35-rectum_&_urinary_..
... internal iliac. It supplies the muscular coat. (3) Inferior rectal: It arises from the internal pudendal. It anastomoses with the middle rectal. ...
... internal iliac. It supplies the muscular coat. (3) Inferior rectal: It arises from the internal pudendal. It anastomoses with the middle rectal. ...
End of chapter review excretory system
... 4. How is excretory system different from the other three body systems: circulatory, respiratory and digestive systems? ...
... 4. How is excretory system different from the other three body systems: circulatory, respiratory and digestive systems? ...
M1 - M3 Modules Summary
... It attaches medially to the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and laterally to the middle facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The primary function of the infraspinatus is extension, horizontal (transverse) extension and lateral rotation of humerus at the shoulder joint. It is the major ex ...
... It attaches medially to the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and laterally to the middle facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The primary function of the infraspinatus is extension, horizontal (transverse) extension and lateral rotation of humerus at the shoulder joint. It is the major ex ...
biceps tendonitis (long head of biceps tendonitis)
... What causes biceps tendonitis? As mentioned above, this condition often occurs as a result of overuse. It can be caused by excessive overhead motions such as throwing or swimming. With these types of activities, there is excessive wear on the tendon, but other factors may contribute to the problem. ...
... What causes biceps tendonitis? As mentioned above, this condition often occurs as a result of overuse. It can be caused by excessive overhead motions such as throwing or swimming. With these types of activities, there is excessive wear on the tendon, but other factors may contribute to the problem. ...
5 SYSTEMATICS AND MORPHOLOGY Objectives After completing
... divided into two equal halves through that axis along any plane. eg. Sea anemone, Sand dollar. ...
... divided into two equal halves through that axis along any plane. eg. Sea anemone, Sand dollar. ...
Systems of the Human Body Study Guide
... ___________________ in it. 10. The left side of the heart pumps blood to the _______________. This blood is full of ________________. 11.The heart is divided into 4 ______________________. 12.______________________ is the process that breaks food into forms that your cells can use. 13.Digestion begi ...
... ___________________ in it. 10. The left side of the heart pumps blood to the _______________. This blood is full of ________________. 11.The heart is divided into 4 ______________________. 12.______________________ is the process that breaks food into forms that your cells can use. 13.Digestion begi ...
Thoracic wall and pleural cavities
... sternum moves downward and backward. This ' pump handle' type of movement changes the ...
... sternum moves downward and backward. This ' pump handle' type of movement changes the ...
Trunk Muscles
... Their functions are the same as those of the external obliques. • Transversus abdominis. The transversus abdominis is the deepest muscle of the abdominal wall and has fibers that run horizontally across the abdomen. It arises from the lower ribs and iliac crest and inserts into the pubis. This muscl ...
... Their functions are the same as those of the external obliques. • Transversus abdominis. The transversus abdominis is the deepest muscle of the abdominal wall and has fibers that run horizontally across the abdomen. It arises from the lower ribs and iliac crest and inserts into the pubis. This muscl ...
Lab Practical III â Study Guide
... example of each? 7. What are the two types of symmetry? What is a sponge? Know anterior/posterior/dorsal/ventral. 8. What’s the difference between a protostome and deuterostome? What are some examples of each? 9. Why are females often larger than males? ...
... example of each? 7. What are the two types of symmetry? What is a sponge? Know anterior/posterior/dorsal/ventral. 8. What’s the difference between a protostome and deuterostome? What are some examples of each? 9. Why are females often larger than males? ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/resources/Grzimek_fish/structure_function/digestive_system.jpg/medium.jpg ...
... http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/resources/Grzimek_fish/structure_function/digestive_system.jpg/medium.jpg ...
Jeopardy-Rvw_Appendicular Skeleton
... bones are joined in the front Daily Double: What is the name of the ridge that runs along the top part of the ilium of the pelvis? Hint: part of hip bone you can feel ...
... bones are joined in the front Daily Double: What is the name of the ridge that runs along the top part of the ilium of the pelvis? Hint: part of hip bone you can feel ...
period of contraction
... of individual twitches combine by the process of summation. • If the sustained contraction lacks any relaxation, it is called a tetanic contraction. • An increase in the number of activated motor units within a muscle at higher intensities of stimulation is called recruitment. Individual muscle cell ...
... of individual twitches combine by the process of summation. • If the sustained contraction lacks any relaxation, it is called a tetanic contraction. • An increase in the number of activated motor units within a muscle at higher intensities of stimulation is called recruitment. Individual muscle cell ...
Skeletal Muscle Contraction
... of individual twitches combine by the process of summation. • If the sustained contraction lacks any relaxation, it is called a tetanic contraction. • An increase in the number of activated motor units within a muscle at higher intensities of stimulation is called recruitment. Individual muscle cell ...
... of individual twitches combine by the process of summation. • If the sustained contraction lacks any relaxation, it is called a tetanic contraction. • An increase in the number of activated motor units within a muscle at higher intensities of stimulation is called recruitment. Individual muscle cell ...
The Appendicular Skeleton
... Supports our body weight and serves as a lever that allows us to propel or move our bodies forward when we walk or run Tarsus makes up the ankle It is composed of seven tarsal bones Most weight is carried by two tarsal bones: Calcaneus or heel bone Talus (ankle bone) located between the tibia & the ...
... Supports our body weight and serves as a lever that allows us to propel or move our bodies forward when we walk or run Tarsus makes up the ankle It is composed of seven tarsal bones Most weight is carried by two tarsal bones: Calcaneus or heel bone Talus (ankle bone) located between the tibia & the ...
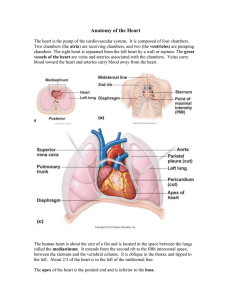
Anatomy of the Heart
... The heart is the pump of the cardiovascular system. It is composed of four chambers. Two chambers (the atria) are receiving chambers, and two (the ventricles) are pumping chambers. The right heart is separated from the left heart by a wall or septum. The great vessels of the heart are veins and arte ...
... The heart is the pump of the cardiovascular system. It is composed of four chambers. Two chambers (the atria) are receiving chambers, and two (the ventricles) are pumping chambers. The right heart is separated from the left heart by a wall or septum. The great vessels of the heart are veins and arte ...
Unit 4 - Skeletal System Review
... __Clavicle____ 4. The bone that is intermediate to the sternum and humerus ___Radius____ 5. The bone in the forearm that articulates with the wrist __Ilium_______ 6. These bones make up the pelvic girdle __Ischium____ ____Pubis_____ ...
... __Clavicle____ 4. The bone that is intermediate to the sternum and humerus ___Radius____ 5. The bone in the forearm that articulates with the wrist __Ilium_______ 6. These bones make up the pelvic girdle __Ischium____ ____Pubis_____ ...
Osteopathic Medicine
... According to the World Osteopathic Health Organization, Osteopathy is a “…system of healthcare which relies on manual contact for diagnosis and treatment. It respects the relationship of body, mind and spirit in health and disease; it lays emphasis on the structural and functional integrity of the b ...
... According to the World Osteopathic Health Organization, Osteopathy is a “…system of healthcare which relies on manual contact for diagnosis and treatment. It respects the relationship of body, mind and spirit in health and disease; it lays emphasis on the structural and functional integrity of the b ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.