Spectra and Atomic Structure
... Formation of Spectral Lines Absorption can boost an electron to the second (or higher) excited state Two ways to decay: 1. to ground state 2. cascade one orbital at a time ...
... Formation of Spectral Lines Absorption can boost an electron to the second (or higher) excited state Two ways to decay: 1. to ground state 2. cascade one orbital at a time ...
Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review Study Island
... everything else about the rabbits' living environment the same, including the amount of water and food provided. After a month, she measures the body fat of the rabbits in both groups. What is the control in Dr. Grey's experiment? A. the group of rabbits that are given the drug B. the group of rabbi ...
... everything else about the rabbits' living environment the same, including the amount of water and food provided. After a month, she measures the body fat of the rabbits in both groups. What is the control in Dr. Grey's experiment? A. the group of rabbits that are given the drug B. the group of rabbi ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... 2. Covalent Bonds - Classical “molecules” where valence electrons are shared between two nonmetals ...
... 2. Covalent Bonds - Classical “molecules” where valence electrons are shared between two nonmetals ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... 3. The ELEMENTS in each GROUP have similar PHYSICAL and CHEMICAL properties because they have the SAME number of VALENCE electrons *a. VALENCE ELECTRON(S) are the ELECTRONS found on the OUTER-MOST portion of the electron CLOUD (energy orbital FARTHEST from the NUCLEUS) of an ATOM, which allows the ...
... 3. The ELEMENTS in each GROUP have similar PHYSICAL and CHEMICAL properties because they have the SAME number of VALENCE electrons *a. VALENCE ELECTRON(S) are the ELECTRONS found on the OUTER-MOST portion of the electron CLOUD (energy orbital FARTHEST from the NUCLEUS) of an ATOM, which allows the ...
Explain APE MAN NOTES TEACHER PAGE
... Explain: Determining the Subatomic Particles of Atoms 8.5 B - identify that protons determine an element's identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity. ...
... Explain: Determining the Subatomic Particles of Atoms 8.5 B - identify that protons determine an element's identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity. ...
filled in teacher version, level 1 only
... • The atomic mass for each element on the periodic table reflects the relative abundance of each isotope in nature. • The mass on the periodic table is NOT the atomic mass number (A) ...
... • The atomic mass for each element on the periodic table reflects the relative abundance of each isotope in nature. • The mass on the periodic table is NOT the atomic mass number (A) ...
Key III
... In an experiment, a 1.452g sample of L-ascorbic acid (C6H8O6) is burned completely in a bomb calorimeter. The calorimeter is surrounded by 1319g of water. During the combustion the temperature increases from 24.21 to 27.15 oC. Assuming that no energy is lost to the surroundings, calculate the molar ...
... In an experiment, a 1.452g sample of L-ascorbic acid (C6H8O6) is burned completely in a bomb calorimeter. The calorimeter is surrounded by 1319g of water. During the combustion the temperature increases from 24.21 to 27.15 oC. Assuming that no energy is lost to the surroundings, calculate the molar ...
Figure 2: Alternative Periodic Table
... Placed in table above using blue electrons. We predict it to be a colorless gas with low electrical conductivity and high electrical reactivity. c) Are there any elements that have not yet been discovered? If so, what would their properties be? This table has room for four more elements. The element ...
... Placed in table above using blue electrons. We predict it to be a colorless gas with low electrical conductivity and high electrical reactivity. c) Are there any elements that have not yet been discovered? If so, what would their properties be? This table has room for four more elements. The element ...
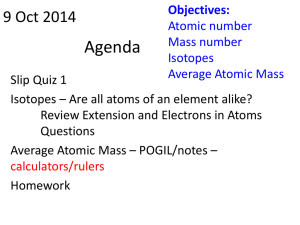
weighted average atomic mass
... take up too much space to include information about 2, 3 or more isotopes for each element. (It would be confusing to read also.) ...
... take up too much space to include information about 2, 3 or more isotopes for each element. (It would be confusing to read also.) ...
Ch 11 HW
... Use the definitions below to unscramble the vocabulary words. 1. weighted average of the mass of all naturally occurring isotopes of the same element ...
... Use the definitions below to unscramble the vocabulary words. 1. weighted average of the mass of all naturally occurring isotopes of the same element ...
Chemistry
... o Be able to write numbers in scientific notation and standard form o Know the major units of measurement o Be able to identify the number of significant figures in a measurement o Be able to perform calculations using scientific notation and significant figures o Be able to correctly round a number ...
... o Be able to write numbers in scientific notation and standard form o Know the major units of measurement o Be able to identify the number of significant figures in a measurement o Be able to perform calculations using scientific notation and significant figures o Be able to correctly round a number ...
Student Activity PDF - TI Education
... 3. For each word equation given on page 2.10, use the Chemical Balance tool on page 2.11 to balance the equation and record it in the table. First, write the balanced equation using the element symbols. Record the number of atoms of each element in the reactant (left side) and the products (right si ...
... 3. For each word equation given on page 2.10, use the Chemical Balance tool on page 2.11 to balance the equation and record it in the table. First, write the balanced equation using the element symbols. Record the number of atoms of each element in the reactant (left side) and the products (right si ...
Atoms and bonds in molecules and chemical explanations
... 1. different sorts of atoms are naturally associated with unequal quantities of electricity 2. a mass of electrical matter, or electricity, may be regarded as composed of electrical atoms, just as a mass of ordinary matter contains ordinary atoms; and thus the sphere of electricity which surrounds a ...
... 1. different sorts of atoms are naturally associated with unequal quantities of electricity 2. a mass of electrical matter, or electricity, may be regarded as composed of electrical atoms, just as a mass of ordinary matter contains ordinary atoms; and thus the sphere of electricity which surrounds a ...
molecular formula
... Formula or molecular mass = S of atomic masses in the chemical formula Molecular mass = mass in amu for a molecule, from nonmetal elements forming covalent bonds Molecule is a covalent compound’s smallest unit, made of nonmetals in covalent bonds Formula mass = mass in amu for a formula unit or for ...
... Formula or molecular mass = S of atomic masses in the chemical formula Molecular mass = mass in amu for a molecule, from nonmetal elements forming covalent bonds Molecule is a covalent compound’s smallest unit, made of nonmetals in covalent bonds Formula mass = mass in amu for a formula unit or for ...
atoms - Wylie ISD
... Order of Electron Fill: Just about the time you think you are "getting the hang of this" there is an exception. After the 3p fills up you would think the 3d would fill, but it is not so. Electrons will fill the areas which require the least amount of energy, and it takes less energy to fill the 4s t ...
... Order of Electron Fill: Just about the time you think you are "getting the hang of this" there is an exception. After the 3p fills up you would think the 3d would fill, but it is not so. Electrons will fill the areas which require the least amount of energy, and it takes less energy to fill the 4s t ...
Final Exam Practice Questions for General Chemistry NOTICE TO
... 4. Which one of the following statements is incorrect for an ideal gas, according to the Kinetic Molecular Theory? a) Molecules of a gas are widely separated from one another. b) Molecules of a gas occupy negligible volume. c) Molecules of a gas move with an average speed determined by the temperatu ...
... 4. Which one of the following statements is incorrect for an ideal gas, according to the Kinetic Molecular Theory? a) Molecules of a gas are widely separated from one another. b) Molecules of a gas occupy negligible volume. c) Molecules of a gas move with an average speed determined by the temperatu ...
chemistry -- questions -
... __ 17. Which pair has similar chemical properties? a) 1H and 22Na b) 12C and 28Si c) 16O and 32S d) 12C and 14C e) 1H and 2He __ 18. Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15, so what will be the distribution of its electrons? a) The first energy level will have 8 and the second will have 7. b) The firs ...
... __ 17. Which pair has similar chemical properties? a) 1H and 22Na b) 12C and 28Si c) 16O and 32S d) 12C and 14C e) 1H and 2He __ 18. Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15, so what will be the distribution of its electrons? a) The first energy level will have 8 and the second will have 7. b) The firs ...
Powerpoint slides
... An atom with its electrons in their lowest-energy locations is said to be in its ground state. When electromagnetic energy collides with an atom, and the amount of electromagnetic energy is just right, an electron can be kicked up from its usual energy level to a higher one. With one of its electron ...
... An atom with its electrons in their lowest-energy locations is said to be in its ground state. When electromagnetic energy collides with an atom, and the amount of electromagnetic energy is just right, an electron can be kicked up from its usual energy level to a higher one. With one of its electron ...
Periodicity - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... FAMILIES OF ELEMENTS Dimitri Mendeleev invented the periodic table ...
... FAMILIES OF ELEMENTS Dimitri Mendeleev invented the periodic table ...
Example
... number of particles (and the mass on the periodic table expressed in grams). 1 mol of C = 12.01 g of C= 6.022 x 1023 atoms of C 1 mol of O2 = 32.00 g of O2= 6.022 x 1023 molecules 1 mol of NaCl = 58.44 g of NaCl= 6.022 x 1023 formula units of NaCl ...
... number of particles (and the mass on the periodic table expressed in grams). 1 mol of C = 12.01 g of C= 6.022 x 1023 atoms of C 1 mol of O2 = 32.00 g of O2= 6.022 x 1023 molecules 1 mol of NaCl = 58.44 g of NaCl= 6.022 x 1023 formula units of NaCl ...
Question 1. Phosgene was used during the World War - IQ
... Question 5. In a lecture on covalent bonds, a student, making associations between H and Li in terms of number of electrons on the valence shell, asks the teacher if it is possible the existence of a molecule Li2, as the molecule H2 exists. (a) Using your understanding on chemical bond, show if it i ...
... Question 5. In a lecture on covalent bonds, a student, making associations between H and Li in terms of number of electrons on the valence shell, asks the teacher if it is possible the existence of a molecule Li2, as the molecule H2 exists. (a) Using your understanding on chemical bond, show if it i ...
Lesson 5: Current Atomic Model
... protons but have different masses. The difference is due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. These are called isotopes. One example is carbon. It has three main isotopes. ...
... protons but have different masses. The difference is due to the different number of neutrons in the nucleus. These are called isotopes. One example is carbon. It has three main isotopes. ...
2 Atomic Theory Development of Theory Historical Atomic Models
... A defined region (shape) of space, where it is most probable to find an electron. Each orbital contains 0, 1, or 2 e’s. There are four classes of orbitals: s, p d, f. Each class of orbital can have certain types. For instance the p-orbital has 3 types: px, py, pz. Each orbital is hourglass shaped an ...
... A defined region (shape) of space, where it is most probable to find an electron. Each orbital contains 0, 1, or 2 e’s. There are four classes of orbitals: s, p d, f. Each class of orbital can have certain types. For instance the p-orbital has 3 types: px, py, pz. Each orbital is hourglass shaped an ...
Honors-Final-Review-2014
... f. reactant not totally used up in the lab g involves mass relationships in a chemical reaction h. combined mass of all the atoms in a compound. i. this determines the maximum amount of product that will form ...
... f. reactant not totally used up in the lab g involves mass relationships in a chemical reaction h. combined mass of all the atoms in a compound. i. this determines the maximum amount of product that will form ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.