pH 3? pH 3 2. Which of the following pH values indicates the greater concentration of base: pH 8 or pH 10? pH 10 pH 7 or pH 11? pH 11 3. What does a pH of 7 indicate? ...
Chapter 2
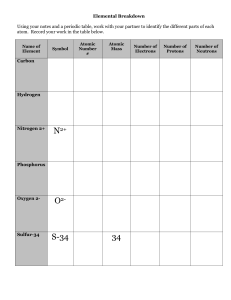
... All atoms of Carbon will be identified by Atomic Number 6, having this number of protons within its nucleus. The nuclei of most carbon atoms contain also 6 neutrons giving a combines mass number of 12. But statistically, a very small proportion of carbon atoms in nature have 8 neutrons, thus giving ...
... All atoms of Carbon will be identified by Atomic Number 6, having this number of protons within its nucleus. The nuclei of most carbon atoms contain also 6 neutrons giving a combines mass number of 12. But statistically, a very small proportion of carbon atoms in nature have 8 neutrons, thus giving ...
document
... A. A reaction in which one substance breaks down into its parts. 2. Ion B. A bond that is formed by sharing electrons. 3. Charge C. A charged atom. D. The number of electrons an 4. Covalent Bond element is willing to gain, lose, or share to form compounds. 5. Ionic Bond E. States that all elements w ...
... A. A reaction in which one substance breaks down into its parts. 2. Ion B. A bond that is formed by sharing electrons. 3. Charge C. A charged atom. D. The number of electrons an 4. Covalent Bond element is willing to gain, lose, or share to form compounds. 5. Ionic Bond E. States that all elements w ...
Atom
... •Atoms are mainly empty space •Nucleus of protons & neutrons •Electrons in empty space around nucleus ...
... •Atoms are mainly empty space •Nucleus of protons & neutrons •Electrons in empty space around nucleus ...
Unit - III - E
... Early concepts in covalent bonding arose from this kind of image of the molecule of methane. Covalent bonding is implied in the Lewis structure that indicates sharing of electrons between atoms. 2. Write a note on Resonance Many bonding situations can be described with more than one valid Lewis Dot ...
... Early concepts in covalent bonding arose from this kind of image of the molecule of methane. Covalent bonding is implied in the Lewis structure that indicates sharing of electrons between atoms. 2. Write a note on Resonance Many bonding situations can be described with more than one valid Lewis Dot ...
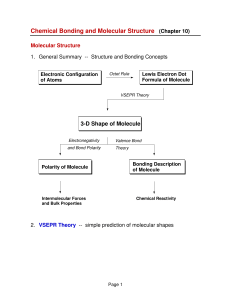
3-D Shape of Molecule
... *accounts for paramagnetism of O2 (VB theory fails here!) 4. Delocalized Molecular Orbitals By combining AO's from three or more atoms, it is possible to generate MO's that are "delocalized" over three or more atoms ...
... *accounts for paramagnetism of O2 (VB theory fails here!) 4. Delocalized Molecular Orbitals By combining AO's from three or more atoms, it is possible to generate MO's that are "delocalized" over three or more atoms ...
atoms
... • The Greek philosopher Democritus (460 B.C. – 370 B.C.) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms (from the Greek word “atomos”) – He believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible – His ideas did agree with later scientific theory, but did not explain chemical behavior, and wa ...
... • The Greek philosopher Democritus (460 B.C. – 370 B.C.) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms (from the Greek word “atomos”) – He believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible – His ideas did agree with later scientific theory, but did not explain chemical behavior, and wa ...
Chapter+4+Ques Honorst
... 11. What did Rutherford experiment find about the atom? 12. What is a nucleus? 13. Describe or draw what the new model (Rutherford’s model) looks like: 14. What was Rutherford’s contribution to the Atomic Theory? Chp 4-2 1. What are the three subatomic particles? 2. What is a proton? Charge? Locatio ...
... 11. What did Rutherford experiment find about the atom? 12. What is a nucleus? 13. Describe or draw what the new model (Rutherford’s model) looks like: 14. What was Rutherford’s contribution to the Atomic Theory? Chp 4-2 1. What are the three subatomic particles? 2. What is a proton? Charge? Locatio ...
chemical foundations, 020916
... Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen make-up about 96 percent of the mass of the human body. Much of the remaining 4 percent consists of 7 elements. Less than 0.01 percent of the human body are trace elements essential to life. ...
... Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen make-up about 96 percent of the mass of the human body. Much of the remaining 4 percent consists of 7 elements. Less than 0.01 percent of the human body are trace elements essential to life. ...
sub
... Isotopes are used in many ways. Many are used in cancer therapy. Some are used to help identify the age of objects and locate buried cables. The gas hydrogen has three isotopes. The most common isotope of hydrogen has a nucleus that is made up of one proton and no neutrons. More than 99% of hydrogen ...
... Isotopes are used in many ways. Many are used in cancer therapy. Some are used to help identify the age of objects and locate buried cables. The gas hydrogen has three isotopes. The most common isotope of hydrogen has a nucleus that is made up of one proton and no neutrons. More than 99% of hydrogen ...
Midterm Review answers - Nutley Public Schools
... 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles that Today we know that atoms are divisible into protons, neutrons are called atoms. and electrons 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles that Today we know that atoms are divisible into protons, neutrons are called atoms. and electrons 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Station 2: Atomic Models
... Because matter is electrically neutral, there must be a positively charged particle that balances the negative charge on the electrons in an atom. If electrons are very light, these positively charged particles must carry the mass of the atom. Thomson therefore suggested that atoms are spheres of po ...
... Because matter is electrically neutral, there must be a positively charged particle that balances the negative charge on the electrons in an atom. If electrons are very light, these positively charged particles must carry the mass of the atom. Thomson therefore suggested that atoms are spheres of po ...
Quiz: The Atom (Open Notes)
... 11. T or F A proton has a charge that is equal in force but opposite in charge to each electron. 12. T or F Protons and electrons are about equal in mass. 13. T or F The mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. 14. The atomic number of an atom is determined by th ...
... 11. T or F A proton has a charge that is equal in force but opposite in charge to each electron. 12. T or F Protons and electrons are about equal in mass. 13. T or F The mass of an atom depends on the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. 14. The atomic number of an atom is determined by th ...
Metals
... • What is matter made of? • The ancient Greeks thought that everything in the universe was made up of a combination of 4 “elements”: air, fire, water, and earth. People believed this for many centuries! • In the late 1600s, early chemists began to discover that this was not the case, that there are ...
... • What is matter made of? • The ancient Greeks thought that everything in the universe was made up of a combination of 4 “elements”: air, fire, water, and earth. People believed this for many centuries! • In the late 1600s, early chemists began to discover that this was not the case, that there are ...
Section 6.1: Covalent Bonding Basics
... water molecule consists of two hydrogen and one oxygen atom covalently bonded together. Another example is the formula C12H22O11 molecule found in sugar. Ionic compounds consist of a collection of individual positive and negative ions in an orderly array or lattice that is held together by opposite ...
... water molecule consists of two hydrogen and one oxygen atom covalently bonded together. Another example is the formula C12H22O11 molecule found in sugar. Ionic compounds consist of a collection of individual positive and negative ions in an orderly array or lattice that is held together by opposite ...
BONDING
... Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a covalent bond. First proposed by Linus Pauling in 1932 as a development of valence bond theory, it has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties ...
... Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a covalent bond. First proposed by Linus Pauling in 1932 as a development of valence bond theory, it has been shown to correlate with a number of other chemical properties ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 2 of 12
... each chemical symbol show its electronic structure. Moving across each period, you can see that the number of occupied energy levels is the same as the period number. As you go across each period ...
... each chemical symbol show its electronic structure. Moving across each period, you can see that the number of occupied energy levels is the same as the period number. As you go across each period ...
atoms
... Suggested that all matter was made up of tiny spheres that were able to bounce around with perfect elasticity and called them ...
... Suggested that all matter was made up of tiny spheres that were able to bounce around with perfect elasticity and called them ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... He asked: Could matter be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times a piece of matter could be divided? ...
... He asked: Could matter be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times a piece of matter could be divided? ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.